Instructions
- Answer ALL the questions

QUESTIONS
- Discuss the criteria for testing purity in liquids.(3mrks)
- Give two examples of:
- Temporary physical change.(2mrks).
- Temporary chemical change.(2mrks)
- Permanent change.(2mrks)
-
- State two long-term effects of drug abuse. (2 marks)
- Explain why most laboratory apparatus are made of glass. (2 marks )
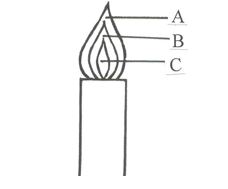
- The following diagram represents a non-luminous flame of the Bunsen burner.
- Name the parts labeled
- A _____________________________________ (1 mark )
- B _____________________________________ (1 mark )
- C _____________________________________ (1 mark)
- Which of the parts in (c i) above is the hottest? (1 mark)
- Give two reasons why a non-luminous flame is preferred for heating. (2 mark)
- Name the parts labeled
-
- Name the other type of flame produced by a Bunsen burner. (1 mark )
- Under what conditions does the Bunsen burner produce the flame you have named in d(i) above? (1 mark)
- After use, a non-luminous flame should be put off or adjusted to the other flame.Explain. (1 mark)
- Given below are pH values of different solutions P, Q and S. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
Solution pH P 1 Q 7 S 14 - Which two solutions would react together to give a solution with a pH of 7.0? (2mk)
- Which solution can be considered to be an oxide of hydrogen? (1mk)
- Nitrogen, oxygen and argon are obtained from the air using fractional distillation of air. Dust, carbon (IV) oxide and water vapour are removed from the air before fractional distillation is carried out.
- Name the compound used to absorb carbon (IV) oxide gas from the air (1mk)
- Explain how water vapour is removed from the air (2mks)
- At what temperature are the gases liquefied? (1mk)
- The boiling points of nitrogen, oxygen and argon are -196, -183 and -186 respectively. State the order in which the three are distilled off starting with the first to be distilled off. (1mk)
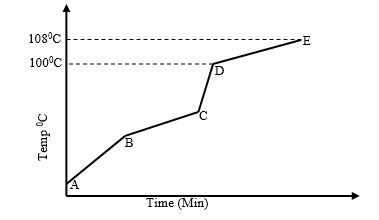
- Study the diagram shown below to answer the questions that follow. The curve shows the heating curve of water in the laboratory.
- At what temperature does the water boil? (1 Mark)
- Is the curve for a pure water or impure water? Give a reason for your answer (2 Mark)
- Give two effects of impurities on the boiling point of water (2 Mark)
- Give two effects of impurities on the melting point of ice (2 Mark)
- Dilute hydrochloric acid can react with calcium carbonate, copper (II) oxide and magnesium metal to form some products.
- Write a word equation for the above reaction between calcium carbonate and dilute hydrochloric acid (1 Mark)
- Write a word equation for the above reaction between magnesium metal and dilute hydrochloric acid (1mk)
- Write a word equation for the above reaction between copper (II) oxide and dilute hydrochloric acid (1mk)
- Excess magnesium ribbon sample was heated in equal volumes of:-
- Pure oxygen gas
- Air
- Why was the mass of the resulting product in (ii) more than in (i)? (2 Mark)
- Write the word equations for the reactions in part (ii) (2 Marks)
- Write the word equations for the reactions between dilute hydrochloric acid and each of the following.
- Zinc metal.(1mrk)
- Calcium hydrogen carbonate.(1mrk)
- Magnesium oxide.(1mrk)
- Potassium hydroxide.(1mrk)
- Sodium hydroxide.(1mrk)
- Oxygen gas can be prepared in the laboratory by heating potassium nitrate.
- Write a word equation of reaction to show the decomposition of potassium nitrate (1 Mark)
- State two physical properties of oxygen gas (2 Mark)
- Outline four uses of oxygen gas (4 Mark)
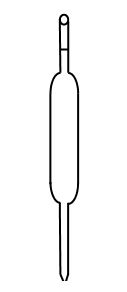
- The apparatus below is commonly used in a chemistry laboratory to measure volumes.
- Give its name (1 Mark)
- Name any other three apparatus which can be used to measure volumes of liquids (3mks)
- Give its name (1 Mark)
- The chromatogram of two inks and three dyes is drawn below.
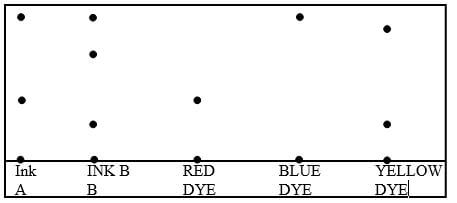
- Name the colours of dyes present in ink A (2 Mark)
- Suggest how separated dyes can be recovered (2 Mark)
- What properties of the dyes make this method of separation possible? (2 Mark)
- Name the method that can be used to separate the following:
- Ethanol and water mixture (1mk)
- Kerosene and water mixture (1mk)
- Common salt and iodine mixture (1mk)
- In temperate countries, salt is sprayed on roads to melt icet and clear roads but the long term effect on this practice is costly to motorist.
- Explain why salt help in melting the ice. (2mark)
- Explain why the long term effect is costly to motorist. (1mark)
-
- The diagrams below are some common laboratory apparatus. Name each apparatus and state its use. (4 Marks)

Name ………………………………….. Name …………………………..
Use ……………………………………. Use ……………………………...
- The diagrams below are some common laboratory apparatus. Name each apparatus and state its use. (4 Marks)
- Excess iron fillings were allowed to rust in 1000cm3 of moist air and the volume of the remaining air was measured each day as shown in the table below:
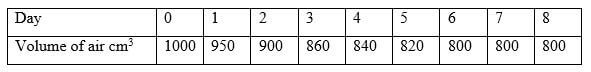
- Why did the volume of air remain constant from day six? (2 mark)
- Determine the percentage of oxygen in air using the data given in the table. (2 mark)
- Give two reasons why air is a mixture but not a compound. (2 mark)

MARKING SCHEME
- The purity of Liquids can be tested by evaporating on an evaporating dish or by measuring its boiling point. Pure liquid compounds possess sharp melting and boiling points. Therefore, melting and boiling points of a compound can be used as a criteria of purity. Some of the analytical purity testing methods include titration, infrared spectroscopy, paper chromatography, and optical rotation, among others
-
-
- folding of a paper sheet
- melting of wax
- freezing and boiling water
- melting of ice
- condensation
- vaporization
- magnetizing a compass needle
- dissolving sugar in water
- All chemical change is permanent and irreversible and
-
- burning of paper
- burning of fuel
- rusting of iron
- the souring of milk
- growth in a living being
- cooking
- digestion of food
- burning of wood
-
-
-
- Addiction and dependency √½
- Stress / depression √½
- Hallucination √½
-
- Glass does not rust. √½
- Glass is transparent. √½
- Glass can withstand heating. √½
-
-
- A – Pale blue zone √½
- B – Green blue zone √½
- C – Almost colourless zone √½
- The pale blue zone
-
- It’s the hottest √½
- It’s a clean flame √½
-
-
- The luminous flame.
- When the air hole is closed.
- Non-luminous flame is clear √½ such that it's difficult to be seen. Thus it's adjusted to the luminous flame which is visible due to its brightness √½ // saves on fuel
-
-
- P and S
- Q
-
- conc sodium hydroxide//KOH ✔1 mark
- Cooled to -25oc and turns to ice ✔1 mark
- -200 ºc ✔1 mark
- N2, Ar, O2 ✔1 mark
-
- Between (100 and 108)ºC. ✔1
-
- Impure water ✔ (½ Mark)
- It boils over a temperature range √ (½ Mark)
- It raises the boiling point of the water. ✔1
-
- CaCO3+ HCl -> CaCl2 + CO2 + H2O ✔ 1 (in words: calcium carbonate+ dilute hydrochloric acid + carbon dioxide+ water)
- 2 HCl + Mg → MgCl 2 + H 2 ✔ 1 (in words: hydrochloric acid + magnesium → magnesium chloride + hydrogen gas)
- CuO + 2 HCl → CuCl2 + H2O.✔ 1 (in words: copper Oxide+ dilute hydrochloric acid → copper chloride + water)
-
- It reacts with the oxygen ✔ ½ present there and also with nitrogen ✔½ gas present there.
-
- 2Mg (s) + O2 (g) → 2MgO (s) ✔ 1 Mark
- 3Mg(s) + N2 (g) → Mg3N2(s) ✔ 1 Mark
-
- Zn + HCl → ZnCl2 + H2(in words: Zinc metal+ dilute hydrochloric acid → zinc chloride + hydrogen gas)
- Ca (HCO3)2 +HCL →CaCL2 + 2H2O + 2CO2 (in words: calcium bicarbonate + dilute hydrochloric acid → calcium chloride + water + carbon dioxide)
- MgO + 2 HCl → MgCl 2 + H 2O(in words: magnesium oxide + dilute hydrochloric acid → magnesium chloride + water)
- KOH + HCl → KCl + H2O (in words: Potassium hydroxide + dilute hydrochloric acid → potassium chloride + water)
- NaOH+ HCL → NaCl + H2O (in words: Sodium hydroxide+ dilute hydrochloric acid → sodium chloride + water)
-
- lead (II) nitrate(Decomposition)→ lead (II) oxide + nitrogen (IV) oxide +Oxygen gas
-
-
Colourless
-
Oduorless
-
Slightly soluble in water
-
Slightly denser than air
-
-
-
Oxyacetylene flame for welding ✔ ½ mark
-
In hospitals for patients with breathing difficulties ✔ ½ mark
-
In respiration ✔ ½ mark
-
When mixed helium it is used by deep sea divers and mountain climbers ✔ ½ mark
-
-
- Pipette
-
- Volumetric flask
- Measuring cylinder
- Syringe
- Burette (any three)
-
- Red ✔ ½ and blue ✔ ½
- By solvent extraction
-
- Unequal solubilities
- Different absorption abilities
-
- fractional distillation
- Separating funnel
- sublimation
-
- It acts as an impurity in the ice hence lowering its melting point. ✔ 1
- Salt accelerates the rate of rusting of the iron parts of the motor vehicles. ✔ 1
- Name: Desiccator Name: Evaporating dish
Use: Drying or keeping substances from moisture Use: Evaporating liquids to obtain crystals -
- All the oxygen was used up
-
1000-800=200;
(200/1000)x100=20% -
- It can be separated by physical means
- The components are not chemically combined
Download Chemistry Form 1 Questions and Answers - Term 3 Opener Exams 2021.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students