INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- This paper has two section: A and B
- Answer all questions in section a.
- In section B answer question 6 and any other two questions.
-
- Define the term earth movement (2 marks)
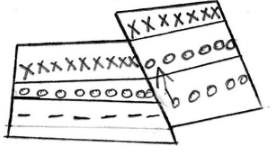
- State three effects of horizontal earth movement on the earth's crush. (3 marks)
- Explain how magma movement causes earth movement. (4 marks)
- Name two forces that causes earth movement. (2 marks)
-
- The Pangaea broke into two separate landmasses. Namely:
- Explain the plate tectonics theory. (5 marks)
-
- The uplifted part of a fold are known as .......and down folded parts are known ...........(2 marks)
- Apart from the Fold Mountains name three other features formed due to folding, (3 marks)
- Using diagrams differentiate between:
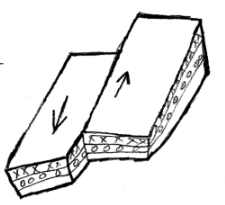
- Reverse fault (3 marks)
- Tear fault (3mks)
-
- Identify the four main sections of the east African rift valley (4mks)
- Name two other rift valley found outside East Africa (7mks)
-
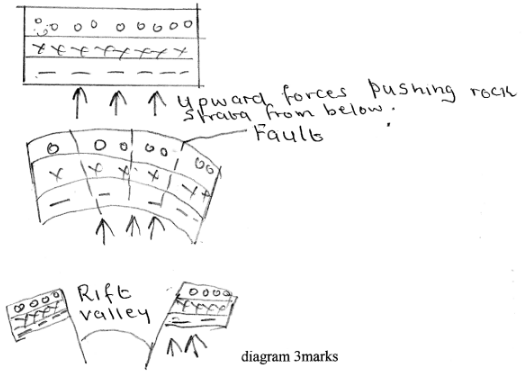
- Explain how the rift valley was formed through anticlinical arching (7mks)
- Outline three negative effects of faulting (3 marks)
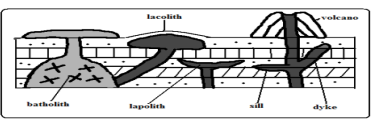
- Use diagrams to differentiate the following features (4 marks)
- Lacolith
- Lopoliths
-
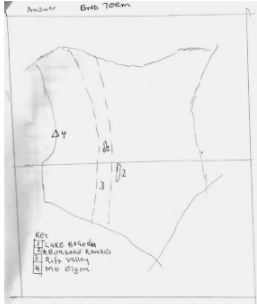
- Draw a map of Kenya on it mark and name: (5 marks)
- Lake Bogoria
- Aberdare ranges
- The rift valley
- Mount Elgon
- Name any escarpment found in Kenya (4 marks)
- Draw a map of Kenya on it mark and name: (5 marks)
- Distinguish between magma and lava (2 marks)
- Explain how acid lava dome is formed (5 marks)
-
- Name two craters found in Kenya (2 marks)
- Give examples of crater lavas found in Kenya (4 marks)
-
- Define the following geographical terms
- Moffette
- Solfatra
- Dommant volcano
- The following are examples of extinct volcanoes in East Africa. Indicate where they are found
(3 marks)
Mountain Country- Muhavura
- Mt Kenya
- Ngorongoro
- Define the following geographical terms
- Describe how a caldera is formed (4 marks)
- Outline the importance of vulcanicity to man (5 marks)
-
- What is the point of origin of earthquakes inside the earth (1 mark)
- Explain how the following causes earthquakes.
- Vulcanicity (3 marks)
- Gravitative Pressure (3 marks)
-
- Mention three types of seismic wave (3 marks)
- State two effects of earthquakes on the coast

MARKING SCHEME
-
- Earth movement occurs within the rocks of the earth’s crust due to tectonic forces.
1*2 2 marks - Effects of horizontal earth movement
- Stretching
- Shortening
- Shearing/tearing any
1*3 3 marks
- Magma movement
- Weak line occurs in the sima rocks.
- Magma moves through that line of weakness and invades the rocks of the earth crust.
- Magma occupies space within the crusted rocks.
- This makes the displaced crystal rocks to move away vertically / horizontally.
- If the movement of the rocks is vertical the land becomes uplifted and the surface bulges.
- If the crystal rocks moves side ways away from intruding magma horizontal earth movements are experienced.
Any 4*1 4 marks
-
- Tension
- Compression force
- Earth movement occurs within the rocks of the earth’s crust due to tectonic forces.
-
-
- Laurasia
- Gondwanaland,
- Plate tectonics theory
- The earth’s lithosphere (sial and sima) is a series of semi-rigid blocks called tectonic plates
- The plates are separated from one another by distinct boundaries.
- Keep moving relative to each other on the underlying partly molten layer of the upper mantle.
- The cause of the movement is due to convection current.
- A long the boundaries the plates that move either away from each other or past each other.
- These movements trigger earthquakes / vulcanicity.
- Where plates move away from each other creates an extension boundary where they move towards each other they form compression boundary / destructive boundary.
- When an oceanic plate meets the continental plate the oceanic plate sink below the continental plate in a movement called subduction.
- Sediments in the sea floor may be compressed to form mountains.
- When two oceanic collide there is subduction, resulting into formation of trench
- Sometimes the plate may move past each other. Any 5 * 1
-
-
- Anticline
Syncline -
- Rolling plains
- Intermontane plateau
- Ridge and valley landscape
- Significance of Fold Mountains.
- Fold Mountain receive high rainfall on leeward side encouraging growth of forests
- Forms source of rivers which provide water for domestic / industrial / generation of hep and irrigation.
- In the Northern hemisphere the south facing slope are warmer encouraging agriculture.
- In the process of folding valuable minerals are brought to the surface.
- The mountain landscape provides an unique scenery which attract tourists e.g. the Swiss alps.
- Fold Mountains act as protective barriers during the war. Any 5*1 5 marks
- Anticline
-
- Reverse Fault
- The side block pushed over the middle block
- Tear fault
- The land slide against each other.
- Reverse Fault
-
- Main sections of the Rift Valley
- The Ethiopian Rift system
- The Gregory Rift Valley
- The Western rift Valley
- The Malawi Rift Valley.
-
- Rhine Rift Valley
- Benue Rift Valley
- Main sections of the Rift Valley
-
- How the Rift Valley was formed through anticlinal arching
Explanation- Vertical forces push the earth crust upwards making it to arch. causes a lot of stress at the crest of the anticline.
- Continued upward push
- Upward arching could lead to development of series of cracks! faults.
- If more upward force is exerted the outermost blocks will be pushed much higher than the middle block.
- The middle block will form the floor of the Rift valley.
any 4*1 4 marks
- Negative effects of faulting
- Fault scarps make it difficult and expensive to construct roads and railways through the slope.
- Steep slopes / fault scarps hinder agriculture / settlement.
- Steep slopes are prone to landscape which are dangerous to life.
- Faulting disrupts and destroys forms of transport such roads / railways / pipelines.
- It leads to tremor earthquakes that may be destructive.
- How the Rift Valley was formed through anticlinal arching
-
- Laccolith destructive
- It is doomed shaped igneous intrusion with a flat floor which lies between the bedding plane of the country rock 1*2 2 marks
- Lopolith
- Is a very large saucer shaped mass of igneous intrusion. 1*2 2 marks
- Laccolith destructive
-
-
- Two escarpments found in Kenya.
- Kikuyu escarpment
- Nguruman escarpment
- Mau escarpment
- Tugen escarpment
- Sondu - Kendu escarpment
any 2*1 2 marks
-
- Magma is the molten rock found inside the earth’s crust while lava is the molten rock found on the surface of the earth.
- Formation of acid lava dome
- It is dome-shaped volcanic hill made up of acidic intermediate lava
- Magma pushes its way to the surface through a vent.
- On reaching the surface the magma is no longer explosive.
- The lava does not flow for a long distance since it is viscous
- It accumulates around the vent and hardens quickly on its outer surface.
- A steep sided dome with convex side is formed by eruption.
- If an eruption occurs the magma is unable to reaven the surface is covered with solidified.
- Magma pushes the hardened outer layers of the dome outwards.
- This increases the height of the dome while its width increases slightly.
Any 5*1
-
- Craters found in Kenya
- Menengai
- Longonot
-
-
- Mofette
This is a crack on the earth surface from where carbon IV Oxide is emitted. - Solfatara
It is vent through which sulphur dioxide gases are emitted from the ground. - Dormant Volcano
This is a volcano which was active but become inactive but can erupt anytime.
- Mofette
- Mountain Country
- Muhavura Uganda
- Mt. Kenya Kenya
- Ngorongoro Tanzania
-
- Caldera
- Lava pouring out of a central vent forms a volcanic cone.
- The vent may be sealed when lava solidifies in it.
- The solidified plug block the gases and steam beneath from escaping.
- There is pilling up of pressure below the plug.
- The pressure leads to a violent eruption that blows off the top of the cone forming a depression.
- The resulting large circular depression on the top of the (now lower) volcano is called caldera.
OR
A subsidence caldera - Lava pouring out of a central vent forms a volcanic cone.
- The magma resevoir below the crust is left empty/has a void/cavity.
- With time the weight of rocks of the volcano exerts pressure on the crustal rocks below.
- The pressure/earth movements cause cracks to develop making the volcano unstable.
- Over time the middle portion of the volcano subsides/collapses into the void forming a depression.
- The resulting large circular depression on the top of the (now lower) volcano is called caldera.
OR
Outward collapsing - Volcanic eruption of ash and cinder/pyroclasts through a central vent forms a volcanic cone.
- Several eruptions results to a high, steep and unstable volcano.
- The weight of the upper materials exerts pressure on the ones beneath causing instability on the lower part.
- The material at the base begin spreading outwards.
- The top of the volcano collapses inwards forming a depression.
- The resulting large circular depression on the top of the volcano is called caldera
-
- Volcanic lava especially basalt weather to give rise fertile soils that are good for farming
- Volcanic features e.g. craters, geysers are major tourists attraction sites
- Volcanicity has resulted to formation of valuable minerals.
- Geysers e.g. in Ol Karia a source of geothermal power.
- Volcanic mountains receive heavy rainfall on the windward since thus encourages settlement / farming.
- Volcanic mountains form catchments areas which source of rivers that provide water for irrigation /industrial/ domestic help generation.
- Many varieties of volcano rocks are used in building e.g. trachytes, phonolites etc.
- Fishing is carried out in some crater lakes e.g. Lake Katwe in Uganda.
- Hot springs are used as spas. Any 5*1 5 marks
-
- Epicentre
-
- Vulcanicity
- Magma movement within the earth’s crust can cause tremors due to crusted rocks displaced suddenly.
- A sudden eruption of molten magma under oceans can cause earth tremors.
- Violent volcanic explosion! violent emissions of volcanic gasses can shake or shake rocks.
Any 3*1 3 marks
- Gravitative Pressure
- The crustal rocks are overlying the hollow! void through which the volcano erupts.
- The rocks are under pressure from the force of gravity which is pushing them inwards.
- The rocks eventually sink due to pressure causing the ground to shake. 3*1 3 marks
- Vulcanicity
-
- Types of waves
- Primary waves
- Secondary waves
- Surface longitudinal waves
- Effects on Coastal regions
- Parts of the sea floor can be raised! Lowered & Coastal regions can be raised or lowered.
- Sometimes can cause huge waves called tsunamis.
- Can cause destruction of property / loss of lives
Any 2*1 2 marks
- Types of waves
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Geography Questions and Answers - Form 2 Mid Term 2 Exams 2021.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students