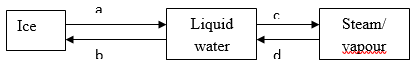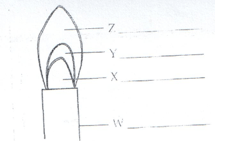Chemistry Form 1 End Term 2 Exams 2021 with Marking Schemes
- Explain why most laboratory apparatus are made of glass. (2mks)
-
- What is drug abuse? (1mk)
- Name three drugs that are commonly abused. (3mks)
- State two ways of preventing drug abuse. (2mks)
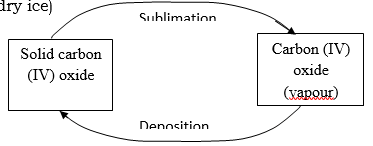
- Study the diagram below and answer the question that follows.
- Name the process labeled a, b, c and d. (2mks)
- Draw a similar diagram to show the effect of temperature on solid carbon (IV) oxide (dry ice) (2mks)
- Identify the elements present in the following compounds.
- Magnesium oxide. (1mk)
- Zinc chloride. (1mk)
- Sodium sulphate. (1mk)
- Aluminium nitrate. (1mk)
- State three differences between luminous and non luminous flame. (3mks)
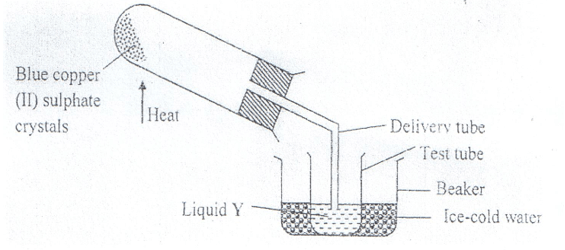
- The diagram below shows the effect of heat on hydrated copper (II) sulphate crystals.
- State the colour of hydrated copper (II) sulphate crystals. (1mk)
- What observations are made inside the boiling tube after heating has taken place? (1mk)
- What is the use of ice-cold water in the beaker? ( ½ mk)
- Name liquid Y. ( ½ mk)
- What will be observed if the residue in the boiling tube is cooled and a few drops of liquid Y added to it? (1mk)
- What type of chemical change is exhibited by copper (II) sulphate? (1mk)
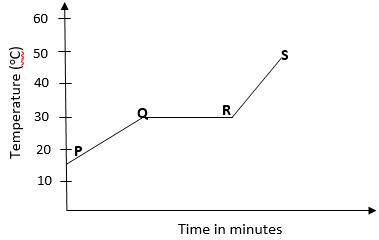
- The graph below shows the shape of the curve obtained by a student when solid X was heated to boiling.
- Determine the melting point of solid X. (1mk)
- After the experiment the student concluded that substance x was pure substance. Explain why he concluded so. (1mk)
- If candle wax was used in the above experiment the portion QR would be horizontal. What does this tell us about candle wax? (1mk)
-
- What is the effect of impurities on the melting and boiling point of substances? (2mks)
- Explain the following:
- During extraction of metals from their molten compounds for example calcium chloride is added to rock salt during the extraction of sodium from sodium chloride. (1mk)
- In temperate counties there is spreading of common salt in the roads during winter. (1mk)
- Distinguish between temporary physical and permanent chemical changes. (2mks)
-
- Write the names of the elements represented by symbols. (3mks)
- K –
- Cl –
- Fe –
- Mg –
- C –
- Be –
- Define:
- Atom. (1mk)
- Compound. (1mk)
- Element. (1mk)
- Write the names of the elements represented by symbols. (3mks)
-
- Complete the following. (3mks)
- Acid + metal →
- Acid + Base →
- Acid + Carbonate →
- Write word equations for the following reactions.
- Zinc and hydrochloric acid. (1mk)
- Potassium hydroxide and sulphuric (VI) acid. (1mk)
- Magnesium carbonate and nitric (V) acid. (1mk)
- Complete the following. (3mks)
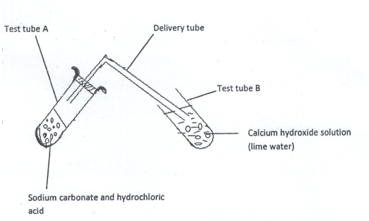
- Study the diagram below for the reaction between sodium carbonate and hydrochloric acid and answer the questions that follow.
- Explain what was observed in:
- Test tube A. (1mk)
- Test tube B. (1mk)
- Write a word equation for the reaction which took place in test tube. (1mk)
- Explain what was observed in:
- State whether solutions with the following pH values are acidic, basic or neutral. (2mks)
- pH 3 –
- pH 11 –
- pH 14 –
- pH 7 –
- Is air a mixture or a compound? Explain. (2mks)
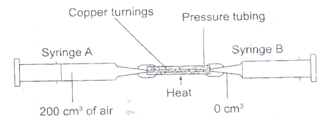
- The apparatus below were used to determine the volume of oxygen in air. About 200cm3 of air were passed repeatedly from syringe A to syringe B over heated copper turnings as shown in the diagram.
After sometime, the volume of air in the syringe A was 160cm3 and syringe B, 0cm3- Calculate the percentage of oxygen in the initial sample of air. (2mks)
- The percentage of oxygen calculated above was slightly less than the percentage of oxygen in air. Explain why. (1mk)
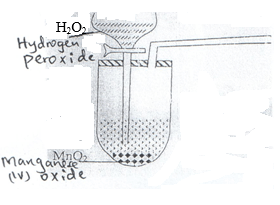
- The set-up below was used to prepare a sample of oxygen gas. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Complete the diagram to show how oxygen can be collected. (2mks)
- Write a word equation for the reaction that produces oxygen above. (1mk)
- State two physical properties of oxygen gas. (2mks)
- State two uses of oxygen. (2mks)
- Candle wax is an example of a hydrocarbon.
- What is a hydrocarbon? (1mk)
- Name the two products formed when hydrocarbons burn in oxygen. (1mk)
- Study the figure below and use it to answer the following questions.
- Name the parts labeled X and Y. (1mk)
- Identify the flame. (1mk)
- Which part of the flame is the hottest? (1mk)
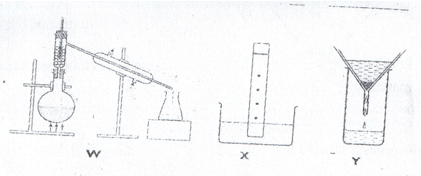
- The diagrams below show some physical methods of separating mixtures.
- Name the methods of separation labeled W, X and Y.

MARKING SCHEME:
- Explain why most laboratory apparatus are made of glass. (2mks)
- Glass is easy to clean.
- Glass does not react with most reagents.
- Glass is transparent hence allow one to see clearly the reactions taking place. (any 2 x 1 = 2mks)
-
- What is drug abuse? (1mk)
- It is the overdose or under dose of a prescribed drug.
- The use of drugs for a purpose other than what is intended for.
- Name three drugs that are commonly abused. (3mks)
- Alcohol
- Tobacco
- Bhang
- Miraa (khat)
- Mandrax
- Cocaine
- State two ways of preventing drug abuse. (2mks)
- Avoid peer pressure.
- Avoid taking drugs without the doctor’s advice.
- Avoid taking drugs for pleasure.
- Avoid company of drug users.
- What is drug abuse? (1mk)
- Study the diagram below and answer the question that follows.
- Name the process labeled a, b, c and d. (2mks)
a – melting
b – freezing.
c – evaporation.
D – condensation. (4 x ½ = 2mks) - Draw a similar diagram to show the effect of temperature on solid carbon (IV) oxide (dry ice) (2mks)
- Name the process labeled a, b, c and d. (2mks)
- Identify the elements present in the following compounds.
- Magnesium oxide. (1mk)
Magnesium and oxygen. - Zinc chloride. (1mk)
Zinc and chlorine - Sodium sulphate. (1mk)
Sodium, sulphur and oxygen. - Aluminium nitrate. (1mk)
Aluminium, nitrogen and oxygen
- Magnesium oxide. (1mk)
- State three differences between luminous and non luminous flame. (3mks)
Luminous Non-luminous - Burns quetly
- Has four zones
- Large and wavy.
- Produce a lot of soot.
- Fairly hot.
- Bright yellow in colour.
- Produce a lot of light- Burns with a roaring sound.
- Has three zones.
- Short and steady.
- Does not produce soot.
- Very hot.
- Pale blue in colour.
- Produce less light. - The diagram below shows the effect of heat on hydrated copper (II) sulphate crystals.
- State the colour of hydrated copper (II) sulphate crystals. (1mk)
Blue - What observations are made inside the boiling tube after heating has taken place? (1mk)
- Blue hydrated copper (II) sullphate changes colour to white.
- A colourless liquid collect at the cooler parts of the boiling tube.
- What is the use of ice-cold water in the beaker? ( ½ mk)
To condense the vapour to liquid water. - Name liquid Y. ( ½ mk)
Water - What will be observed if the residue in the boiling tube is cooled and a few drops of liquid Y added to it? (1mk)
The white anhydrous copper (II) sulphate will change to blue. - What type of chemical change is exhibited by copper (II) sulphate? (1mk)
Temporary chemical change.
- State the colour of hydrated copper (II) sulphate crystals. (1mk)
- The graph below shows the shape of the curve obtained by a student when solid X was heated to boiling.
- Determine the melting point of solid X. (1mk)
30oC. - After the experiment the student concluded that substance x was pure substance. Explain why he concluded so. (1mk)
The melting point of the substance was sharp. - If candle wax was used in the above experiment the portion QR would be horizontal. What does this tell us about candle wax? (1mk)
Candle wax is not pure substance, it is made up of mixture of substances.
- Determine the melting point of solid X. (1mk)
-
- What is the effect of impurities on the melting and boiling point of substances?
- impurities lower the melting point of pure substances and it raises the boiling point of substances.
- Explain the following:
- During extraction of metals from their molten compounds for example calcium chloride is added to rock salt during the extraction of sodium from sodium chloride. (1mk)
Calcium chloride is added as an impurity to lower the melting point of sodium chloride hence making the process economical. - In temperate counties there is spreading of common salt in the roads during winter. (1mk)
Common salt lowers the melting point of ice.
- During extraction of metals from their molten compounds for example calcium chloride is added to rock salt during the extraction of sodium from sodium chloride. (1mk)
- What is the effect of impurities on the melting and boiling point of substances?
- Distinguish between temporary physical and permanent chemical changes. (2mks)
Temporary physical Permanent chemical 1. No new substance is formed
2. Change is easily reversible.
3. No change in mass
4. Heat energy is not absorbed or evolved.1. New substances are formed
2. Change is irreversible.
3. There is change in mass.
4. Heat energy is absorbed or evolved -
- Write the names of the elements represented by symbols.
- K – potassium
- Cl – chlorine
- Fe – iron
- Mg –magnesium
- C – carbon
- Be – beryllium
- Define:
- Atom (1mk)
Is the smallest particle of an element which can take part in chemical change. - Compound (1mk)
A pure substance made up of two or more elements chemically combined. - Element (1mk)
A pure substance which cannot be split into simpler substance by chemical means
- Atom (1mk)
- Write the names of the elements represented by symbols.
-
- Complete the following. (3mks)
- Acid + metal → salt + Hydrogen
- Acid + Base → Salt + Water
- Acid + Carbonate → Salt + Carbon (IV) oxide + Water
- Write word equations for the following reactions.
- Zinc and hydrochloric acid. (1mk)
Zinc + Hydrochloric acid → Zinc chloride + Hydrogen - Potassium hydroxide and sulphuric (VI) acid. (1mk)
Potassium hyrdoxide + Sulphuric (VI) acid → Potassium sulphate + water - Magnesium carbonate and nitric (V) acid. (1mk)
Magnesium carbonate + Nitric (V) acid → Magnesium nitrate + Carbon (IV) oxide + Water
- Zinc and hydrochloric acid. (1mk)
- Complete the following. (3mks)
- Study the diagram below for the reaction between sodium carbonate and hydrochloric acid and answer the questions that follow.
- Explain what was observed in:
- Test tube A. (1mk)
- Effervescence took place / bubbles of gas produced.
- A colourless gas was produced.
- Test tube B. (1mk)
Calcium hydroxide (lime water) formed a white precipitate.
- Test tube A. (1mk)
- Write a word equation for the reaction which took place in test tube A. (1mk)
Sodium carbonate + Hydrochloric acid -> Sodium Chloride + Carbon (IV) Oxide + water
- Explain what was observed in:
- State whether solutions with the following pH values are acidic, basic or neutral. (2mks)
pH 3 – Acidic
pH 11 – Basic
pH 14 – Basic
pH 7 – Neutral - Is air a mixture or a compound? Explain. (2mks)
- A mixture √ (1mk)
- Its components are gases which can be separated by physical means.
- The apparatus below were used to determine the volume of oxygen in air. About 200cm3 of air were passed repeatedly from syringe A to syringe B over heated copper turnings as shown in the diagram.
After sometime, the volume of air in the syringe A was 160cm3 and syringe B, 0cm3- Calculate the percentage of oxygen in the initial sample of air. (2mks)
=(200 - 160)cm3 x 100%
200
=40/200 x 100
= 20% - The percentage of oxygen calculated above was slightly less than the percentage of oxygen in air. Explain why. (1mk)
- Not all oxygen reacted/ was used up
- Due to experimental errors.
- Calculate the percentage of oxygen in the initial sample of air. (2mks)
- The set-up below was used to prepare a sample of oxygen gas. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Complete the diagram to show how oxygen can be collected. (2mks)
- Write a word equation for the reaction that produces oxygen above. (1mk)
Hydrogen peroxide -Manganese(iv oxide)-> Water + Oxygen - State two physical properties of oxygen gas. (2mks)
- Colourless and odourless gas.
- Boils at -183o
- Slightly soluble in water.
- State two uses of oxygen. (2mks)
- Used in hospitals by patients with breathing difficulties.
- Used by mountain climbers and deep sea divers.
- Used for welding as oxyhydrogen flame or oxyacetylene flame.
- Candle wax is an example of a hydrocarbon.
- What is a hydrocarbon? (1mk)
A compound of carbon and hydrogen only. - Name the two products formed when hydrocarbons burn in oxygen. (1mk)
- Carbon (IV) oxide.
- Water
- What is a hydrocarbon? (1mk)
- Study the figure below and use it to answer the following questions.
- Name the parts labeled X and Y. (1mk)
X – almost colourless zone.
Y – green blue zone.
( ½ mk each) - Identify the flame. (1mk)
Non-luminous - Which part of the flame is the hottest? (1mk)
Z – pale blue zone.
- Name the parts labeled X and Y. (1mk)
- The diagrams below show some physical methods of separating mixtures.
- Name the methods of separation labeled W, X and Y.
- W – Fractional distillation.
- X – Paper chromatography.
- Y – Filtration.
- Name the methods of separation labeled W, X and Y.
Download Chemistry Form 1 Questions and Answers- End Term 2 Exams 2021.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students