BIOLOGY
FORM 1
MID TERM 2
INSTRUCTIONS:
- Answer all the questions
- Mathematical tables and electronic calculators may be used
- All working MUST be clearly shown where necessary.
QUESTIONS
- Biology is derived from two Greek words bios and logos. What is the meaning of
- Bios (1mk)
- Logos (1mk)
- List three main branches of biology and for each give its definition (6mks)
- Describe six characteristics observed among living organisms (12mks)
- Identify the following apparatus and for each state the function (6mks)
-
- Name
- Function
-
- Name
- Function
-
- Name
- Function
-
- Outline the four precautions to be observed during collection and observations of organisms during practical study. (4mks)
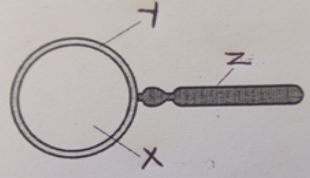
- The diagram below shows an instrument used in the laboratory
- Name the instrument (1mk)
- Label the parts (3mks)
- X
- Y
- Z
- What is the function of the instrument?
- The student observed the housefly whose actual length was 8cm. she used the apparatus named above 6(a) above and the total magnification was X4. Calculate the length of the drawing. Show your working. (3mks)
-
- What is classification? (1mk)
- What is the need for classification? (4mks)
- Fill the table below by identifying the correct kingdom and appropriate representative in each case (5mks)
kingdom representative Hydra Protozoa Yeast Monera Garden pea -
- Distinguish between magnification and resolution (2mks)
- Fill the table below (3mks)
Eye-piece lens Objective lens Total magnification X30 X600 X14 X5 X40 X2000 - Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow
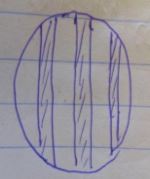
The diagram represents the field of view observed under the light microscope during the form one practical lesson.
If the students counted 10 cells across the field of view, calculate the size of one cell in micrometers. Show your working. (3mks)
- What is the importance of the following practices in biological preparation of the specimen?
- Cutting very thin sections (1mk)
- Staining the cells using common dyes (1mk)
- Adding a drop of water on the cell (1mk)
- Distinguish between unicellular and multicellular organisms. (2mks)
- Identify three types of cells found in plants. (3mks)
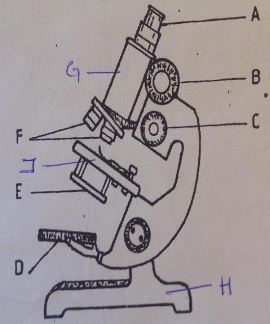
- The figure shows a microscope
- Name the parts of the microscope shown below. (4mks)
- A
- C
- J
- D
- State the functions of the parts (5mks)
- B
- E
- F
- G
- H
- Name the parts of the microscope shown below. (4mks)
- State three importance of studying biology (3mks)
- For the table below, identify the cell organelle and state the appropriate function (10mks)
CELL ORGANELLE FUNCTION Cell wall Add carbohydrates to protein and transport them in the cell Nucleus Nucleolus Protein synthesis Chloroplast Contain lytic enzymes Rough endoplasmic reticulum Transport lipids Site for respiration - Name the taxonomic units of classification in order of hierarchy (7mks)
-
- What is the name given to the double naming of living organisms? (1mk)
- The scientific name of a cat is Felis catas. Which taxonomic group does the name Felis and catas refer to? (2mks)
- Felis
- Catas
- Outline four principles used in double naming system of living organisms (4mks)
MARKING SCHEME
-
- Bios-life
- Logos-knowledge
-
- Botany-study of plants
- Zoology- study of animals
- Microbiology- study of microscopic organisms (micro-organisms)
-
- Nutrition-process by which organisms acquire and utilize nutrients;
- Respiration-process by which food substances are broken down in cells to release energy;
- Gaseous exchange-process by which respiratory gases (oxygen and carbon (IV) oxide) are passed across the respiratory surface;
- Excretion-process by which waste or harmful materials resulting from metabolic reactions within cells of organisms are eliminated
- Growth and development-Growth is the irreversible increase in size and mass while development is the irreversible change in complexity of structure of living organisms;
- Reproduction-is the process by which living things give rise to new individuals of the same kind;
- Irritability-is the ability of living things to perceive changes in their surroundings and respond to them appropriately;
- Movement-is the change in position by part of an organism while locomotion is where the whole organism moves or change in position
-
-
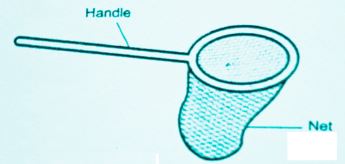
- Name-sweep net;
- Function-used for catching flying insects’ e.g. bees;
-
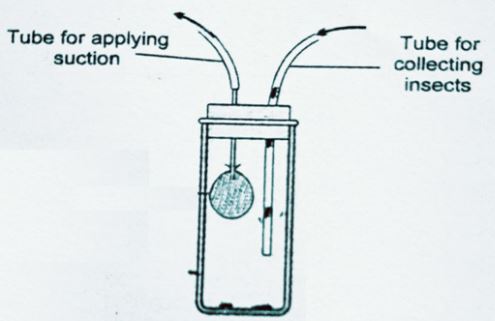
- Name-pooter;
- Function-used for sucking small animals from rock surfaces or barks of trees e.g. ants and termites;
-
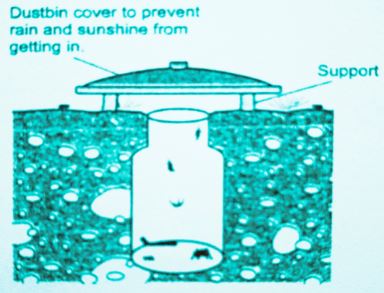
- Name-pitfall trap;
- Function-used for catching small crawling animals e.g. millipedes, spiders and cockroach;
Rej-function if the name is wrong.
Rej-if name are function are interchanged.
-
-
- Collect only the number of specimen needed to avoid wastage;
- Not to destroy the natural habitat of the specimens.
- Dangerous / injurious specimens to be handled with care as stinging insects or plants can sting or injure a person; a pair of forceps or hand gloves should be used for protection;
- Do not harm/injure the specimen during the collection exercise; to avoid distorting the features of the specimen.
- live specimens should be returned to their habitats whenever possible ; to maintain ecological balance
- Highly mobile animals to be immobilized using suitable chemical substance tetrachloromethane or chloroform, ethoxyethane;
(mark the first 4)
-
- Hand lens;
-
- X-convex lens ;
- Y-Frame;
- Z-Handle;
- Used to enlarge objects (external features of collected specimens)
- Magnification=lengh of the drawinglenght of the object;
Length of the drawing= drawing magnification X length of the object
X4 x X8cm;
=32cm;
-
- It is the grouping of living organisms based on their structures;
-
- Grouping brings together living things with similar characteristics but separates those with different features;
- helps in placing living organisms in their correct group for reference;
- helps us to arrange information about living organisms in an orderly manner to avoid chaos and confusion that could arise if these were done arbitrarily;
- helps us to understand the evolutionary relationships between different organisms;
-
Rej: wrong spellingskingdom representative Animalia Hydra Protoctista Protozoa Fungi Yeast Monera Bacteria Plantae Garden pea -
- Magnification is the ratio of an object’s image to its real size( enlargement of specimen compared to its real size); while resolution is the ability to distinguish two structures that are very close together as district entities;
-
Eye-piece lens Objective lens Total magnification X30 X20; X600 X14 X5 X70 X50 X40 X2000
Rej- if X (magnification) is missing. -
1mm=1000 micrometers (μm)
4mm=?
4mm x 1000 μm= 4000 μm;
1mm
Length of 1 cell =diameter of field of view in μmno.of cells counted along the diameter of field of vie
Cell length = 4000 m10
Length of 1 cell=400 m
-
- To allow light to pass through;
- For clear visibility/ to make observations clear;
- To make the cells turgid/ to avoid dehydration;
- Unicellular organisms- are organisms with one cell. Multicellular organisms- are organisms with many cells;
-
- Root hair cell
- Guard cell
- Palisade cell.
-
- A -Eye piece;
- C -Fine adjustment knob;
- J -Stage;
- D -Mirror; ( reg: wrong spellings)
-
- B –(Coarse adjustment knob)- brings image into rough focus by raising and lowering the body tube;
- E – (Diaphragm)-an aperture that regulates the amount of light passing through the condenser to illuminate the specimen;
- F – (Objective lens)-contains a second set of lenses used in combination with eye-piece lenses to bring the desired magnification;
- G – (Body tube) - holds the eye piece and the resolving nose piece (in position);
- H – (Base)-provides firm and stable support;
-
-
- Enables one to understand the development stages in human body;
- Enables one to pursue careers i.e. medicine(any other relevant);
- Imparts/enables one to acquire scientific skills i.e. drawing, observing, measuring, classifying, analyzing and evaluating data;
- Used to solve environmental problems e.g. food shortage, pollution, drought, poor health and conservation of resources like forests, wildlife and soil;
- Used to enhance/promote international co-operation in medicine, environmental conservation; (mark the 1st three)
-
CELL ORGANELLE FUNCTION Cell wall give cell a definite shape; provide mechanical support;provides protection against mechanical injury; Golgi bodies(golgi apparatus); Add carbohydrates to protein and transport them in the cell Nucleus Control all activities of the cell; Nucleolus Manufacture ribosomes; Ribosomes ; Protein synthesis Chloroplast Contain chlorophyll that traps light energy that is used during photosynthesis; Lysosomes ; Contain lytic enzymes Rough endoplasmic reticulum Transport proteins; Smooth endoplasmic reticulum; Transport lipids Mitochondria; acc motochondrion Site for respiration -
- Kingdom ;
- Phylum/division;
- Class ;
- Order;
- Family;
- Genus;
- Species;
Rej- if order is not followed.
-
- Binomial nomenclature
-
- Felis –genus;
- Catus-species
-
- The first part of the scientific name i.e. genus and should begin with a capital letter and the specific name should be written in small letters;
- Scientific names should be printed in italics in books and printed works, but in hand written manuscripts should be underlined as separate words;
- Specific name a times is written with the name of a scientist who first adequately described and named the organism (who invented);
- Biologist must give a latinised name for a newly described animal or plant species;
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Biology Questions and Answers - Form 1 Mid Term 2 Exams 2021.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students