Biology Form 1 End Term 2 Exams 2021 with Marking Schemes
- Name the branch of biology involved in the study of
- Relationships of living with each other and their environment.(1mrk)
- Identification and classification of organisms.(1mrk)
- The binomial name of housefly is MUSCA DOMESTICA.
- State two mistakes in the way the scientific name is written. (2mks)
- Re-write the name in correct manner following the rules of binomial nomenclature. (1mrk.)
- State the use of each of the following apparatus: (3mrks)
- Bait trap
- Specimen bottle
- Pitfall trap
-
- Give the functions of the following parts in a light microscope.(3mrks)
- Diaphragm
- Condenser
- Objective lens
- Why is it not likely to use an electron microscope in a school laboratory? 2mks
- Give the functions of the following parts in a light microscope.(3mrks)
- Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow:
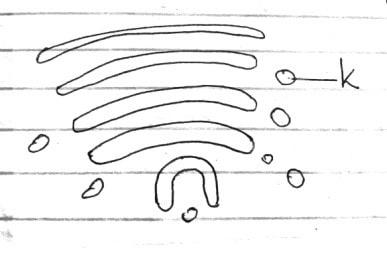
- Identify the organelle. 1mk
- Name the structure labelled K 1mk
- State two functions of the organelle named in (a) above. 2mks
- What is the importance of carrying out the following procedures when preparing temporary slides in the laboratory? (3mks).
- Adding water to the specimen.
- Staining the specimen.
- Using a sharp blade to make sections.
- A student estimating a cell size of an onion epidermal cells observed the following on the microscope field of view using a transparent ruler.
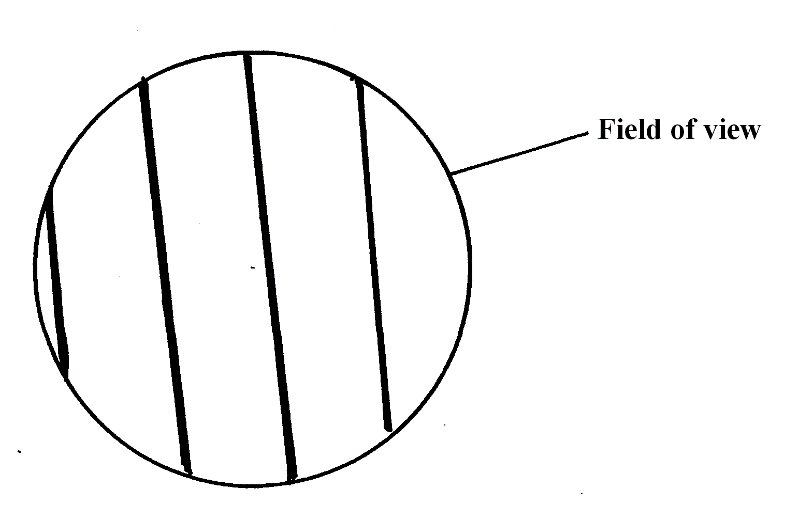
The student identified 20 cells across the field of view. Calculate the size of the cell in Micrometers (show your working) (3mks) - Define the term physiology(1mrk)
-
- Name the principal components of cell membrane (3mrks)
-
- Why would a cell allow some substances to pass through it but not others? (1mrks)
- Other than the property of semi- permeability stated in b (i) above, state two other properties of a cell membrane (2mrks)
- Explain what would happen to the red blood cells if placed in concentrated salt solution. 3mks
- Define the following terms(6mrks)
- Isotonic solution
- Hypotonic solution
- Hypertonic solution
- What is meant by the following biological terms?
- Crenation (2mk)
- Haemolysis (2mk)
- What role does osmosis play in plants?(2mks)
- Distinguish between diffusion and active transport (2mks)
- Define the term nutrition(2mrks)
- Name and explain the two types of nutrition(4mrks)
- Differentiate between Chemotropism and Phototropism(4mrks)
- Draw a well labelled diagram of a leaf showing the external features. (3mrks)
- Define the term photosynthesis(2mrks)
- What four conditions are needed for photosynthesis to occur?(4mrks)
-
- What is the importance of photosynthesis in nature?(2mrks)
- The organelle below is important in the process of Nutrition.
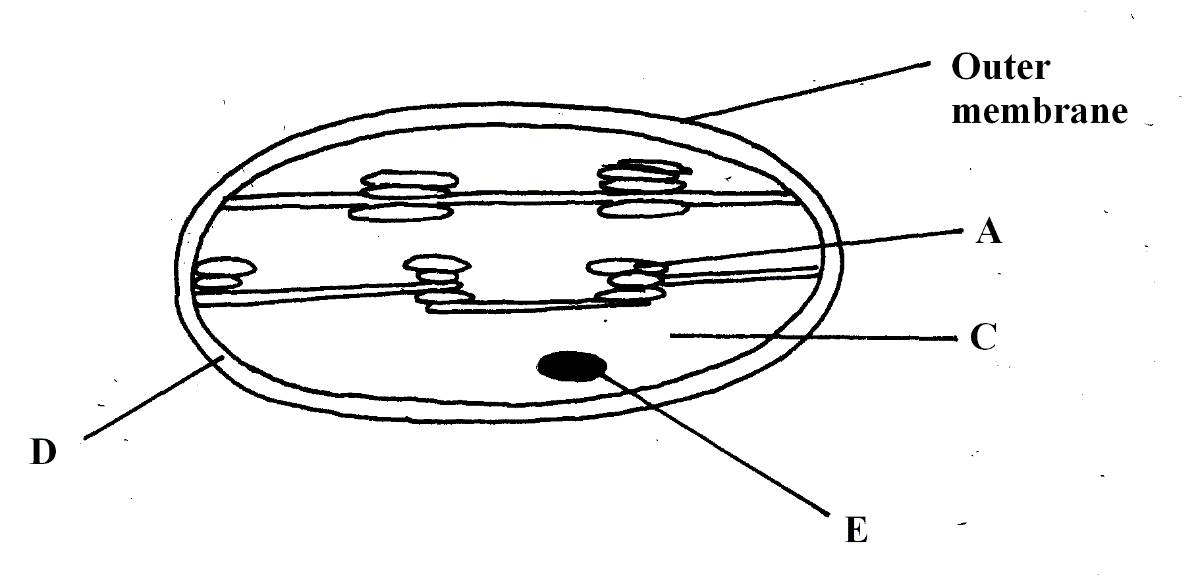
- Identify the organelle. (1mk)
- Name the part labeled (2mk)
A
C
- Name the part where the following stages of photosynthesis occur(2mrks)
- Light independent stage
- Dark stage
- State the role of light in the processes of photosynthesis(1mrk)
- Name the building blocks of ;(3mrks)
- Proteins
- Carbohydrates
- Fats
- What are enzymes?(1mrks)
- State the main properties of enzymes (2mrks)
Marking Scheme
- Name the branch of biology involved in the study of
- Relationships of living with each other and their environment.(1mrk)
Ecology - Identification and classification of organisms.(1mrk)
Taxonomy
- Relationships of living with each other and their environment.(1mrk)
- The binomial name of housefly is MUSCA DOMESTICA.
- State two mistakes in the way the scientific name is written. (2mks)
- Species name written in capital letters;
- Two names are not underlined; (separately)
- Re-write the name in correct manner following the rules of binomial nomenclature. (1mrk.)
Musca domestica
- State two mistakes in the way the scientific name is written. (2mks)
- State the use of each of the following apparatus: (3mrks)
- Bait trap– for attracting and trapping small animals;
- Specimen bottle - for keeping / storing collected specimen;
- Pit fall trap - for catching crawling animals;
-
- Give the functions of the following parts in a light microscope.(5mrks)
- Diaphragm - Regulates the amount of light that is allowed to pass through the specimen.
- Condenser (light director) - Concentrates light before it passes through the specimen.
- Objective lens - brings image into focus and magnifies it.
- Why is it not likely to use an electron microscope in a school laboratory? 2mks
- Specimen illuminated with a beam of electrons.
- Uses electromagnetic lenses
- Stains used are made from heavy metals such as lead that are expensive
- Give the functions of the following parts in a light microscope.(5mrks)
- Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow:
- Identify the organelle. 1mk
Golgi bodies/apparatus - Name the structure labelled K (1mk)
Secretory vessicles - State two functions of the organelle named in (a) above. 2mks
- Packaging and transport of glycoproteins
- Involved in secretion of synthesized proteins and carbohydrates.
- Involved in the formation of lysosomes.
- Identify the organelle. 1mk
- What is the importance of carrying out the following procedures when preparing temporary slides in the laboratory? (3mks).
- Adding water to the specimen.
To maintain turgidity of cells - Staining the specimen.
Making parts distinct - Using a sharp blade to make sections
to avoid distortion of cell structures
- Adding water to the specimen.
- A student estimating a cell size of an onion epidermal cells observed the following on The microscope field of view using a transparent ruler.
The student identified 20 cells across the field of view. Calculate the size of the cell in Micrometers (show your working) (3mks)
Field of view = 4mm
Field of view in micrometers = 4 x 1000 = 4000 um;
Size of cell =
Field of view
Number of cells
=4000/20; = 200Um; - Define the term physiology(2mrk)
The study of the functions of the different parts of the cell. -
- Name the principal components of cell membrane (3mrks)
Two protein layers, phospholipid layer and pores. -
- Why would a cell allow some substances to pass through it but not others? (1mrks)
Has pores. - Other than the property of semi- permeability stated in b (i) above, state two other properties of a cell membrane (2mrks)
- Sensitivity to changes in temperatures and PH.
- Possesses electrical charges
- Explain what would happen to the red blood cells if placed in concentrated salt solution. (3mks)
The solution is hypertonic to the red blood cell cytoplasm; water molecules will move from red blood cells by osmosis; the red blood cell will become crenated;
- Why would a cell allow some substances to pass through it but not others? (1mrks)
- Name the principal components of cell membrane (3mrks)
- Define the following terms(6mrks)
- Isotonic solution
The solutions of equal concentration and are separated by a semi-permeable membrane - Hypotonic solution
This is where the solution has a lower concentration of solutes and high concentration of water molecules than the cytoplasm of a cell. - Hypertonic solution
This is where the solution has a higher concentration of solutes and low concentration of water molecules than the cytoplasm of a cell.
- Isotonic solution
- What is meant by the following biological terms?
- Crenation (2mk)
Shrinking of red blood cells/ animal cells as a result of water loss by osmosis (when placed in hypertonic solution); - Haemolysis (2mk)
Bursting of red blood cells as a result of uptake of water by osmosis (when placed in hypotonic solution);
- Crenation (2mk)
- What role does osmosis play in plants?(2mks)
- Uptake of water by the plants from the soil;
- Maintain turgidity of cells by herbaceous plants;
- Opening and closing of stomata;
- Distinguish between diffusion and active transport (2mks)
- In diffusion substances move from a highly conc. Region to a lowly conc. Region while in active transport molecules move from a lowly concentration region to a highly conc. Region .
- Diffusion molecules move along conc. Gradient while in active transport molecules move against conc. Gradient.
- No energy is required in diffusion while energy is required in active transport
- Active transport requires carrier molecules while carrier molecule not required in diffusion
- Define the term nutrition(2mrks)
Process by which living things obtain and utilize food substances. - Name and explain the two types of nutrition(4mrks)
- Autrophic nutrition. This is where living organism manufactures its own complex food substances from simple substances such as carbon (iv) oxide, water, light or chemical energy.
- Heterotrophic nutrition. This is where organisms takes in complex food materials such as carbohydrates, proteins and fats obtained from bodies of plants and animals.
- Differentiate between Chemotropism and Phototropism 4mrks.
- Chemotropism is where organisms called chemotrophs make their own food using energy from special types of chemical reactions.In phototropism, the organisms use carbon (iv) oxide water and energy from sun to make their own food.
- Draw a well labelled diagram of a leaf showing the external features. (3mrks)
Drawing=1mrk, Labelling two parts =2mrks - Define the term photosynthesis(2mrks)
This is the manufacture of food materials using light energy from the sun. It mostly takes place in green plants. - What four conditions are needed for photosynthesis to occur? 4mrks
- Water
- Carbon (iv) oxide
- Light
- Chlorophyll
-
- What is the importance of photosynthesis in nature?(2mrks)
- Replaces oxygen in air which is continuously used up by all living things for respiration.
- Photosynthesis uses carbon IV oxide from the air and incorporates it into carbon found in food substances.
- Plants make their own food and animals depend directly or indirectly on plants for their food. Food contains energy from the sun stored as chemical energy.
- The organelle below is important in the process of Nutrition.
- Identify the organelle. (1mk)
Chloroplast; - Name the part labeled (2mk)
A Granum
C Stroma;
- Identify the organelle. (1mk)
- What is the importance of photosynthesis in nature?(2mrks)
- Name the part where the following stages of photosynthesis occur(2mrks)
- Light independent stage - Granum
- Dark stage - the stroma
- State the role of light in the processes of photosynthesis(1mrk)
Used to split up water molecules into hydrogen ions and oxygen atoms - Name the building blocks of ;(3mrks)
- proteins - amino acids
- Carbohydrates - monosaccharides
- Lipids - fatty acids and glycerol.
- What are enzymes?(2mrks)
- Organic catalyst which are protein in nature
- State the main properties of enzymes (2mrks)
- Enzymes are protein in nature. They are therefore affected by temperature and PH.
- Enzymes are substrate-specific.
- Enzymes are efficient in small amounts since they are not affected by the reactions they catalyze. They can be used again and again.
- Enzymes are catalysts that speed up the rate of cellular reactions. They are not used up in the reactions they catalyze.
- Many of the enzyme-catalyzed reactions are reversible.
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Biology Form 1 Questions and Answers - End Term 2 Exams 2021.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

