END OF TERM 3 EXAMS
BIOLOGY
FORM 2
-
- What is respiration? (1mk)
- State any two importance of respiration. (2mks)
-
-
- Name the blood vessel that supplies the cardiac muscles with its requirements.(1mk)
- State the corgenical defect of the above blood vessel resulting from prolonged large intake of cholesterol in the blood. (1mk)
- What is the importance of the thicker muscular wall of the left ventricle of a mammalian heart? (2mks)
-
-
-
- Name the respiratory surface in insects. (1mk)
- State any one feature that adapts the structured named in a (i) above to its functions. (1mk)
- Why are the fish gills highly vascularized? (1mk)
-
-
-
- What would happen if a person secreted less A.D.H? (1mk)
- Name the condition described in a(i) above. (1mk)
- What is the role of the loop of Henle in homeostasis? (1mk)
-
-
- Name the products of anaerobic respiration in plants. (1mk)
- Give any two economic importance of the products named in (a) above. (2mks)
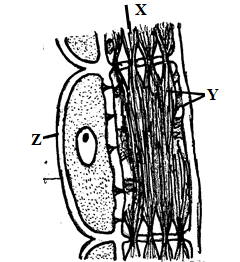
- The diagram below illustrates part of phloem tissue.
- Name the parts labeled. (2mks)
X
Y - State the function of the part labeled Z (1mk)
- Name the parts labeled. (2mks)
- Name the monosaccharides that make up the disaccharides below
- Sucrose (1mk)
- Lactose (1mk)
- Maltose (1mk)
- State one use of the following excretory products of plants (2mks)
- Latex
- Colchicine
- .
- Define respiratory quotient (1mk)
- Given the equation below, calculate the respiratory quotient (RQ) (2mks)
C6H12O6+6O2 →6H2O+6CO2+2880kJ
- State the importance of the following
- Reversed stomatal rhythm to desert plants (1mk)
- Closing of stomata on a hot dry sunny day (1mk)
- How does wind affect transpiration rate? (1mk)
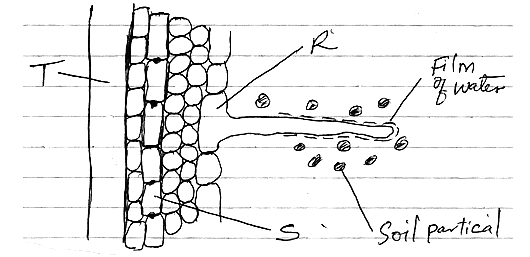
- The diagram below represents the pathway of water from soil into the plant.
- Name the structures labeled T and S.
T:_____(1mk)
S:_____(1mk) - State two ways in which the structure labeled R is adapted to its functions.(2mks)
- Name the structures labeled T and S.
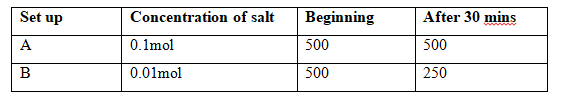
- A student added equal amounts of blood to equal volumes of salt of different concentrations. She observed and counted the red blood cells at the beginning of the experiment and at end of the experiment. The results were as shown:-
- Set up A (2mks)
- Set up B (2mks)
- Below is a dental formula of certain organisms. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
I (0/3), C (0/1), PM (3/2), M (3/3)- Calculate the total number of teeth in the mouth of the organisms. (2mks)
- Name the organisms. (1mk)
- Identify the mode of nutrition of the organisms. (1mk)
-
- Give a reason why glucose does not normally appear in urine even though it is filtered in mammalian Bowman’s capsule. (2mks)
- Which hormones are involved in the salt-water balance in human body? (2mks)
-
- State two functions of the blood other than transport. (2mks)
- Name one defect of the circulatory system in humans. (1mk)
-
- State two ways in which human body is naturally protected against harmful bacteria. (2mks)
- State one way in which the composition of blood in the pulmonary artery and that of pulmonary vein differ. (1mk)
- Describe the path taken by Carbon (IV) Oxide released from the tissues of a cockroach into the atmosphere. (2mks)
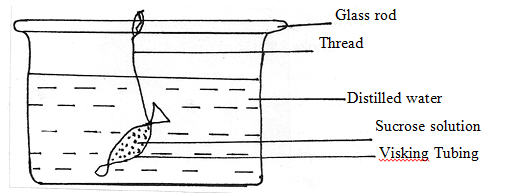
- Form One student set up an experiment shown below to investigate a certain physiological process. The set up was left for 30 minutes.
- Name the process under study. (1mk)
- State the expected results after 30 minutes. (1mk)
- Explain your answer in (b) above. (3mks)
- Explain why it is important to stain specimen to be observed under a light microscope. (2mks)
- What is wilting? (2mks)
- State the significance of the following steps while testing for disaccharides in food sample. (2mks)
- Addition of dilute hydrochloric acid
- Addition of sodium bicarbonate.
-
-
- Name the fluid produced by sebaceous gland. (1mk)
- State two function of the fluid named in 5 a) (i) above. (2mks)
- Explain malpighian layer of the skin is adapted to perform its function. (1mk)
-
- Outline three functions of colon. (3mks)
- Explain four reasons why the study of biology is important ( 4mks)
- Define the term physiology (1mk)
MARKING SCHEME
-
-
- The break down of glucose /food nutrient in the cells to release energy
-
- Produce energy for cell division;
- Produce energy for transmission of nerve impulse;
- Produce energy for maintenance of body temperature;
- Produce energy for active transport/secretion;
-
-
-
- Coronary artery;
- Coronary thrombosis;
- Generate higher/sufficient pressure with which blood is pumped to the body tissues;
-
-
-
- Tracheole;
-
- Moist to dissolve diffusing gases;
- Highly branched to increase S.A for diffusion of diffusing gases;
- One – cell thick/thin wall ti shorten distance covered by diffusing gases;
-
- Rapid transport of diffusing gases; to maintain a steep diffusion gradient for efficient gaseous exchange;
-
-
-
- Production of large amount of urine/diuresis;
- Diabetes insipidus;
- Osmoregulation
-
-
- Alcohol ,Carbon (IV) Oxide and energy;
-
- Brewing;
- Baking;
-
- X – sieve pore;
Y – Cytoplasmic strands /filaments; -
- Has (numerous) mitochondria that provides energy for translocation;
- Provides food nutrient to the sieve element;
- X – sieve pore;
-
- Glucose and fructose;
- Glucose and galactose;
- Glucose and glucose
-
- Latex - Rubber and gum products
- Colchicine - medicinal purposes( used to reduce uric acid in joints), gout
-
- Is the ratio of carbon dioxide produced to Oxygen used during respiration;
- RQ=
-
- Help plants conserve water during the day allowing maximum gaseous exchange at night;
- Reduce amount of water loss;
- Windy conditions blow away water from leaf surface increasing transpiration rate;
-
- T – Xylem vessel;
S – Endodermis; - Root hair cell;
- Narrow and elongated to increase surface area for absorption of water and mineral salts.
- Thin to reduce diffusion distance.
- T – Xylem vessel;
-
- A – Concentration of salt was isotonic; to that of the cytoplasm of the Red blood
cells hence no change; - B – most cells haemolysed; due to hypotonic salt solution;
- A – Concentration of salt was isotonic; to that of the cytoplasm of the Red blood
-
- (3 + 3 + 3 + 1 + 2 + 3) x 2= 15 x 2 = 30; teeth
Or (I 0/3, C 0/1, PM 3/2, M 3/3) x 2; 30 - Herbivore
- Heterotrophic;
- (3 + 3 + 3 + 1 + 2 + 3) x 2= 15 x 2 = 30; teeth
-
- Its actively reabsorbed back to blood system within the proximal convoluted tubule;
- -Anti-diuretic hormone (ADH)
-Aldosterone
-
-
- Regulation of body temperature.
- Regulation of pH of fluids;
- Defence against disease-causing micro-organism / pathogens; rej. diseases;
- Prevent bleeding / enhancing clotting;
- Coronary thrombosis / varicose veins / arteriosclorosis / Antheroma / cerebral thrombosis;
-
- .
- Presence of antibodies; and white blood cells in blood that kill / destroy pathogens;
- Higher concentration of oxygen in pulmonary vein / higher concentration of carbon (IV)
oxide in pulmonary artery;
- Haemocoel →Trachea → Ostia → Spiracles
- Naming
- For the arrows direction
-
- Osmosis;
- The visking tubing will become turgid / increase in volume / bulge / become big / expand;
- Water moves from beaker into visking tubing; by osmosis; the semi-permeable tubing;
making tubing turgid, big, expand / bulge, increase in volume
- Different structures absorbs stain differently hence become more distinct/clearer, visible.
- Rate of water absorption is more than water loss/transpiration and plant droops
-
- Hydrolyse (breaks down disaccharide/Non reducing sugar to monosaccharide/reducing sugar.
- Neutralize the dilute hydrochloric acid
-
-
- Sebum
-
- antiseptic -kill pathogens
- Makes skin hair be soft/oily
- Makes hair flexible/waterproof
-
- actively dividing cells giving rise to the granular layer
- contain melanocyte cells that produce melanin that gives the skin its colour/protects skin against ultra violet rays.
-
-
- absorption of water
- Packaging of indigestible food material to form feaces
- Secretion of mucus
- Absorption of mineral salts
- Helps to solve environmental problems, enable one to into certain careers, enables one to develop scientific skills, facilitate international cooperation.
- Study of body functions
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Biology Questions and Answers - Form 2 End Term 3 Exams 2021.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students