QUESTIONS
- State the name given to the study of (2mks)
- Insects
- Classification of living organisms.
-
- Name the products of complete hydrolysis of sucrose. (1mk)
- What happens to these products named in (a) above, when they are excess in the body of man. (2mks)
-
- State the roles of light in plant nutrition. (2mks)
- Give a reason why glucose formed at the end of photosynthesis is converted at once into starch. (1mk)
-
- State the formula for calculating linear magnification of a specimen when using a hand lens. (1mk)
- Give one functional advantage of use of the following microscopes. (2mks)
- Light Microscope
- Electron Microscope.
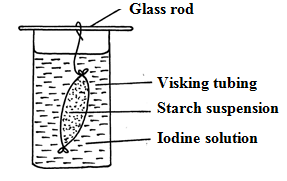
- An investigation was set up as shown in the diagram below.
After 30 minutes, starch suspension had turned blue-black while iodine solution retained its colour.- Name the physiological process that was being investigated in the experiment. (1mk)
- Account for the results observed after 30 minutes. (3mks)
- Define the term osmosis. (2mks)
-
- Distinguish between homodonts and heterodonts. (1mk)
- A certain mammal has no incisors, no canines, 6 premolars and 6 molars in the upper jaw.
In the lower jaw, there are 6 incisors, 2 canines, 6 premolars and 6 molars.- Write down the dental formular of this mammal. (1mk)
- What is the mode of nutrition of this mammal? ( 1mk)
- The reaction represented by equation below occurs in the body
Hydrogen peroxide → Oxygen + Water- Name enzyme Z (1mk)
- Name an organ in the human body where this reaction occurs (1mk)
- State the biological importance of the reaction above (1mk)
- State how each of the cells below are specialized to carry out their functions
- Palisade cell (1mk)
- A sperm cell (1mk)
- State the functions of each of the following organelles.
- Ribosomes (1mk)
- Golgi apparatus (1mk)
- Name the bond that exists between amino acids during condensation process of forming proteins? (1mk)
- Explain how the following factors affect the rate of photosynthesis
- Concentration of carbon (iv) oxide. (1mk)
- Light intensity (1mk)
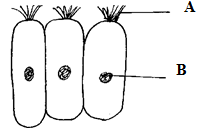
- Study the figure below which shows a type of epithelial tissue
- State the name of structure A. (1mk)
- Give an example in humans where this epithelium is found (1mk)
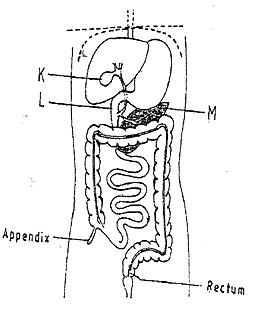
- The diagram below represents part of the human digestive system.
Name the organs labeled L and M. (2mks)
L: ………………………………………………………………………………………………
M: …………………………………………………………………………………………….. - Some form one students wanted to collect the following animals for study in the Laboratory. State the suitable apparatus they should use.
- Flying insects ........................................................... (1mark)
- Crawling stinging insects .................................................... (1mark)
- Small animals from tree barks ................................................... (1mark)
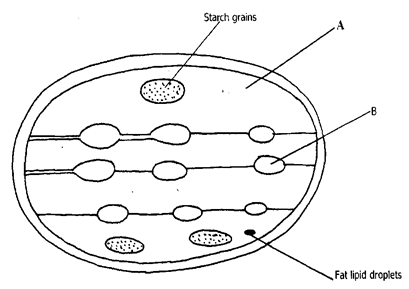
- Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follows
- Identify the structures labeled A and B (2marks)
- What process takes place in the parts labeled A and B (2mark)
- A student estimated the diameter of a field of view to be 2.8mm. The diameter was occupied by four onion cells. Estimate in micrometers the diameter of onion cell. Show your working. (2 marks)
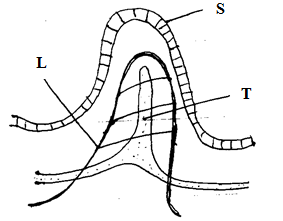
- The diagram below represents structure found in the walls of ileum.
- Identify the structure shown in the diagram. (1 mark)
- Name parts labeled S, T and L. (3 marks)
S .................................................................
T .................................................................
L ................................................................. - Name products of digestion which are absorbed into; (2 marks)
L ..............................................................................
T ............................................................................... - State how the above structure is adapted to its function. (2 marks)
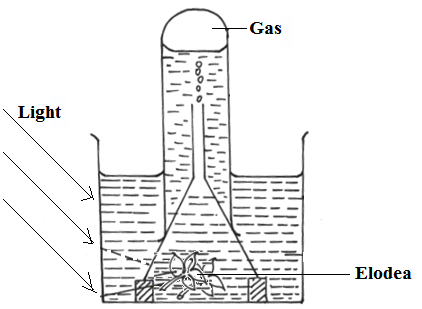
- The diagram below represents a set up that was used to investigate a certain process in a plant.
- State the process that was being investigated. (1 mark)
- Other than the factors shown, state two factors that would affect the process named in (a) above. ( 2 mark)
- Outline two roles of active transport in human beings. ( 2 marks)
- Write the role of the following parts of microscope. (3marks)
- Mirror
- Diaphragm
- Coarse adjustment knob
- Explain w hy plant cells do not burst when immersed in distilled water.(2mks)
-
- State two functions of bile juice in the digestion of food? (2marks)
- How does substances concentration affect the rate of enzyme reaction? (1mark)
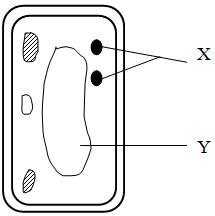
- The diagram below represents a cell
- Name the parts labeled X and Y (2marks)
X ...........................................................................................................................
Y .......................................................................................................................... - State why the structures labeled X would be more on one side than the other side.(1mark)
- Name the parts labeled X and Y (2marks)
-
- What is diffusion (2marks)
- How does diffusion gradient affect the rate of diffusion? (1mark)
MARKING SCHEME
-
- Entomology;
- Taxonomy;
-
- Glucose and fructose;
- Oxidized (in the cells) to release energy;
Converted (by the liver cells) into glycogen;
-
- Photosynthesis to provide hydrogen atoms required in the dark stage of photosynthesis;
Synthesis of more/additional ATP required in the dark stage of photosynthesis; - Starch is insoluble /osmotically inactive( hence does not affect the O.P of plant cells);
- Photosynthesis to provide hydrogen atoms required in the dark stage of photosynthesis;
-
- Magnification = Length of drawing/image rj Mg =
Corresponding length on specimen. -
- Studying /viewing live specimen;
- Higher power of resolution;
Higher power of magnification;
- Magnification = Length of drawing/image rj Mg =
-
- Diffusion; rj osmosis
- Visking is semi-permeable; allowing the smaller molecules of iodine to pass across ( to the starch suspension) while the larger starch molecules cannot across ( to the iodine solution);
- Osmosis is the movement of water molecules from a region of high water concentration to a region of low water concentration across a semi pemeable membrane.
-
- Homodonts posses the same type/kind of teeth while heterodonts posses different types/ kinds of teeth;
- I 0 , C 0, pm 3, m 3 ;
3 1 3 3 - Herbivorous; rj herbivore.
- I 0 , C 0, pm 3, m 3 ;
-
- Catalase;
- Liver;
- Breakdown of hydrogen peroxide into harmless products/water and Oxygen
-
- Has numerous chloroplast;
- Has long tail; acrosome; large nucleus. Full of DNA; a chromatin material/numerous mitochondria;
-
- sites for protein synthesis
- packaging and transportation of glycoproteins
- Peptide bond
-
- Rate of photosynthesis increase as the CO2 concentration increases up to optimum level (and vice versa)
- Rate of photosynthesis increases as light intensity increases up to optimum level; (and vice versa)
-
- A – ciliated epithelium
- Nasal / trachea epithelium.
- L-ileum
M-pancrease -
- Sweep net
- Pair of forcep
- Pooter
-
- A-Stroma
B-Granular - A Photosythesis (accept balanced equation)
B Carbon iv oxide fixation (accept a balanced equation)
- A-Stroma
- Diameter of cell = diameter of field of view ✓
number of cells
= 2.8 ✓
4
= 0.7mm x 1000✓
= 700μm -
- Villus
- S – Epithelium
T – Lacteal
L – Blood capillaries - L – Amino acids, glucose
T – Fatty acids and glycerol - Supplied with blood capillaries – to transport absorbed products of digestion
Presence of lacteals – To transport fatty acids and glycerol
Lined with thin epithelium for faster absorption of products of digestion
-
- Photosynthesis;
- Carbon (IV) oxide concentration; (the valency power correctly)
Temperature;
Amount of chlorophyll; (b) is tied to (a)
(Any two correct 1x2 =2mks)
-
- (It facilitates the) reabsorption of useful substances in the kidney tubules into the blood stream;
- (It facilitates the) absorption of digested food from the gut into the blood stream;
- (It helps in the) movement of waste products from body into the blood stream/excretion of waste products from the body cells into the blood stream; (Any first two correct 2x1 = 2mks)
-
- Reflect light from the source for the microscope specimen;
- Regulate amount of light entering the microscope/reaching the specimen;
- Move body up and down in order to obtain a rough focus of image/specimen; (3mks)
- Plant cells have cell wall; cell wall is rigid/cellulose cell wall is strong and rigid to withstand turgor pressure; Or water is absorbed by osmosis; cells become turgid; cell wall create inward pressure that prevent cell from bursting;
-
- Emulsification of fats, forms an alkaline medium for enzymes functions,
Absorption of fats, iron, calcium - Increasing substrate Concentration increases the rate of enzyme reaction.
- Emulsification of fats, forms an alkaline medium for enzymes functions,
-
- X-Chloroplasts;
Y-Vacuole(s); - Move to upper part of the cell in order to receive maximum light for photosynthesis ( in dimlight); (3mks)
- X-Chloroplasts;
-
- Movement of molecule/ions/atoms (acc substances) from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration; (2mks)
- Diffusion gradient (2mk)
The higher the diffusion gradient the faster the higher the rate of diffusion; (Acc the converse)
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Biology Questions and Answers - Form 1 End Term 3 Exams 2021.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students