CHEMISTRY
FORM 1 OPENER EXAM
TERM 3 2022
INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Write your name and admission number.
- Answer ALL the questions in this question paper.
- All your answers must be written in the spaces provided in this question paper.
- Students must answer all questions in English
-
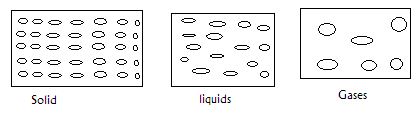
- In the boxes provided below show how molecules are spaced in solids, liquids and gases in terms of kinetic theory. (3mks)
- What conclusion can you make regarding densities of solids, liquids and gases as per the packaging of molecules in 1 (a) above. (1mk)
- In the boxes provided below show how molecules are spaced in solids, liquids and gases in terms of kinetic theory. (3mks)
- State whether the substances given below are elements, compounds or mixtures. (4mks)
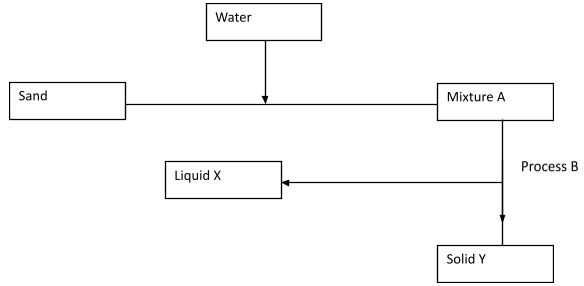
Substance Piece of Aluminium metal Sugar Solution of common salt Crude oil - Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follows.
- Name process B. (1mk)
- Give one reason why it’s possible to separate the mixture A above using process B. (1mk)
- Give the name for
- Liquid X (1mk)
- Solid Y (1mk)
- Give one application of process B in day to day life. (1mk)
- State the method of separation suitable for the following mixtures.
- Iron fillings and sulphur powder. (1mk)
- Dye from flowers. (1mk)
- Petrol from crude oil. (1mk)
- Oil from nuts. (1mk)
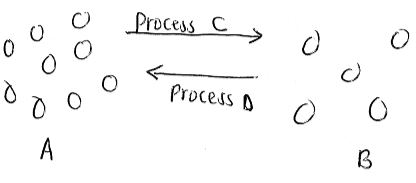
- The diagram below represents arrangement of particles in a substance. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Name process C. (1mk)
- Name two substances that undergo sublimation. (2mks)
- What name is given to process D? (1mk)
-
- If common salt is added to wax, what effect will it have on the temperature at which it melts? (1mk)
- When alcohol is heated, it changes to gas at 780C.
- What is the name given to this temperature? (1mk)
- What will happen to this temperature if an impurity like salt is added to ethanol? (1mk)
- Given the following substances and their PH values, indicate whether they are neutral, strongly acidic, weakly acidic, weakly alkaline or strongly alkaline. (7mks)
Substance PH Value Nature Sugar solution 7.0 Blood 7.4 Sulphuric (VI) acid 1.0 Tooth paste 8.0 Black coffee 5.0 Sodium hydroxide solution 14.0 Urine 6.0 - State 2 ways through which the youth of Kenya can avoid abusing drugs. (2mks)
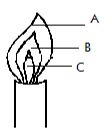
- A form one student at Moja High School lit a Bunsen burner with its air hole fully open.
- Which colour was the part labeled A? (1mk)
- Identify the hottest part of the flame. (1mk)
- Which was the almost colourless region? (1mk)
- Classify each of the following substances as either conductors or non-conductors. (5mks)
- Copper metal
- Paraffin
- Glass
- Graphite
- Magnesium
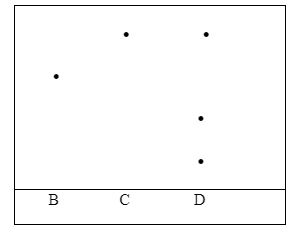
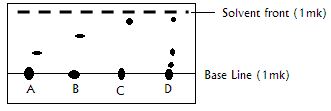
- Three pure pigments were prepared and their spots placed on a filter paper as shown below. The pure pigments are A, B and C. A mixture D was also placed on the filter paper at the same time with the pure pigments.
The filter paper was then dipped in ethanol solvent and left for an hour. The results obtained were as shown below.- Which of the three pure pigments is most sticky? Give a reason for your answer. (2mk)
- Which pure pigment is not present in the mixture D? (1mk)
- Show on the diagram the solvent front and the base line. (2mks)
-
- What is an acid-base indicator? (1mk)
- Name any three common indicators used in chemistry and give their colours in acid solution. (3mks)
Indicator Colour in acid (i) (ii) (iii) - What is the advantage of universal indicator over other common acid-base indicators? (1mk)
- Citric acid, lactic acid, methanoic acid and hydrochloric acid are found in various substances in plants and animals. State where these acids occur. (4mks)
Acid Where found (i)Citric acid (ii)Lactic acid (iii)Methanoic acid (iv)Hydrochloric acid -
- A student mixed iron fillings with sulphur powder in a watch glass. The mixture was heated and a new substance was formed.
- Is this a physical or chemical change? (1mk)
- Give two reasons to support your answer in (a) above. (2mks)
- What name is given to the substance formed after heating sulphur and iron together? (1mk)
- Determine whether the following substances undergo chemical or physical changes when heated. (4mks)
Substance Type of change Ice Zinc oxide Iodine crystals Copper (II) Carbonate
- A student mixed iron fillings with sulphur powder in a watch glass. The mixture was heated and a new substance was formed.
- Write simple word equations for the following reactions. (5mks)
- Magnesium and oxygen.
- Carbon and oxygen (excess)
- Zinc and Hydrochloric acid
- Sodium Carbonate and Hydrochloric acid
- Calcium oxide and Sulphuric (VI) acid.
-
- Give the chemical name of rust (1mk)
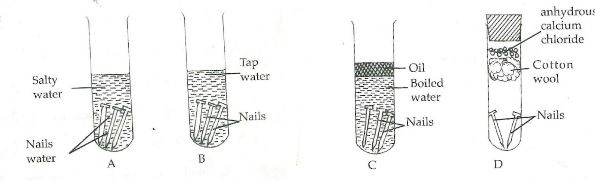
- A form one student set up the following experiments to investigate the conditions necessary for rusting.
- What observations were made in each of the test tubes after four days. (3mks)
- Why was the water in test tube C
- Boiled (1mk)
- Covered with oil (1mk)
- What was the purpose of anhydrous calcium chloride in test tube D? (1mk)
- From the above experiment, what conditions are necessary for rusting? (2mks)
- Name a substance that accelerates rusting. (1mk)
- State 2 methods used to prevent rusting. (2 mks)
- Explain why cars in Mombasa rust faster than in Nairobi. (1mk)
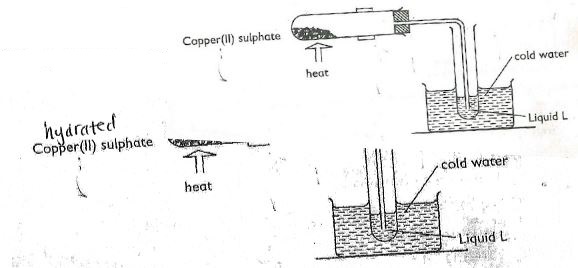
- The diagram below shows the effect of heat on hydrated Copper (II) Sulphate.
-
- What is the colour of hydrated Copper (II) Sulphate? (1mk)
- State one observation made at the end of the experiment. (1mk)
- Name liquid L. (1mk)
- Name one test that can confirm the purity of liquid L. (1mk)
-
- Name two apparatus that can be used to measure the volume of a gas. (2mks)
- The table below shows liquids that are miscible and those that are immscible.
Use the above information to answer the questions that follow.Liquid Y Z W Miscible Miscible X Miscible Immiscible - Name the method that can be used to separate a mixture of W and Y. (1mk)
- Describe how a mixture of liquid X and Z can be separated. (2mks)
- State one use of each of the following substances.
- Sulphuric (VI) acid. (1mk)
- Magnesium hydroxide (1mk)
- Nitric (V) acid. (1mk)
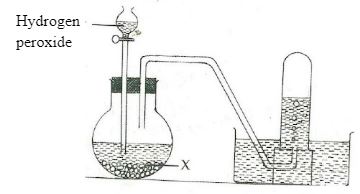
- The diagram below shows preparation of oxygen gas in the laboratory.
-
- Name the reagent labeled X. (1mk)
- Write a word equation for the reaction that occurs in the flask. (1mk)
- What is the purpose of solid x in the experiment? (1mk)
- State two physical properties of oxygen. (2mks)
- State two uses of oxygen. (2mks)
-
MARKING SCHEME
-
- In the boxes provided below show how molecules are spaced in solids, liquids and gases in
terms of kinetic theory. (3mks) - What conclusion can you make regarding densities of solids, liquids and gases as per the packaging of molecules in 1 (a) above. (1mk)
- Solids have very high density, liquids have high density gases have low density.
- In the boxes provided below show how molecules are spaced in solids, liquids and gases in
- State whether the substances given below are elements, compounds or mixtures. (4mks)
Substance Piece of Aluminium metal Element Sugar Compound Solution of common salt Mixture Crude oil mixture - Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follows.
- Name process B. (1mk)
- Filtration
- Give one reason why it’s possible to separate the mixture A above using process B. (1mk)
- It contains an insoluble solid.
- Give the name for
- Liquid X filtrate (1mk)
- Solid Y residue (1mk)
- Give one application of process B in day to day life. (1mk)
- Filtering water for domestic use.
- Purification of drinking water in water treatment plants.
- Name process B. (1mk)
- State the method of separation suitable for the following mixtures.
- Iron fillings and sulphur powder. (1mk)
- Magnetism
- Dye from flowers. (1mk)
- Chromatography.
- Petrol from crude oil. (1mk)
- Fractional distillation
- Oil from nuts. (1mk)
- Solvent extraction.
- Iron fillings and sulphur powder. (1mk)
- The diagram below represents arrangement of particles in a substance. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Name process C. (1mk)
- Evaporation/vaporisation
- Name two substances that undergo sublimation. (2mks)
- Iodine crystals
- Dry ice
- Benzoic acid
- Ammonium chloride
- Aluminium chloride
- Iron (III) Chloride
- What name is given to process D? (1mk)
- condensation
- Name process C. (1mk)
-
- If common salt is added to wax, what effect will it have on the temperature at which it melts? (1mk)
- The melting point will be lowered.
- When alcohol is heated, it changes to gas at 780C.
- What is the name given to this temperature? (1mk)
- Boiling point
- What will happen to this temperature if an impurity like salt is added to ethanol? (1mk)
- It will be increased.
- What is the name given to this temperature? (1mk)
- If common salt is added to wax, what effect will it have on the temperature at which it melts? (1mk)
- Given the following substances and their PH values, indicate whether they are neutral, strongly acidic, weakly acidic, weakly alkaline or strongly alkaline. (7mks)
Substance PH Value Nature Sugar solution 7.0 Neutral Blood 7.4 Weakly alkaline Sulphuric (VI) acid 1.0 Strongly acidic Tooth paste 8.0 Weakly alkaline Black coffee 5.0 Weakly acidic Sodium hydroxide solution 14.0 Strongly alkaline Urine 6.0 Weakly acidic - State 2 ways through which the youth of Kenya can avoid abusing drugs. (2mks)
- Proper use of leisure time. E.g. religious activities helping the elderly and sick etc to keep themselves busy.
- Avoiding wrong peer groups that may influence them wrongly on drugs.
- Educate the youth on the effects of drug abuse.
- A form one student at Moja High School lit a Bunsen burner with its air hole fully open.
- Which colour was the part labeled A? (1mk)
- Blue
- Identify the hottest part of the flame. (1mk)
- A
- Which was the almost colourless region? (1mk)
- C
- Which colour was the part labeled A? (1mk)
- Classify each of the following substances as either conductors or non-conductors. (5mks)
- Copper metal - Conductor.
- Paraffin - Non-Conductor
- Glass - Non-Conductor
- Graphite - Conductor
- Magnesium Conductor
- Three pure pigments were prepared and their spots placed on a filter paper as shown below. The pure pigments are A, B and C. a mixture D was also place on the filter paper at the same time with the pure pigments
- Which of the three pure pigments is most sticky? Give a reason for your answer. (2mk)
- A – Has moved the shortest distance from the baseline.
- Which pure pigment is not present in the mixture D? (1mk)
- B
- Show on the diagram the solvent front and the base line. (2mks)
- Which of the three pure pigments is most sticky? Give a reason for your answer. (2mk)
-
- What is an acid-base indicator? (1mk)
- A substance which has one colour in an acid and a different one in a base.
- Name any three common indicators used in chemistry and give their colours in acid solution. (3mks)
Indicator Colour in acid litmus paper Red phenolphthalein Colourless methyl orange Red - What is the advantage of universal indicator over other common acid-base indicators?(1mk)
- It shows the strength of an acid or base unlike other indicators.
- What is an acid-base indicator? (1mk)
- Citric acid, lactic acid, methanoic acid and hydrochloric acid are found in various substances in plants and in various substances in plants and animals. State where these acids occur. (4mks)
Acid Where found Citric acid Citrus fruits Lactic acid Sour milk Methanoic acid Bee/Ant sting, Nettle plant Hydrochloric acid Stomach -
- A student mixed iron fillings with sulphur powder in a watch glass. The mixture was heated and a new substance was formed.
- Is this a physical or chemical change? Chemical. (1mk)
- Give two reasons to support your answer in (a) above. (2mks)
- Its irreversible
- A new substance was formed
- What name is given to the substance formed after heating sulphur and iron together? (1mk)
- Iron (II) Sulphide.
- Determine whether the following substances undergo chemical or physical changes when heated. (4mks)
Substance Type of change Ice Physical Zinc oxide Physical Iodine crystals Physical Copper (II) Carbonate Chemical
- A student mixed iron fillings with sulphur powder in a watch glass. The mixture was heated and a new substance was formed.
- Write simple word equations for the following reactions. (5mks)
- Magnesium and oxygen.
- Magnesium + oxygen → magnesium oxide
- Carbon and oxygen (excess)
- Carbon + oxygen (excess) → carbon (IV) oxide
- Zinc and Hydrochloric acid
- Zinc + Hydrochloric acid → Zinc Chloride + Hydrogen
- Sodium Carbonate and Hydrochloric acid
- Sodium Carbonate + Hydrochloric acid → Sodium Chloride + Carbon (IV) Oxide + water
- Calcium oxide and Sulphuric (VI) acid.
- Calcium oxide + sulphuric acid → Calcium Sulphate + water
- Magnesium and oxygen.
-
- Give the chemical name of rust (1mk)
- Hydrated Iron (III) Oxide.
- A form one student set up the following experiments to investigate the conditions necessary for rusting
- What observations were made in each of the test tubes after four days. (3mks)
- Nails in test tubes A and B rusted.
- The nails in test tubes C and D did not rust.
- The nails in tube A rusted more compared to the nails in B.
- Why was the water in test tube C
- Boiled (1mk)
- To remove the dissolved oxygen from the water.
- Covered with oil (1mk)
- To prevent further entry of oxygen.
- Boiled (1mk)
- What was the purpose of anhydrous calcium chloride in test tube D? (1mk)
- To absorb the moisture in the test tube.
- From the above experiment, what conditions are necessary for rusting? (2mks)
- Oxygen
- Water
- Name a substance that accelerates rusting. (1mk)
- Salt.acid
- State 2 methods used to prevent rusting. (2 mks)
- Galvanising
- Electroplating
- Painting
- Oiling and greasing
- Sacrificial protection
- Alloying
- Explain why cars in Mombasa rust faster than in Nairobi. (1mk)
- Water in Mombasa is salty and salt accelerates rusting.
- What observations were made in each of the test tubes after four days. (3mks)
- Give the chemical name of rust (1mk)
- The diagram below shows the effect of heat on hydrated Copper (II) Sulphate.
-
- What is the colour of hydrated Copper (II) Sulphate? (1mk)
- Blue
- State one observation made at the end of the experiment. (1mk)
- A white solid is formed / hydrated copper(II) sulphate turns from blue to red
- A Colourless liquid.
- Name liquid L. (1mk)
- Water
- Name one test that can confirm the purity of liquid L. (1mk)
- Checking/Testing the boiling point.
- What is the colour of hydrated Copper (II) Sulphate? (1mk)
-
- Name two apparatus that can be used to measure the volume of a gas. (2mks)
- Measuring cylinder
- Calilbrated (graduated) gas jar.
- Syringe (any 2)
- The table below shows liquids that are miscible and those that are immscible.
Liquid Y Z W Miscible Miscible X Miscible Immiscible
Use the above information to answer the questions that follow.- Name the method that can be used to separate a mixture of W and Y. (1mk)
- Fractional distillation
- Describe how a mixture of liquid X and Z can be separated. (2mks)
- Since the two liquids are immiscible, place them in a separating funnel (1mk) turn on the tap the liquid at the bottom is collected in a beaker while the liquid at the top remains in the separating funnel. (1mk)
- Name the method that can be used to separate a mixture of W and Y. (1mk)
- State one use of each of the following substances.
- Sulphuric (VI) acid. (1mk)
- In car batteries
- To manufacture sulphate fertilizers
- To manufacture detergents, paints, dyes e.t.c
- Magnesium hydroxide (1mk)
- As an anti-acid tablet
- Nitric (V) acid. (1mk)
- To manufacture nitrate fertilizers.
- Sulphuric (VI) acid. (1mk)
- The diagram below shows preparation of oxygen gas in the laboratory.
-
- Name the reagent labeled X. (1mk)
- Manganese (IV) oxide.
- Write a word equation for the reaction that occurs in the flask. (1mk)
- Hydrogen peroxide Manganese (IV)Oxide → Oxygen + Water.
- Name the reagent labeled X. (1mk)
- What is the purpose of solid x in the experiment? (1mk)
- It acts as a catalyst in the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide.
- State two physical properties of oxygen. (2mks)
- Its colourless
- Its odourless
- It’s slightly soluble in water.
- It has almost the same density as air.
- It has a low boiling point of -183°C.
- State two uses of oxygen. (2mks)
- In welding and cutting of metals.
- In deep sea diving.
- In mountain climbing
- In hospitals by patients with breathing problems.
- To remove iron impurities during manufacture of steel.
-
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Chemistry Questions and Answers - Form 1 Opener Exam Term 3 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students