INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES.
- Answer ALL the questions in the spaces provided in the question paper.
- KNEC Mathematical tables and electronic calculators may be used for calculations.
- All working MUST be clearly shown where necessary.
- Candidates should answer the questions in English.
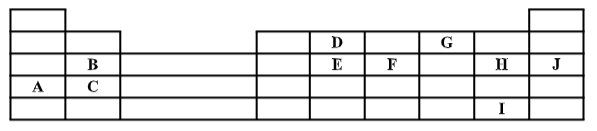
- The grid below represents part of the periodic table. Study it and answer the questions that follow. The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements.
- State the elements that can form ions with a charge of -1. Give a reason for your answer. (2 marks)
- What type of structure exists in the oxide of A. Give a reason for your answer? (1 mark)
- How does the reactivity of I compare with that of H. Explain. (1 mark)
- The oxide of D has a low melting point than the oxide of element C. Explain. (1 mark)
- With a reason choose the most;
- Electropositive element (2 marks)
- Electronegative element (2 marks)
- Compare the atomic radius of;
- B and H (1 mark)
- D and E (1 mark)
- State and explain the observations made when concentrated Nitric (V) acid is added to turnings of copper. (2 marks)
- The flow chart below shows how nitric (v) acid is produced on a large scale. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
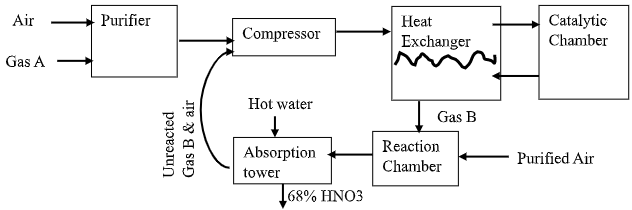
- State the functions of:
- Purifier (1mark)
- Heat exchanger (1mark)
- Identify
- Gas A (½ mark)
- Gas B (½ mark)
- Catalyst C (½mark)
- Write equations for the reaction that take place;
- in catalytic chamber. (1mark)
- in absorption tower. (1mark)
- Calculate the molarity of the commercial nitric (v) acid, given that it is 68% pure and has a density of 1.42g/cm3 . (N=14, H=1,)=16) (3mark)
-
- State the observation made when concentrated nitric (v) acid is added to acidified sulphur powder and warmed. (1mark)
- Give a reason for the answer given in c (i) above. (1mark)
- State the functions of:
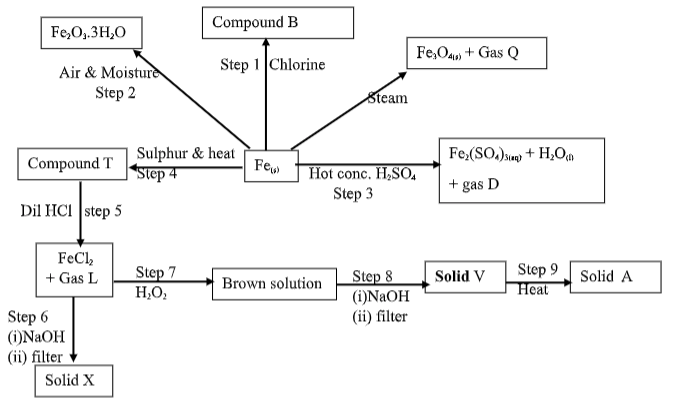
- Study the flow chart below starting from iron metal.
- Name gases (1½mk )
- D……….……………………………………………………………………………………
- L……….…………………………………………………………………………………....
- V……….…………………………………………………………………………….............
- Identify the following substances. (2 ½mk)
- Compound B……….……………………………………………………………………….
- Compound T……….……………………………………………………………………….
- Solid A……….……………………………………………………………………………..
- Solid V……….……………………………………………………………………………..
- Solid X……….…………………………………………………………………...................
- What name is given to the reaction in step 2? (½mk )
- State the colour of solid X (½mk)
- Write balanced equations for the reactions that occurred in:- (2mks)
- Step 1……….…………………………………………………………………………………...
- Step 5……….…………………………………………………………………………………...
- What property of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2 ) is indicated in step 7 of the flow chart? (1mk)
- Name gases (1½mk )
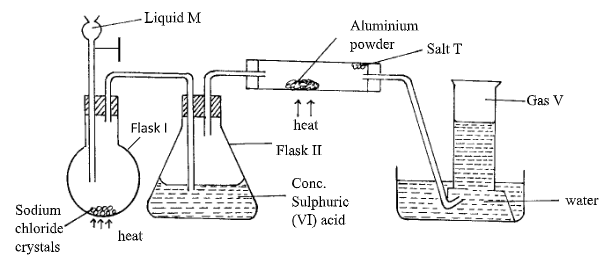
- The set up below was used to prepare hydrogen chloride gas and salt T.
-
- Name the following
- Liquid M (½ mark)
- Gas V (½ mark)
- Write the formula of Salt T (1mark)
- Name the following
- Write balanced chemical equations for reactions that occur at
- Flask I (1mark)
- Combustion tube. (1mark)
- Name the process that formed salt T as shown in the diagram. (1mark)
- Sulphuric (VI) acid is used as a drying agent in this experiment. Explain why calcium oxide is unsuitable for the same purpose in this reaction (2marks)
- The water in the trough was found to have a pH of 2.0 at the end of the experiment. Explain. (1mark)
- Calculate the mass of salt T formed if 480cm3 of hydrogen chloride gas measured at r.t.p was reacted with aluminium powder. (Al=27, Cl = 35.5, MGV=24dm3 ) (2marks)
- In the space provided below, draw a well labelled diagram showing how you would dissolve hydrogen chloride gas in water. (1mark)
- A solution of hydrogen chloride in methylbenzene does not react with carbonates. However, on adding water and then shaking the resulting mixture, there is vigorous effervescence. Explain the above observation. (2marks)
- Using equation, state the observation made when a gas jar containing hydrogen chloride gas is opened near an open bottle of liquid ammonia. (1mark)
-
-
- Name each of the processes described below which takes place when salts are exposed to air for sometime.
- Anhydrous copper (II) sulphate becomes wet. (1 mark)
- Common table salt forms an aqueous solution (1 mark)
- Fresh crystals of sodium carbonate Na2CO3.10H2O becomes covered with white powder of formula Na2CO3.H2O. (1mark)
- Write the formula of the complex ion formed in each of the reactions described below.
- Zinc metal dissolves in hot potassium hydroxide solution (1mark)
- Copper hydroxide dissolves in excess ammonia solution (1mark)
- A hydrated salt has the following composition by mass. Iron 20.2%, Oxygen 23%, Sulphur 11.5% and water 45.3%. Its relative formula mass is 278. Determine the formula of the hydrated salt. (Fe = 56, S = 32, O = 16, H = 1) (3marks)
- Describe how a solid sample of lead (II) chloride can be prepared using the following reagents:- dilute nitric acid, dilute hydrochloric acid and lead carbonate. (3marks)
- Name each of the processes described below which takes place when salts are exposed to air for sometime.
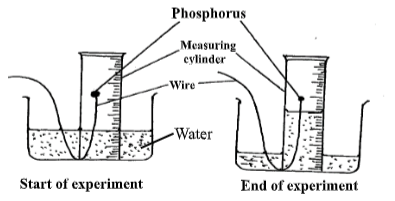
- A student set-up the apparatus shown below in order to determine the percentage by volume of oxygen in the air. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
-
- State one observations made in the measuring cylinder at the start of the experiment. Explain. (2mks)
- The PH of the contents of the beaker at the end of the experiment was found to be 4.
Explain the observation. (2marks) - The volume of air in the measuring cylinder at the end f the experiment was measured. study the data given below and answer the questions that follow.
- Volume of air at start of the experiment = 30.65 cm 3
- Volume of air at the end of the experiment = 24.28 cm 3
Determine the percentage volume of oxygen in the air. (2marks)
- State and explain the observation made when a mixture of zinc powder and copper (II) oxide is heated in a crucible. (2marks)
- State two air pollutants produced by motor vehicles. (1mark)
- A group of students burnt a piece of magnesium ribbon in air and its ash collected in a Petri dish. The ash was found to comprise of magnesium Oxide and Magnesium nitride
- Write an equation for the reaction leading to formation of the magnesium nitride. (1mk)
- A little water was added to the products in the Petri dish. State and explain the observation made. (2mks)
- A piece of blue litmus paper was dipped into the solution formed in (b) above. State the observation made. (1mk)
-
-
- A compound has an empirical formula C3H6O and a relative formula mass of 116.
- Determine its molecular formula. (H =1, C = 12, O =16) (2 marks)
- Calculate the percentage composition of carbon by mass in the compound. (1 mark)
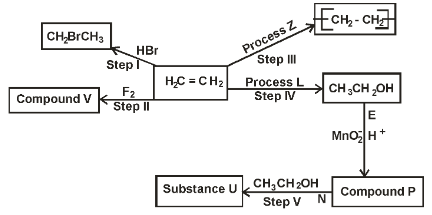
- Study the scheme below and answer the questions that follow.
- State the conditions for process in step V. (1 mark)
- Name the reaction represented by process.
- Z (1 mark)
- L (1mark)
- E 1 mark)
- N (1 mark)
- Draw and name the structure of the substance.
- V (1 mark)
- P (1 mark)
- U (1 mark)
- A compound has an empirical formula C3H6O and a relative formula mass of 116.
MARKING SCHEME
-
- H✓½ I✓½ group VII✓½ gains one electron✓½ to form ion
- Giant ionic structure✓½ - A is a metal, oxygen is a non-metal hence form ionically, bounded compound✓½
- H ✓ is more reactive than I . H is more ✓½ electronegative element
- The oxide of D is covalently bounded hence has simple molecular structure ✓½and weak van der waals forces while that of C has ionic bond, hence giant ionic structure ✓½
-
- A ✓½ the most electropositive element the only element in group I✓½ i.e. metallic element in group I has the highest ability to ✓½ loose valence electron from ion. Due to weakest electrostatic ✓½ forces
- H ✓½is the most electronegative element. the only element in group VII✓½ which has the shortest/shorter✓½ atomic radius, has the highest✓½ ability to gain electron to form iron✓½
-
- B has larger✓½ atomic radius than H, B belong to group II. B has less charge nuclear charge✓½ than H:
- E has large✓½ atomic radius than D for E has 3 energy levels i.e. belongs in third period while D has✓½ two energy levels, in 2nd period.
- The brown ✓½ solid of copper changes to blue½ solution of copper (II) nitrate solution brown gas ✓½ of nitrogen (IV) oxide gas formed. The copper metal is oxidized by conc HNO3 to Cu2+ while the acid is reduced to NO2 gas and water
-
-
- Purifies – removes dust particles and other impurities that would otherwise poison the catalyst. √ (½)
- Heat exchanger – Heats the ammonia – air mixture reactions from the compressor while it cools the hot gaseous products from the catalytic chamber√ (½)
-
- Gas A – Ammonia /NH3 √( ½)
- Gas B – Nitrogen (II) Oxide /NO √ (½)
- Catalyst C– Platinum – rhodium √ (½)
-
- 4NH3(g) + 5O2(g) → 4NO(g) + 6H2O(g) ✓ 1
- 2NO2 (g) + H2O (l) → HNO3 (aq) + HNO2 (aq) ✓1
- RFM HNO3 = 1 + 14 + 48 = 63 √( ½)
1cm3 (1.42 x 68/100) √ (½) g of HNO3 = 0.9656g
1cm3 → (1.42 x 68 ) √ (½) moles of HNO3 = 0.015326 moles √ (½)
63 100
∴ 1000 1000 x 1.42 x 68 √ (½)
1 63 100
= 15.33 M (½) total 3 mk -
- Effervescence of red / brown gas / fumes are produced(√ 1)
- Hot conc. HNO3 oxidizes sulphur to sulphuric (VI) acid and itself is reduced to nitrogen (IV) oxide (√ 1). Or
S(s) + 6HNO3 (aq) → H2SO4 (aq) + 6NO2 (g) + 2H2O (l)
-
-
-
- Gas D – Sulphur (IV) Oxide // Sulphure dioxide ✓ ½
- Gas L – Hydrogen Sulphide ✓ ½
- Gas V – Hydrogen gas✓½ Accept – name only 1½mk
-
- Compound B – Iron (III) Chloride // FeCl3 ✓½
- Compound T – Iron (II) Sulphide // FeS ✓ ½
- Solid A – Iron (III) oxide // Fe2O3 ✓½
- Solid V – Iron (III) hydroxide // Fe(OH)3 ✓½
- Solid X – Iron (II) hydroxide // Fe(OH)2 ✓ ½
Accept – name or formula. Rej if name and formula do not tally 2½mk
- Rusting ✓ 1 1mk
- Dirty green/green ✓1
-
- Step 1 2Fe(s) + 3Cl2(g)
 2FeCl3 ✓1 1mk
2FeCl3 ✓1 1mk - Step 5 FeS(s) + 2HCl2(ag)
 2FeCl2(s) + H2 S(g)✓ 1
2FeCl2(s) + H2 S(g)✓ 1
Deny ½ if state symbols are wrong or missing.
- Step 1 2Fe(s) + 3Cl2(g)
- An oxidizing agent ✓1 1mk
-
-
-
-
- Conc. Sulphuric (VI) acid ✓ ½ / sulphuric acid Acc. formula
- Hydrogen gas // H2✓ ½
- AlCl3 ✓ 1
-
-
- NaCl(s) + H2SO4(l)
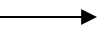 NaHSO4(aq) + HCl(g) ✓1 1 mk or Deny ½ if state symbols wrong or missing
NaHSO4(aq) + HCl(g) ✓1 1 mk or Deny ½ if state symbols wrong or missing
H2SO4(l) + Cl-(aq)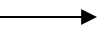 H2SO4(aq) + HCl(g)
H2SO4(aq) + HCl(g) - 2Al(s) + 6HCl (g)
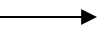 2AlCl3(s) + 3H2(g) ✓1 1 mk
2AlCl3(s) + 3H2(g) ✓1 1 mk
- NaCl(s) + H2SO4(l)
- Sublimation ✓ ½
- Gas is acidic ✓1 therefore reacts ✓ ½ with the basic ✓½ calcium oxide 2mk
- Unreacted HCl ✓½ gas dissolves forming a strong acidic ✓½ solution
acc- correct equation 1mk - moles of HCL = 480 = 0.02 mols ✓½
24000
Moles ratio HCl : AlCl3 is 3:1
Moles of AlCl3 = 0.02 x 1/3
= 0.0066 moles ✓ ½ 2mk
RFM ✓ ½ = 133.5
Mass of T = 0.0066 x 133.5 = 0.8811 g ✓ ½ -
1mk
- Hydrogen Chloride does not dissociate into ions in methylbenzene (it exists in molecular form). ✓ On addition of water, HCl dissociates ✓ and H+(aq) reacts with carbonates evolving Carbon (IV) Oxide gas (CO2 (g))
- HCl(g ) + NH3(g)
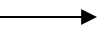 NH4Cl (s) ✓ ½ 1mk
NH4Cl (s) ✓ ½ 1mk
White Fumes ✓ ½
The observation must be mentioned / indicated
-
-
-
- Hygroscopy
- Deliquescence
- efflorescence
-
- [(Zn(OH)4)] 2+ ✓1mk
- [CU(OH)4]2+ √1
-
Empirical formula is FeSO4.7H2Oelement
Fe
S
O
H2O
mass
20.2
11.5
23.0
45.3
Ram
56
32
16
18
mols
0.36
0.36
1.44
2.52✓1mk
Mole ratio
1
1
4
7
n(FeSO4.7H2O)=278
278n=278
n=1✓1mk
Formula FeSO4.7H2O✓1mk -
- Add excess lead carbonate to dilute HNO3 acid ✓ 1mk
- Filter ✓1/2mk
- Add excess dilute HCl to the filtrate ✓1/2mk
- Filter the residue is lead(ii) chloride ✓1/2mk
- Rinse residue with distilled water and dry between filter paper to obtain solid PbCl2✓1/2mk
-
-
-
- phosphorous smolders ✓1
Its reaction with air is exothermic ✓1 - phosphorous (iii)oxide formed is an acidic oxide which dissolves in water to form phosphoric oxide. phosphoric(iii) acid ✓1
- volume of air used = 30.65 – 24. 28 = 6.37 cm3
percentage volume = 6.37/30.65 x 100 = 20.78%✓1
- phosphorous smolders ✓1
-
- black powder changes to red brown bead and White ash formed ✓1
- Zn reduces CuO to copper metal and Zn is oxidized to MgO✓1
-
- carbon (II) oxide ✓1
- Sulphuric (IV) oxide ✓1
- Nitrogen (IV) oxide
- Carbon (iv) oxide
-
- 3Mg(s) + N2(g)
 Mg3N2(s)
Mg3N2(s) - a colourless gas with a characteristic pungent smell is produced. Magnesium nitride is hydrolyzed by water producing ammonia gas.
- blue litmus paper remained blue
- 3Mg(s) + N2(g)
-
-
-
- R.F.M of E.M.F = 58
R.F.M = 116
n =RFM = 116 ✓½ = 1.7 = 2✓½
RFM of EMp 58
Molecular formula = (Emp formula) x n
= (C3H6O)x ✓½ = C6H12O2 ✓½ - % of C = mass of c × 100%
RFM
= 3 × 12 × 100 = 36 × 100 ✓½ = 31.03%✓½
116 116
- R.F.M of E.M.F = 58
-
- few drops of conc.sulphuric acid✓1
-
- Z -self-addition polymerisation. Reject polymerisation
- L - Hydrolysis✓1
- E -Oxidation of ethanol✓1 by acidified KMnO4
- N - Esterification✓1
-
-
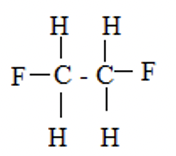 ✓½
✓½
1, 2 – difluoroethane✓½ -
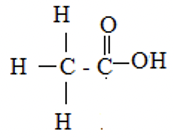 ✓½
✓½
Ethanoic acid ✓½ -
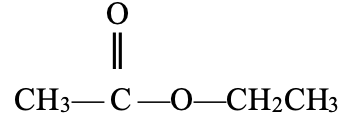 ✓½
✓½
Ethylethanoate ✓½
-
-
Download Chemistry Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Chogoria Murugi Zone Pre Mock Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students