Geography Form 2 End Term 2 Exams 2021 with Marking Schemes
- Define the following terms (6mks)
- Geography
- Vulcanicity
- Earth movements
- Give the three branches of geography (3mks)
- What is solar system (2mks)
-
- List three types of rocks according to their mode of formation (3mks)
- Mention three characteristics of sedimentary rocks (3mks)
- Give two types of earth movements (2mks)
- Differentiate between weather and climate (2mks)
-
- Describe the continental drift theory (6mks)
- Give three evidences supporting continental drift theory (3mks)
-
- Give three extrusive volcanic features (3mks)
- Explain four positive significance of vulcanicity to human activities (8mks)
-
- Define earthquake (2mks)
- Give two scales used to measure earthquake (2mks)
- Differentiate between seismic focus and epicenter (2mks)
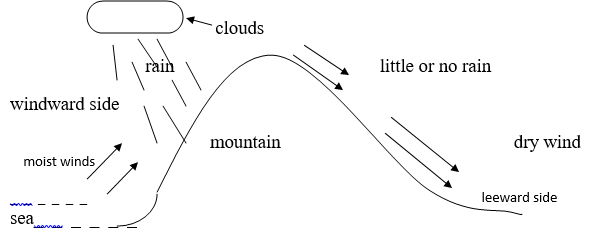
- With the aid of a well labeled diagram describe how orographic rainfall is formed (6mks)
- Distinguish between direction and bearing (2mks)
- Highlight 2 modern methods of showing direction
- Give 4 methods of representing relief on a topographical maps (4mks)
- Differentiate between a picture and a photograph (2mks)
- Briefly describe the three types of ground photograph (6mks)
- Give the three parts of a photograph (3mks)
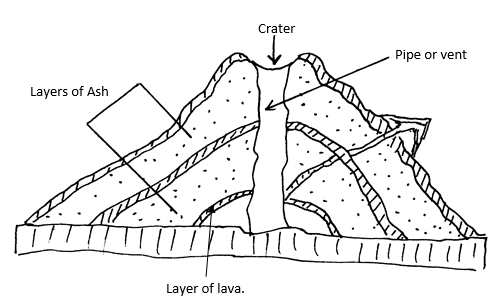
- Describe how a composite volcano is formed (6mks)
- Give two differences between a geyser and a spring (2mks)

Marking Scheme
-
- Geography is the study of the earth as a home of man
- Vulcanicity is the process by which solid ,liquid or gaseous materials are forced out of the interior of the earth in to the earths crust or on to the earth surface
- earth movements is the movement of the crustal rocks caused by forces originating and operating in the interior of the earth known us tectonic forces
- Branches of geography
- practical geography
- physical geography
- human and economic geography
- Solar system consists of the sun, moon the eight known planets and heavenly bodies
-
- Metamorphic rocks
- Igneous rocks
- Sedimentary rocks
- Types of earth movements
- Horizontal earth movement
- Vertical earth movement
- weather is the daily atmospheric conditions of a place at a particular time
Climate is average weather condition s of a given place over a long period of time -
- continental drift theory
It states that land was one land mass called pangea, surrounded by a huge ocean called Panthalasa due to different gravitational process, pangea broke into two parts, Gondwanaland to the south and Laurasia to the north, they were separated by a narrow ocean known Tethys. Gondwanaland and laurasia further raptured and drifted apart form the present six continents of the world. -
- jigsaw fit of continental margins
- seaflow spreading
- climatology
- Geological structures
- Palaenthological evidences
- the mid- atlantic ridge
- paleomagnetic studies
- distribution of the ancient glacial deposits
- continental drift theory
-
-
- Volcano
- basic (basaltic) lava/shield dome
- acid lava cone
- complex cones (stratified and parasitic)
- ash and cidar cones
- volcanic plug
- composite cone/ stratovolcanoes
- volcanic depressions
- plug dome volcano / spine volcano/ plug volcano
-
- site for tourist attraction
- resulted in large central volcanoes (mountains)
- Formation of rich metallic minerals
- Resulted into geothermal steam and power
- Volcanic rocks are valuable as building materials
- Volcanic mountains are water catchment areas
- Some of volcanic rocks are used domestically as scrubbing e.g. pumice
-
-
- shaking or trembling of the rocks on the surface of the earth caused by the shock waves that originates below the surface of the earth
-
- mercalli scale
- richter scale
- seismic focus is the point where the seseimic waves originates while epicenter is the point directly above the seseimic focus
- it is experienced in the highland regions
- it fall in light showers over along period of time
- It is formed over a relief features when moist air reaches the interior areas and forced to raise over mountains as it raises it expands, cools and on reaching condensation levels it condenses to form clouds which falls as rains. The rain is received on the windward side of the mountain.
- The windward side receives a lot of rainfall while the leeward side experiences dry climate
- direction is the distance from a particular known point on the map or on the surface of the earth while bearing is the direction measured as an angle and given in degrees (2mks)
-
- the use of the compass
- The use of bearing (2mks)
-
- contours
- Formlines
- Hacheures
- Spotheights
- Trigonometrical station
- Hill shading
- Cliff and rock drawing
- Layer tinting (2mks)
- a photograph is an image of an object, person or scene in a form of prints or slides recorded by a camera on a film and later transferred onto a specially prepared paper ...... (2mks)
-
- ground close up – the camera is focused on one major object .The object may block out the other things behind it
- Ground general view photographs – the camera is held horizontal to the ground facing area focused on objects become progressively smaller as the distance from the camera increases
- ground oblique - it is taken when the photographer is standing on a higher ground than the object the camera is tilted towards the object (6mks)
-
- foreground
- middle ground
- background (3mks)
-
- Crystal rocks are disturbed by earth movement leading to formation of a vent / pipe.
- Initially crustal rocks experience violent explosion leading to shattering of rocks to form the first layer of Ash.
- As the eruption proceeds, the violence ceases and lava pours out forming a layer on top of the Ash.
- The process is repeated until a dome shaped feature with alternating layer of Ash and lava forms known as a composite volcano. Total marks (6mks)
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Geography Form 2 Questions and Answers - End Term 2 Exams 2021.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students