INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- This paper consists of three sections A, B and C.
- Answer all questions in section A and B.
- Answer any two questions in section C.
SECTION A(Answer all the questions)
- Define the term Agriculture. 1mk
- Give the meaning of the following terms as used in Agricultural Production. 1½mks
- Olericulture
- Pomoculture
- Floriculture
- State four advantages of mixed farming. 2mks
- State four importance of Agriculture. 2mks
- Give four ways in which Health influence Agricultural production. 2mks
- State three negative effects of wind in crop production. 1½mks
- State four aspects of rainfall that influence agricultural production. 2mks
-
- Name two dual purpose cattle breed reared in Kenya (1mk )
- Outline four general characteristics of indigenous cattle breed (2mks)
- Give two reasons why burning is discouraged as a method of clearing land .(1mk)
- State three tertially operations that are carried out in the farm. 1½mks
- Give three importance of carrying out minimum tillage 1½mks
- State four importance of drainage in Agriculture 2mks
- Give three reasons as to why green manure is not commonly used. 1½mks
- State three basic concept of economics. 1½mks
- State four roles of Nitrogen in plants.2mks
- Outline three characteristics of Nitrogenous fertilizers. 1½mks
- State three impotances of testing soil.1½mks
- Give two areas to be avoided when carrying out soil sampling. 1mk
SECTION B(Answer all the questions in this section)
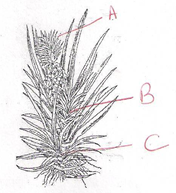
- The following is a diagram of a certain crop. Study it carefully and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the crop ……………………………………………………….. 1mk
- Label the parts labeled A ,B and C. 1½mks
- State four factors to be considered when selecting materials for planting. 2mks
- State four factors which determine the depth of planting. 2mks
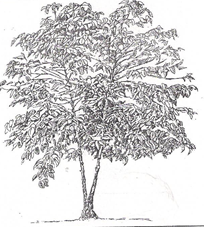
- The following is a pruned crop. Study it carefully and answer the questions that follows.
- Identify the method of pruning. 1mk
- Give four disadvantages of using the above method of pruning. 2mks
- Apart from the above give any other method of pruning coffee. 1mk
- State four factors which determine the time of harvesting crops. 2mks
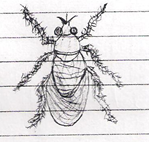
- Study the diagram below and then answer the questions that follows:-
- Identify the parasite shown above (1mk)
- Name the livestock species attacked by the parasite above (112mks)
- How does the above parasite obtain it’s food from the host? (1mk)
- What are the harmful effects of the parasite you have mentioned in (a) above?(2mks)
- How would a farmer control the above parasite (2mks)
SECTION C.
(Answer any TWO questions in this section.)
-
- State five reasons for keeping animals healthy5mks
- State 5 predisposing factors to livestock diseases. 5mks
- Discuss FIVE importances of crop rotation in crop production. 10mks.
-
- State and explain FIVE nursery management practices. 10mks
- Describe 6 factors influencing spacing of crops.. 6mks
- state FOUR methods of preparing planting materials 4mks
-
- Describe importance of Drainage as a land Reclamation method. 6mks.
- Discuss 6 characteristics of fertile soil. 6mks.
- Explain any 4 factors to consider in choosing seedrates. 8mks.

MARKING SCHEME
- Define.
- Agriculture is a art and science of growing crops and rearing livestock. 1x1=1mk
-
- Olericulture:growing of vegetables
- Pomeculture: growing of fruits
- Floriculture: growing of flowers 3x½=1½mks
- Advantages of mixed farming
- mutual benefits
- the farmer does not experience a total loss in case one fails
- High production per unit area
- Flow of income throughout the year
- Maximum utilization of labour. 4x½=2mks
- Importance of Agriculture
- Source of income
- Source of foreign exchange
- Source of employment
- Source of raw materials for industries.
- Act as market for industrial goods. any 4x½=2mks
- Way in which health influence Agricultural production
- Loss of labour.
- Spend a lot of times taking care of the sick
- A lot of money is used in taking care of aids patient instead of National development.
- Orphans become a burden to the society
- Low supply of food. any 4x½=2mks
- Negative effect of wind in crop production.
- Soil erosion agent
- Destruction of farm structures
- Spread pest and diseases
- Blow away rain bearing clouds
- cause lodging of crops.
- Increase the rate of evapotranspiration
- Strong wind leads to destruction of crops. 3x½=1½mks
- Aspects of rainfall 4x1/2=2mks
- Distribution
- Intensity
- Amount
- Reliability any 4x½mkS
-
-
- Sahiwal 2x1/2=1mk
- Simmental
- Redpoll 1 x ½ = ½ mk
- general characteristics of indigenous cattle
- They have humps for storing fat
- Tolerant to high temperatures
- They have a slow growth rate in maturity rate
- Able to resist tropical diseases of E.C.F
- Have relatively long calving interval
- Can walk for long distances without serious loss in condition 4 x ½ = 2mk
-
- Reasons why Burning is not a recommended method of land clearing.
- Destroys the soil structure by burning humus in the soil
- Kill soil living organism
- Burn all the plants
- Fire can spread unwanted areas.
- Leads to excessive loss of moisture
- Lead to air pollution
- Alters the soil pH any 2x½mk
- Tertially operations
- Leveling
- Rolling
- Sub-soiling
- Ridging any 3x½mk=1½mks
- Importance of carrying out minimum tillage
- To reduce cost of production
- Control soil erosion
- Maintain soil structure
- Prevent distribution of roots
- Prevent exposure of humus
any 4x½=2mks
- Importance of drainage
- Increase soil volume
- Increase soil aeration
- Raise soil temperature
- Increase microbial activities
- To reduce soil erosion
- Reduce toxic substances any 4x½=2mks
- Reasons why green manure is not commonly used.
- Most of the crops used are food crops.
- Might use most of the soil moisture leaving very little for the next crop.
- Most of the nutrients are used up by the micro-organisms in the process of decomposition.
- Take time for the green manure crop to decompose. any 3x½= 1½mks
- Basic concepts of economics
- Opportunity cost
- Scarcity
- Preference and choice 3x½=1½mks
- Role of Nitrogen in plants
- Involved in protein formation
- Part of chlorophyll molecule
- Regulate availability of phosphorous.
- Increase the size of grains in cereals 4x½=2mks
- Characteristics of Nitrogenous fertilizers.
- Highly soluble in water
- Has a scorching effect
- It is hygroscopic
- Highly volatile
- Has a corrosive effect
- Easily leached any 3 x½=1½mks
- Importance of soil testing .
- To know the cause of low yield.
- Help to know the amount of fertilizer to be applied.
- Help to know the nutrient in the soil.
- Help the farmer to know the type of crop to be grown.
- Helps to know the type of fertilizer to apply any 3x½=1½mks
- Areas to be avoided when carrying out soil sampling
- Dead furrows
- Areas where there were old manure heaps.
- Along the boundaries
- Terrace stands
- old fences.
- Between slopes any 2x½mks=1mk
SECTION B
-
- Pineapple 1mk
- A-Crown
B-Slip
C-Suckers 3x½=1½ - Factors to be considered when selecting materials for planting.
- suitability to the ecological conditions
- purity of the materials
- Germination percentage
- Certified seeds 4x½=2mks
- Factors which determine the depth of planting.
- Soil type
- soil moisture content
- size of the seeds
- Type of germination 4x½=2mks
-
- Multiple stem pruning 1x1=1mk
-
- Breaking of stems and branches
- Difficulty in gathering barriers from top points.
- Difficult to spray
- Rotting stumps with age. 4x½=2mks
- Single stem pruning 1mk
- Factors which determine time of harvesting.
- Market demand
- chemical concentration
- weather condition
- purpose of the crops
- Market price. any 4x½=2mks
-
- the parasite shown above 1mk
- Tsetse fly
- Name the livestock species attacked by the parasite above
- Cattle
- Sheep
- Horses 3 x ½ = 1½ mks
- How does the above parasite obtain its food from the host?
- By sucking blood from the animal after piercing the skin of the animal 1 x 1 = 1mks
- What are the harmful effects of the parasite you have mentioned in (a) above?
- Damages the skin and hides
- Causes anaemia by sucking blood from the animals.
- Transmits nagana 2 x 1 = 2 mks
- How would a farmer control the above parasite
- Clearing the bush nearby
- Spraying the breeding grounds with the appropriate insecticide 2 x 1 = 2 mks
- the parasite shown above 1mk
SECTION C
-
- reasons for keeping animals healthy
- To produce high quality products.
- Reduce medication costs through treatment.
- To promote high production.
- To enhance fast growth rate hence attaining maturity stage early.
- To ensure healthy and strong offspring are produced.
- To prevent transmission of diseases to other animals and to human beings in cases of zoonotic diseases.
- So that animals can remain in production for long. 5x1=5mks
- To produce high quality products.
- predisposing factors to livestock diseases
- Age of the animal
- Breed of the animal
- Sex of the animal
- Colour of the animal
- Environmental conditions 5x1=5mks
- importance of crop rotation
- control of soil erosion
crops planted in rows should always be alternated with cover crops to protect empty spaces left during establishment from agents of soil erosion. - improvement of soil structures.
A grass hay is established at the end of rotation programme. Their roots bind soil practices together thus improvement of soil fertility. Eg. When leguminous crops are included in the rotation programme they help in improving soil fertility through fixation of nitrogen with the help of the Rhizobia bactaria. This nitrogen is made use of by the subsequent crops in the rotation. - control of weeds-parasite weeds specific to grass family crops can be controlled by planting non-grass crop for a period of time.
- control of soilborne pests and disease -builds up some pests and diseases are specific to various crops
Such pests and diseases will always attack crops of the same family when grown in succession. Such crops should be alternated with crops from different families to control them. - maximum utilization of Nutrients
Different crops vary in their nutrients requirements in terms of type of nutrients and the depth of absorption. 5x2=10mks
- control of soil erosion
- reasons for keeping animals healthy
-
- Nursery management practices
- Mulching: light mulch should be applied on the nursery bed and removed after the seeds start to germinate.
- Watering: done twice in a day morning and evening
- Weed control: Done by uprooting using hand.
- Pricking out: Removal of excess seedlings from a nursery and planting them in an adjacent nursery.
- Shading: Elected over a nursery to the nursery bed. Avoiding dark conditions .
- Pest and diseases control-done by sterilizing the soil through heat treatment and application of appropriate chemical.
- Hardening off: reduction of watering frequencies and shading .to ensure that it adapts well to the harsh ecological condition. any 5x2=10mks
- Factors which influencing the spacing of any crop.
- Growth habit of the crop: spreading crops are widely spaced.
- Purpose of crop: crop to be used as a fodder are closely spaced.
- Type of machinery used: rows should allow free passage of machinery.
- Soil fertility: fertile soil can support more crops therefore closely spaced.
- Size of the crop when mature. Tall crops require wider spacing.
- Moisture availability: In areas with heavy rainfall crops are closely spaced.
- Pest and diseases control: when crops are closely spaced it is hard for pest to grow from one crawl to the other. 6x1=6mks
- methods of preparing planting materials
- seed inoculation
- seed dressing
- breaking seed dormancy
- chitting 4x1=4mks
- Nursery management practices
-
- Importance of Drainage as a land reclamation method.
- to increase soil aeration-plant growth is retarded by excess water around the root zone because it fills the air spaces restricting air movement. Plants roots get enough air for proper growth after water is removed.
- to increase soil volume-amount of soil around the root zone from which roots can easily get nutrients easily is increased,
- soil temperature-it improves the rate at which soil warms up for better plant growth.
- to increase microbial activities-micro-organisms in the soil increase in number due to proper aeration. They help to improve soil structure and make plant food more readily available.
- to reduce soil erosion-well drained soils have high water holding capacity which helps to reduce run off and increase infiltration rate.
- To remove toxic substances –toxic salts are removed through drainage. 6x1=6mks.
- characteristics of a fertile soil
- Good depth-deep soils give plants greater volume to obtain plant nutrients and provide strong anchorage.
- proper drainage-well drained soil is also allow root respiration and reduce build up of carbon dioxide.
- Good water holding capacity-this will ensure that enough water is retained for plant use.
- Adequate nutrients supply- it should supply the nutrients needed by plants in the correct amounts and in a form that is available to the crops.
- corrects soil PH .different crops have different PH requirements. Certain plants nutrients are only available at a specific soil PH.
- Free from excessive infestation of soil borne pest and diseases. 6x1=6mks
- Four factors to consider in choosing seed rates.
- seed purity-loss seeds are required when planting pure seeds with high germination percentage comprised to the use of impure or mixed seeds.
- Germination percentage-less seed is used when its germination percentage is higher. Seed of lower germination percentage is required in a large amount.
- Spacing –at closer spacing more seeds are used than at wider spacing.
- number of seeds per hole-planting 2 or more seeds per hole leads to higher seed rate than when only one seed is planted per hole.
- the purpose of the crop-crops used for silage making has a closer spacing leading to higher seed rate than the crops meant for food production. 4x2=8mks
- Importance of Drainage as a land reclamation method.
Download Agriculture Questions and Answers - Form 2 Term 3 Opener Exams 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students