Instruction to students
- Answer all questions
- All working must be clearly shown where necessary
- Scientific calculators may be used
FOR EXAMINER’S USE ONLY
|
QUESTION |
MAXIMUM SCORE |
CANDIDATE’S SCORE |
|
1 |
12 |
|
|
2 |
10 |
|
|
3 |
10 |
|
|
4 |
10 |
|
|
5 |
13 |
|
|
6 |
12 |
|
|
7 |
13 |
|
|
Total score |
80 |
|

QUESTIONS
- Use the grid below to answer the questions that follow The letters do not represent the actual symbols of elements
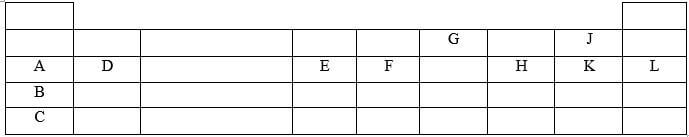
- Give the family name of the group in which elements B and C are members (1 mark)
- State and explain the difference in reactivity between
- A and D (1 mark)
- J and K (1 mark)
- How does the atomic radius of E compare with that of F? Explain (2 marks)
- Element R forms an oxide of the formula RQ2 and belongs to period two Indicate in the grid the position of R (1mark)
- Identify an element with the lowest first ionization energy (1 mark)
- Give the formula of the compound formed between E and K (1 mark)
- Name of type of bond formed when A reacts with K Explain (2 marks)
- Give one use of element L (1 mark)
- Give the electron arrangement of an ion of
C- (1/2 mark)
G- (1/2 mark)
-
- State Hess’s law (1 mark)
- Use the information to answer the questions that follow
C(s) + O2 (g) → CO2 (g) ∆H = -393kJ/mol
H2 (g) + ½ O2 (g) → H2O (g) ∆H = -296KJ/mol
C4H10 + 13/2 O2 (g) → 4CO2 (g) + 5H2O ∆H = -2877KJ/mol- Draw an energy cycle diagram relating heat of formation and combustion of butane (2 marks)
- Define enthalpy of formation (1 mark)
- Calculate the heat of formation of butane (2 marks)
- Draw the energy level diagram of combustion of butane (2 marks)
- The diagram below shows an energy level diagram for the formation of magnesium chloride
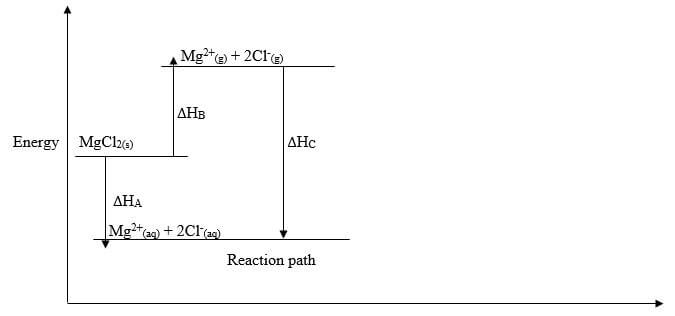
Study it and answer the questions that follow- State the enthalpy changes represented by
- A (1/2 mark)
- B (1/2 mark)
- C (1/2 mark)
- What is the relationship between ∆HA and ∆HB and ∆HC (1/2 mark)
- State the enthalpy changes represented by
-
- Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow
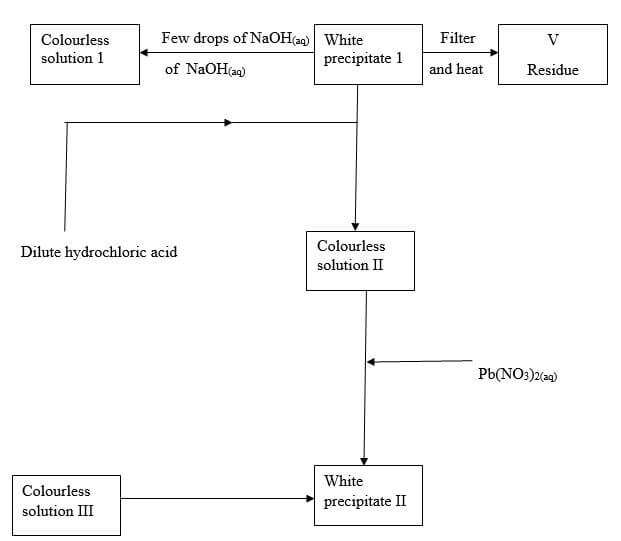
- Identify
- white precipitate I (1 mark)
- Solution II (1 mark)
- Residue V (1 mark)
- Write an ionic equation for the reaction of solution II with Pb(NO3)2(aq) (1 marks)
- Write observations that would be made when ammonia solution is added drop wise till in excess to the colourless solution II (1 mark)
- Identify
- The diagram below represents a set up for large scale manufacture of hydrochloric acid
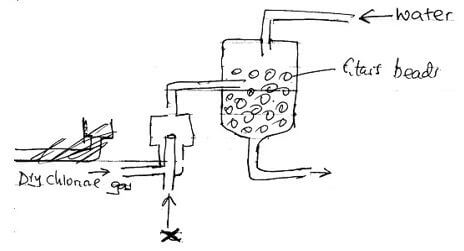
Study it and answer the questions that follow- Name substance X ( 1mark)
- What is the purpose of glass beads? (1 mark)
- Give one source of substance X used in the above process (1 mark)
- Give two uses of hydrochloric acid (2 marks)
- Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow
-
- Define solubility (1 mark)
- The saturated point of sodium nitrate in 100g of water is given for various temperature in ºC
Temperature oC
0
20
40
60
80
100
Saturation point (g/100g of H20)
73
88
104
124
148
180
- Plot a graph of saturation point of sodium nitrate against temperature (3 marks)
- Using the curve determine the solubility at 70ºC (1 mark)
- 100g of solution of sodium nitrate is in saturated conditions of 10ºC How many grams of the salt will have to be added to make the solution just saturation point at 80ºC (2 marks)
- State two uses of solubility curve (2 marks)
- Name a method of separating salts with different solubilities in the same solvent (1 mark)
-
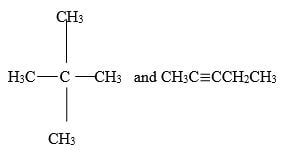
- Give the names of the following compounds
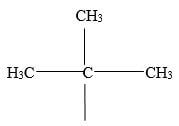
- CH3C≡CCH2CH3
- Describe a chemical test that can be carried out to distinguish between the compounds (2 marks)
- Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow
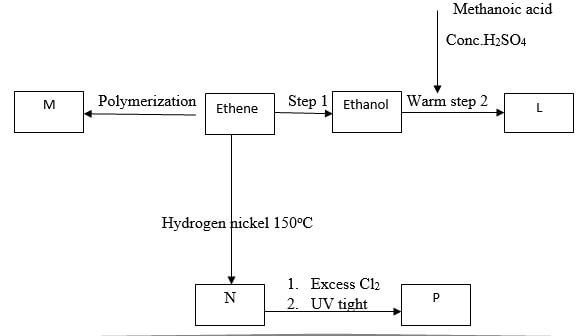
- Name the compounds (2 marks)
- L
- N
- Draw the structural formula of compound M showing three repeating units (1 mark)
- Give the reagent and condition used in step I (2 mark)
- State the type of reaction that takes place in (2marks)
- Step 2
- Step 3
- The molecular formular of compound P is C2H2Cl4 Draw the two structural formulae of compound P (2 marks)
- Name the compounds (2 marks)
- Give the names of the following compounds
-
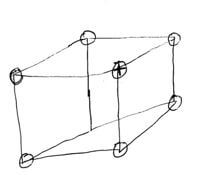
- The diagram below represent part of the structure of a sodium chloride crystal, the position of one of the sodium ions in the crystal is as shown as +
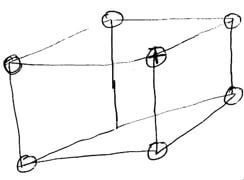
- On the diagram mark the positions of the other three sodium ions (3 marks)
- The melting and boiling points of sodium chloride are 801ºC and 1413ºC respectively Explain why sodium chloride does not conduct electricity at 25ºC but does at temperature between 801ºC and 1413ºC (2 marks)
- Give a reason why ammonia gas is highly soluble in water (1 mark)
- The structure of an ammonium ion is shown below
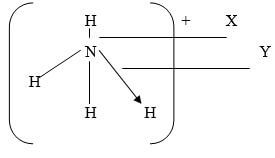
Name the types of bonds represented by the letters x and y (1 mark) - Carbon exist in different crystalline forms some of these forms were recently discovered in soot and are called fullerenes
- What name is given to different crystalline forms of the same elements? (1 marks)
- Fullerenes dissolves in methyl/benzene while other forms of carbon do not Given that soot is a mixture of fullerenes and other solid forms of carbon, describe how crystals of fullerenes can be obtained from soot (3 marks)
- The relative molecular mass of one of the fullerenes is 720 What is the molecular formula of this fullerene (C=12) (1 mark)
- The diagram below represent part of the structure of a sodium chloride crystal, the position of one of the sodium ions in the crystal is as shown as +
- Use the flow chart below to answer the questions that follow
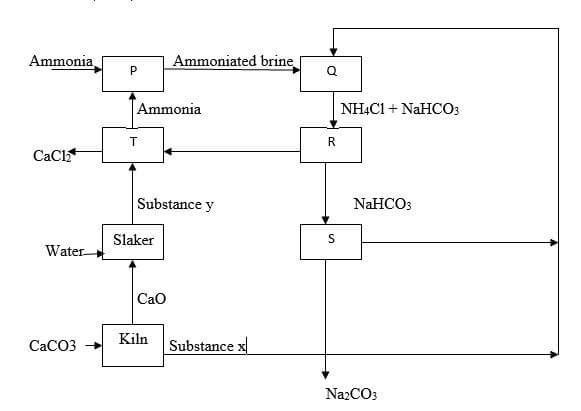
- Name the substance labeled (2 marks)
- X
- Y
- Identify two substances that are recycled in the process (1 mark)
- Name the process that takes place in chamber
- S (1 mark)
- R (1 mark)
- Write an equation for the reaction taking place in the chamber labeled
- Q (1 mark)
- T (1 mark)
- Give any two uses of calcium chloride (2 marks)
- With the aid of an ionic equation, explain how sodium carbonate can be used to soften hard water (2 marks)
- Other than softening of hard water, state two other uses of sodium carbonate (2 marks)
- Name the substance labeled (2 marks)

MARKING SCHEME
-
- Alkali metals √1
-
- A is more reactive than D√1 the outermost energy level electron in D is more firmly held than in A
- J is more reactive than√1/2 K the nuclear electron attraction is higher in J than in K ½
- F has a larger atomic radius than F√1 nuclear change increases across the period√1
- Before G OR
√
G
F
- C√1
- EK3√1 or AlCl3√1
- ionic/electrovalent bond√1 it is formed through transfer of electrons from metal to a non-metal√1
- Use in light bulbs
- C - 2,8,8,8, √1/2
G - 2,8 √1/2
-
- The enthalpy change of a reaction is the same regardless of the reaction happening in one or many steps provided that the initial reactants and products are the same √1
OR
The energy change in converting reactants to products is the same regardless of the route followed. √1 -
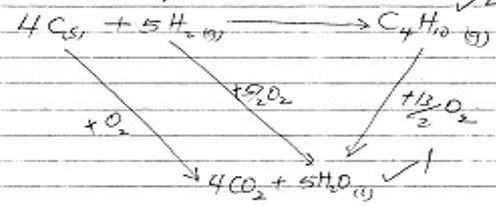
√1/2 √1/2- It’s the energy change when a compound is formed from its constituent element
- ∆H+ = 4 (-393) + 5 (-296) – (-2877) √1
= -1572 – 1480 + 2877
= -3052 + 2877
= -175KJ/mol √1
-
- A - hydration energy√1/2
B - Lattice energy√1/2
C - Heat of solution√1/2 - ∆HC = ∆HA + HB√1/2
- A - hydration energy√1/2
- The enthalpy change of a reaction is the same regardless of the reaction happening in one or many steps provided that the initial reactants and products are the same √1
-
-
-
- Zn(OH)2 (1mk) / Zinc hydroxide√1
- Zinc chloride (1mk) / ZnCl2√1
- Zinc Oxide 1mk /ZnO√1
- Pb2+(aq) + 2Cl-(aq) → PbCl2(s) (1mk) penalize ½ for missing or wrong state symbols
- A white precipitate which dissolves in excess ammonia solution observed√1 (1mk)
-
-
- Hydrogen√1
- To provide a large surface area one which the gas dissolves in water√1
-
- From electrolysis of aqueous sulphuric (VI) acid
- Form electrolysis of brine
- cracking of alkanes
- A by-product of petroleum industry any(1mk)
- Removing rust from iron/decaying of Iron before galvanizing and other metals before Electroplating
- Sewage treatment
- Making dyes
- Manufacture of silver chloride used on photographic films (any 2 for 1 mark each)
-
-
- Solubility is the maximum amount of solute that can dissolve in a solvent at a particular temperature
-
- 136(±1) g/100g
- Saturation at 10ºC = 80g√1/2
at 80ºC = 148g√1/2
Salt added is 148 - 80√1/2 = 68g√11/2 -
- Use to determine the mass of crystals obtained when saturated solution cools
- Used to separate substances of different solubilities
- used to know the effect of temperature on solubility of salts(Any 2 for 2 mk each)
- Fractional crystallisation√1
-
-
- 2,2 – dimethyl/propane√1
- Pent – 2 – yne √1
-
- Ignite each, 2, 2 - dimethyl/Propane burns with a non-sooty flame while pent -2-yne burns with a sooty flame
- Pass each through H+/KMnO4 i. does not decolourise H+/KMnO4 while (ii) decolourise
- Use bromine water in the dark.
-
- L – Ethylmethanoate√1
N – Ethane√1 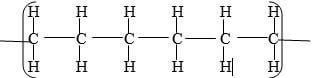
- Reagent - water hydrolysis Reagent-steam√1
Condition conc.H2SO4 (liquid) condition H3PO4 - Step 2 – Extrication
Step 3- Substitution 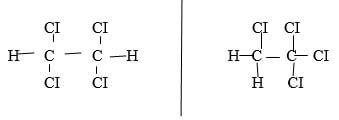
- L – Ethylmethanoate√1
-
-
-
- At 25ºC-solid the ions are at fixed position while at above 801ºc the ions are mobile√1
- It is polar√1 due to hydrogen bonding
- x - covalent√1/2
y - coordinate/Dative√1/2 -
- Allotropes√1
- Add methylbenzene and swirl√1 (stir) to dissolve fullerenes filter√1 to obtain a solution of fullerene in methylbenzene leave the solution in the solution for methylbenzene to evaporate√1
- n = 720/12 = 60 (C60√1/2)
-
-
- x - Carbon (IV) oxide√1
y - Calcium hydroxide√1
(Penalize fully if formula is given) - Ammonia gas/NH3
Carbon (IV) oxide/CO2
Water/H2O
(Any two for ½ mark each) - S - Thermal decomposition√1
R - Filtration√1 - Q – NaCl (aq) + NH3 (g) + CO2 (g) + H2O (l) → NH4cl (aq) + NaHCO3 (s)
T - Ca(OH)2 (aq) + 2NH4c l(aq) → CaCl2 (aq) + 2NH3 (g)+2H2O(l)
(Penalize ½ mk for missing /wrong state symbols) -
- Used in extraction of sodium metal
- used in road surfacing due to its deliquescent nature
- Used for de-frosting snow in cold countries during winter.
(Any two for 1mk each)
- Mg2+ (aq) + CO2-3 (aq) → MgCO3 (s)
OR
Ca2+ (aq) + CO2-3 (aq) → CaCO3 (s) √1
Carbonate ions react with either calcium ion or magnesium ions present in hard water to form insoluble calcium carbonate or magnesium carbonate which is precipitated out √1 -
- Used in paper industry
- Use in glass making
- Manufacture of detergents.
(Any two)
- x - Carbon (IV) oxide√1
Download Chemistry Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Arise and Shine Pre Mock Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
