INSTRUCTIONS
- Answer all the questions
-
- What is the relationship between Geography and Chemistry? (2marks)
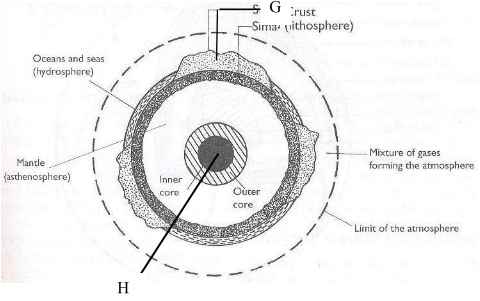
- The diagram below shows the internal structure of the earth.
- Name the parts marked G and H. (2 marks)
- Name the dominant mineral in the mantle. (1 mark)
- Differentiate between absolute and relative humidity. (2 marks)
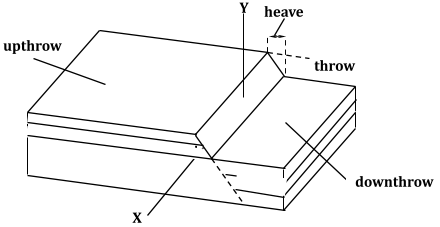
- The diagram below shows some features formed by faulting. (2 marks)
- Name the parts marked X and Y.
- State three effects of faulting on drainage of an area. (3 marks)
-
- Identify two scales used to measure the intensity of an earthquake (2 mark)
- Give three major earthquake zones of the world. (3 marks)
- Explain three economic significance of rocks in Kenya. (3 marks)
- Students carried out a field study on rocks around their school.
- State two importance of stating the objectives for the study. (2 marks)
- Give three reasons why they prepared a route map of the study (3 marks)
- Give three activities that the students where involved in during the field study. (3 marks)
-
-
- What is an orogeny? (2 marks)
- Give two factors that influence the folding process of rocks. (2 marks)
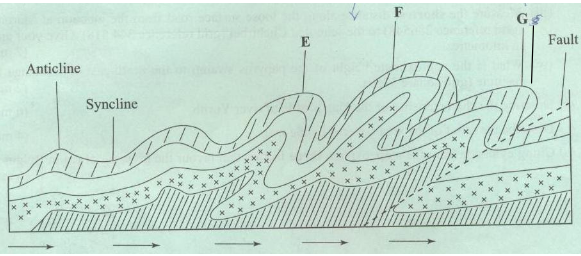
- The diagram below shows some types of folds. Use it to answer the question
- Name the types of folds marked E and F (2marks)
- Describe how an overthrust fold is formed. (4 marks)
- Name the countries in which the following fold mountains are found.
- Atlas (1 mark)
- Alps (1 mark)
- Himalayas (1 mark).
- Andes (1 mark)
-
- Apart from fold mountains, name three other features resulting from folding. (3marks)
- Explain four ways in which fold mountains influence climate .(8marks)
-
-
- Define the term planet (2mks)
- State three characteristics of planet Mercury (3mks)
- Explain two reasons why the interior of the earth is very hot. (4mks)
-
- Suppose air contains 5gm/m3 of water vapour at 22°c. If the same air can hold a maximum of 10gm/m3 at the same temperature, calculate the relative humidity. (2mks)
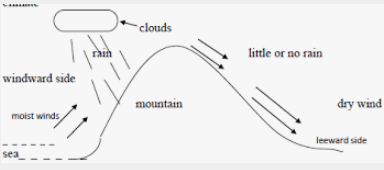
- With the aid of a well labeled diagram, describe how orographic rain is formed. (7mks)

MARKING SCHEME
-
- What is the relationship between Geography and Chemistry? (2 marks)
- Geography applies Chemistry concepts in studying the chemical composition of rocks and soils.
- Chemistry concepts are used in Geography to explain chemical changes that occur in rocks/soils.
- The diagram below shows the internal structure of the earth.
- Name the parts marked G and H. (2 marks)
- G - Continental crust/sial
- H - Inner core
- Name the dominant mineral in the mantle. (1 mark)
- Olivine/ ferromagnesian silicate
- Name the parts marked G and H. (2 marks)
- What is the relationship between Geography and Chemistry? (2 marks)
- Differentiate between absolute and relative humidity. (2 marks)
- Absolute humidity is the actual amount of water vapour or moisture in a given mass of air at a particular temperature while relative humidity is the ratio of the absolute humidity of a given mass of air to the maximum amount of moisture that this mass of air could hold at the same temperature.
- The amount of water vapour determines the amount of energy stored in the atmosphere for the development of storms.
- The diagram below shows some features formed by faulting. (2 marks)
- Name the parts marked X and Y.
- X - Hade
- Y - Fault scarp/escarpment/scarp face.
- State three effects of faulting on drainage of an area. (3 marks)
- Down warping due to faulting may lead to formation of depressions which may be filled by water to form lakes.
- Fault lines due to fracturing of crustal rocks may change the course of river making the river to start flowing a long the fault line forming faulting - guided drainage pattern.
- Fault scarps forming across rivers course may lead to formation of waterfalls.
- Faulting may lead to formation of lines of weakness in earth’s crust which becomes passages for hot water from the underground to the earth’s surface to form hot springs and geysers.
- Name the parts marked X and Y.
-
- Identify two scales used to measure the intensity of an earthquake. (2 marks)
- Rossi forell scale
- Mercalli scale
- Give three major earthquake zones of the world. (3 marks)
- The mid-Atlantic
- The Great Rift Valley region
- The Mediterranean region/Tethyan
- The circum Pacific region
- West coast of South America/ the Andes region
- West coast of N. America/Rockies region
- Himalayas belt
- Explain three economic significance of rocks in Kenya. (3 marks)
- Some rocks such as granite, volcanic peaks may form unique sceneries which attract tourists promoting tourism industry.
- Rocks provide the parent materials through weathered rocks especially volcanic rocks forming fertile volcanic soils for agricultural production.
- Rocks such as sandstone, marble and limestone are strong and resistant to weathering are used in the building and construction industry.
- Minerals and other valuables substances are extracted/mined. Some rocks are used as raw materials for the manufacturing industry.
- Impermiable rocks may act as storage of underground water which can be tapped to supply water for domestic and industrial use.
- Students carried out a field study on rocks around their school.
- State two importance of stating the objectives for the study. (2 marks)
- They direct the actual activities to be carried out during the study.
- They guide the possible areas of data collection to obtain required information.
- They give the aims/purposes for carrying out the field study.
- They guide on the appropriate methods/tools for data collection.
- Give three reasons why they prepared a route map of the study area. (3 marks)
- To identify direction they would take
- To show the features/rocks they are likely to see.
- To help estimate the distance to be carried
- To help estimate the time to be taken.
- To help make/prepare time schedule.
- Give three activities that the students where involved in during the field study. (3 marks)
- Data collection/taking photographs/filming/videoing
- Data recording/ taking notes/tallying/sketching
- Collecting different types of rock samples.
- Classifying collected rock samples
- Labeling of collected rock samples.
- State two importance of stating the objectives for the study. (2 marks)
- Identify two scales used to measure the intensity of an earthquake. (2 marks)
-
-
- What is an orogeny? (2 marks)
- A fold mountain building period.
- Give two factors that influence the folding process of rocks. (2 marks)
- The strength/intensity/magnitude of the compressional forces.
- The nature of the sedimentary rocks/The age of the rocks
- What is an orogeny? (2 marks)
- The diagram below shows some types of folds. Use it to answer the question
- Name the types of folds marked E and F. (2 marks)
- E - Overfold
- F - Recumbent fold
- Describe how an overthrust fold is formed. (4 marks)
- Layers of rocks of the earth’s crust are subjected to compressional forces.
- Intense folding result in the formation of an overfold.
- With increased pressure, the overfold results in the formation of recumbent fold producing a thrust plane.
- The upper part of the recumbent fold slides forward over the lower part along the fault plane resulting to the formation of an overthrust fold.
- Name the types of folds marked E and F. (2 marks)
- Name the countries in which the following fold mountains are found.
- Atlas (1 mark)
- Western Sahara/ Morocco/ Algeria
- Alps (1 mark)
- Austria/ Switzerland/ Italy/ France/ Leichstein.
- Himalayas (1 mark)
- India/Pakistan/Afghanistan/ Bhutan/ Nepal/ China.
- Andes (1 mark)
- Chile/ Peru/ Bolivia/ Argentina/ Venezuela/ Ecuador/ Colombia
- Atlas (1 mark)
-
- Apart from fold mountains, name three other features resulting from folding. (3 marks)
- Synclinal valleys/depressions
- Rolling plains
- Ridges
- Intermontane basins
- Intermontane plateaus
- Explain four ways in which fold mountains influence climate. (8 marks)
- The slopes of mountains which face the sun receive direct sunshine /and are warmer.
- Mountain slopes cause the development of local winds due to variation in pressure between the mountain top and the valley bottom.
- The windward slopes of mountains receive high rainfall due to orographic effect.
- Atmospheric pressure reduces with increasing attitude along a mountain slope.
- Temperature decreases with increasing /altitude along a mountain slope.
- Apart from fold mountains, name three other features resulting from folding. (3 marks)
-
-
- Define the term planet (2mks)
- A planet is a large and fairly spherical heavenly body in space which revolves round a star.
- State three characteristics of planet Mercury (3mks)
- It takes the shortest duration to complete a revolution.
- It is the smallest planet.
- It has no natural satellite
- It is the second hottest planet.
- It is the planet nearest to the sun.
- Explain two reasons why the interior of the earth is very hot. (4mks)
- The earth still retains the original heat which it had before it started cooling – During its formation, the outer parts cooled faster than the inner parts.
- Breakdown of radioactive elements. Through nuclear fission a lot of heat is released and trapped in the interior
- Weight of overlying materials. Crustal rocks and other material exert a lot of pressure towards the center of the earth which generates a lot of heat in the interior.
- Define the term planet (2mks)
-
- Suppose air contains 5gm/m3 of water vapour at 22°c. If the same air can hold a maximum of 10gm/m3 at the same temperature, calculate the relative humidity. (2mks)
= Absolute humidity X 100
Max. moisture the air can hold
1.5gm/m3 X 100% =50%
10gm/m3 - With the aid of a well labeled diagram, describe how orographic rain is formed. (7mks)
- A waterbody such as a lake or sea is heated by solar radiation causing some water to everporate
- Warm moist air form the waterbody is driven by wind towards land
- The moist air is forced to rise on a mountain side
- As the iar rises it expands leading to cooling
- Further cooling of moisture leads to condensation forming clounds.
- when the clounds are heavery, they release the water as relief rainfall mainly on the windward side of the mountain
- Suppose air contains 5gm/m3 of water vapour at 22°c. If the same air can hold a maximum of 10gm/m3 at the same temperature, calculate the relative humidity. (2mks)
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Geography Questions and Answers - Form 2 End Term 1 Exams 2021.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students