INSTRUCTIONS TO STUDENTS:
- Answer all the questions in this paper.
- Define the term ‛habitat’. 2mks
- Give two types of environment. 2mks
- State the relationships between:
- Geography and Mathematics. 2mks
- Geography and History. 2mks
-
- Describe the origin of the earth as proposed by the passing star theory. 3mks
- State two weakness of the passing star theory. 2mks
- Differentiate between asteroids and comets. (2mks)
- Name two instruments that are kept in Stevenson Screen. 2mks
- List two factors that influence atmospheric pressure. 2mks
- State three characteristics of Inter Tropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ. 3mks
- Identify three methods of collecting statistical data. (3mks)
- Given the following set of data:
26,30,25,34,18,19
Calculate the median. 2mks -
- What is marginal information? 2mks
- Mention three common marginal information in a map sheet. 3mks
-
- Define hypothesis. 2mks
- Name and explain two main types of hypothesis. 4mks
- Identify two possible problems likely to be encountered during field work. 4mks
-
- Differentiate between a mineral and a rock. 2mks
- Explain two ways in which metamorphic rocks are formed. 4mks
-
- Give two ways in which minerals occur. 2mks
- Explain two negative effects of open –cast mining. 4mks
- Explain two factors influencing exploitation of trona in L.Magadi. 4mks
-
- Define the term ‛earth movement’. 2mks
- Identify two types of earth movement . 2mks
- Explain the continental drift theory. 4mks
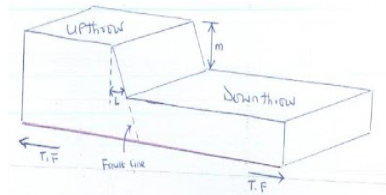
- The diagram below represents parts of the earth’s crust which has been subjected to tensional force. Use the diagram to answer questions that follow.
- Identify the type of fault. 1mk
- State two other types of faults apart from the one mentioned in (a) above. 2mks
- Name the angle L. 1mk
- Name the distance m. 1mk
- Mention two features resulting from faulting. 2mks
- Differentiate between:
- Magnitude and intensity of earthquakes. 2mks
- Seismic and aseismic zones. 2mks
- What are the effects of earthquakes? 4mks
-
- Define the term ‛bearing’ as used in Geography. 2mks
- Explain the following methods of representing relief on topographical maps.
- Pictorial representation. 2mks
- Hachures. 2mks
- Identify the three types of ground photographs. 3mks
- The table below represents sugar cane production in five major factories in Kenya. Use it to answer the following questions:
Factory Production in ‛000’ tones Sony 50 Nzoia 100 Chemilil 200 Muhoroni 250 Mumias 400 - Using the data above, draw a divided rectangle 15cm length. 5mks
- Give the difference in tonnage between sugar produced in Muhoroni and Nzoia factory. (1mk)
- Using the data above, draw a divided rectangle 15cm length. 5mks
-
- Define the term climate 2mks
- What is climate change? 2mks

MARKING SCHEME
- Define the term ‛habitat’. 2mks
- Refer to physical conditions under which certain plants and animals live.
- Give two types of environment. 1x2= 2mks
- Physical environment
- Human environment
- State the relationships between:
- Geography and Mathematics. 1x2= 2mks
- Mathematical principles and formulas are used in geography to calculate distances ,population densities.
- Mathematics applies geographical knowledge about direction and bearing to calculate distances around the globe.
- Geography and History. 2mks
- History is the study of events of the past and present while geography attempts to explain where these events took place.
- History uses geographical tools eg maps and charts to show movements of people in the past
- Geography and Mathematics. 1x2= 2mks
-
- Describe the origin of the earth as proposed by the passing star theory. 3mks
- Suggested that solar system was formed million of years ago, when a star with greater gravitational pull than the sun passed close to the sun and drew off stream of materials in form of gases. The materials split, cooled and condensed to form planets which were set in orbits around the sun.
- State two weakness of the passing star theory. 2mks
- Chances of another star approaching the sun are minimal
- The origin of the passing star and the sun aren’t mentioned
- Materials from the moving star are more likely to disperse than condense.
- Describe the origin of the earth as proposed by the passing star theory. 3mks
- Differentiate between asteroids and comets. (2mks)
- Asteroids are small heavy rocky bodies which revolve round the sun between mars and Jupiter while comets are small heavenly bodies which revolve round the sun and have a head and a tail
- Name two instruments that are kept in Stevenson Screen. 2mks
- Minimum thermometer
- six’s thermometer
- Maximum thermometer
- hygrometer
- List two factors that influence atmospheric pressure. 2mkS
- Temperature
- Altitude
- Rotation of the earth
- State three characteristics of ITCZ. 3mks
- Experience high temperature
- Associated with high convectional rainfall and thunderstorm.
- It’s a zone of low pressure/doldrums
- Is migrates north and south of the equator with the apparent movement of the overhead sun.
- The NE and SE trade winds converge here.
- It located within the tropics.
- Identify three methods of collecting statistical data. (3mks)
- Administering questionnaires
- Interviews
- Direct observation
- Sampling
- Taking measurements
- Experimentation
- Content analysis
- Taking photographs
- Given the following set of data:
26,30,25,34,18,19
Calculate the median. 2mks
Arrange the data in ascending /descending order
18,19,25,26,30,34
25+26 = 51 = 25.5
2 2 -
- What is marginal information? 2mks
- It is the information that is given in the margin of a map sheet.
- Mention three common marginal information in a map sheet. 3mks
- map series
- sheet name and title
- sheet index number
- grid system including northing and easting
- latitude and longitude
- compass direction
- magnetic variation
- scales
- key
- What is marginal information? 2mks
-
- Define hypothesis. 2mks
- it’s a tentative answer to the problems in the topic of study.
- Name and explain two main types of hypothesis. 4mks
- Null hypothesis: - Is a hypothesis that is negatively stated
- Alternative/ declarative/substantive hypothesis - Is a hypothesis that is positively stated
- Identify two possible problems likely to be encountered during field work. 4mks
- Hostile people/respondents who may be unwilling to give information
- Illiteracy /illiterate respondent who may not understand the questions
- Inadequate field work equipment and tools eg magnetic compass,maps.
- Financial constraints which can affect transport,accomondation etc
- Poor transport and communication networks
- Team member/researchers may fall sick during the study
- Adverse weather conditions eg rainfall during the study.
- Transport problems including vehicle breakdown and accidents.
- Attack by wild animals eg snakes.
- Define hypothesis. 2mks
-
- Differentiate between a mineral and a rock. 2mks
- A mineral is a naturally occurring inorganic matter that occur naturally at or beneath the earth surface while a rock refer to inorganic substance which is made up of one or more minerals and form solid part of the earth’s crust
- Explain two ways in which metamorphic rocks are formed. 4mks
- some metamorphic rocks are formed when they are subjected to pressure from compressional forces or weights of overlying rocks.
- Some metamorphic rocks are formed when they are subjected to heat during volcanicity
- Some are formed when the rocks are subjected to both heat and pressure.
- Differentiate between a mineral and a rock. 2mks
-
- Give two ways in which minerals occur. 2mks
- veins and lodes
- beds/layers and seams
- alluvial /placer deposits
- weathering products
- Explain two negative effects of open –cast mining. 4mks
- it leaves large /huge ugly scars /holes on the surface which are filled with rainwater causing water borne diseases.
- Dusts ends up in the atmosphere polluting it.
- It interfere with natural vegetation which is cleared
- Blasting of rocks leads to instability of basement rocks
- Heaps of rocks wastes hinder any land use/create barren landscapes.
- Explain two factors influencing exploitation of trona in L.Magadi. 4mks
- Trona occurs in large quantity hence economical to mine
- Trona is formed on the surface hence cheaper to mine using dredging method.
- Availability of market both from within and outside the country.
- Availability of well established infrastructure eg roads ,railway to transport soda ash.
- Give two ways in which minerals occur. 2mks
-
- Define the term ‛earth movement’. 2mks
- are movements which takes place within the rocks of the earth,s crust due to tectonic forces
- Identify two types of earth movement . 2mks
- horizontal /orogenic movements
- vertical/epeirogenic movement
- Explain the continental drift theory? 4mks
- the earth was originally one large land mass called Pangaea which was surrounded by one big ocean/sea called panthalassa.
- Later Pangaea broke into 2, parts i.e. Laurasia (Northern content) and Gondwanaland (Southern continent).
- The two were separated by a narrow sea called Tethys.
- Laurasia split to form North America, Europe and Asia while Gondwanaland split to form Africa, South America, India, Australia, New Zealand and Antarctica.
- Define the term ‛earth movement’. 2mks
- The diagram below represents parts of the earth’s crust which has been subjected to tensional force. Use the diagram to answer questions that follow.
- Identify the type of fault. 1mk
- Normal faults
- State two other types of faults apart from the in (a) above. 2mks
- Reversed fault
- Shear /tear/slip fault
- Thrust fault
- Anticlinal fault
- Name the angle L. 1mk
- hade
- Name the distance m. 1mk
- Throw
- Mention two features resulting from faulting. 2mks
- Escarpment /fault scarp
- Fault steps
- Block /horst mountains
- Tilt blocks
- Rift valley
- Identify the type of fault. 1mk
- Differentiate between:
- Magnitude and intensity of earthquakes. 2mks
- Magnitude refer to energy given off/produced by the earthquake while intensity of the earthquake refers to how hard /strong the earthquakes shakes the ground.
- Seismic and aseismic zones. 2mks
- Seismic zones are the areas prone to earthquakes while aseismic zones are the areas not prone to earthquakes.
- What are the effects of earthquakes? 4mks
- Loss of lives and destruction of properties.
- Causes permanent vertical and lateral displacement of parts of the land
- Can trigger fire when they disconnect gases and oil pipes. Etc
- Can lower/raise sea floor and cause tsunamis
- Can cause landslides which can claim lives and destroy properties
- Restrict development of towns as seismic areas aren’t ideal for tall buildings.
- Creates anxiety and fear among people.
- Magnitude and intensity of earthquakes. 2mks
-
- Define the term ‛bearing’ as used in Geography. 2mks
- use of degrees to show location of a place in relation to another
- Explain the following methods of representing relief on topographical maps.
- Pictorial representation. 2mks
- Is showing the appearance of the land by the use of pictures /drawings of the relief eg hill,valleys.
- Hachures. 2mks
- Is the use of short lines on a map to show steepness and direction of the slope.
- Pictorial representation. 2mks
- Define the term ‛bearing’ as used in Geography. 2mks
- Identify the three types of ground photographs. 3mks
- Ground close-up photographs
- Ground general view
- Ground oblique photographs
- The table below represents sugar cane production in five major factories in Kenya. Use it to answer the following questions:
Factory Production in ‛000’ tones Sony 50 Nzoia 100 Chemilil 200 Muhoroni 250 Mumias 400 - Using the data above, draw a divided rectangle 15cm length. 5mks
Sony 50/1000 x 15 =0.75cm ½mk
Nzoia 100/1000 x15=1.5cm ½mk
Chemilil 200/1000 x 15=3.0cm ½mk
Muhoroni 250/1000 x 15=3.75cm ½mk
Mumias 400/1000 x 15 = 6cm ½mk
Title :A divided rectangle showing sugarcane production ½ mk
Drawing=2mks - Give the difference in tonnage between sugar produced in Muhoroni and Nzoia factory. (1mk)
250,000 -100,000=150,000 tonnes
- Using the data above, draw a divided rectangle 15cm length. 5mks
-
- Define the term climate 2mks
- Average weather /atmospheric condition of the place over a long period of time, usually 30-35years.
- What is climate change? 2mks
- Is establishment of a new climatic system or a continuous change in climate state
- Define the term climate 2mks
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Geography Questions and Answers - Form 2 Term 3 Opener Exams 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students