INSTRUCTIONS.
Answer all the questions in the spaces provided.
-
- Define nomadic pastoralism. (1mk)
- Nomadic pastoralism is a form of pastoralism in which livestock are herded in order to seek for fresh pastures on which to graze.
- State four disadvantages of carrying out nomadic pastoralism. (2mks)
- Poor health and biosecurity management practices.
- Production of low quantity and quality beef and dairy.
- Conflict.
- Poor lifestyle for herders.
- Define nomadic pastoralism. (1mk)
- List four biotic factors that affect agricultural production. (2mks)
- insects
- rodents
- pests
- aquatic plants
- fish
- amphibians
- algae
- A biotic factor is a living organism that shapes its environment.
- State two implements used during primary tillage. (2mks)
- Wooden Plough
- Iron Plough
- Special Purpose plough
- Outline four practices that can lead to achievement of minimum tillage. (4mks)
- crop rotation
- soil cover are practices related to pesticide and nutrient runoff
- soil erosion
- soil compaction
- List four factors that determine the choice of pipe for water conveyance. (2mks)
- Strength of the pipes;
- Amount of water to be conveyed;
- Cost of the pipe:
- Diameter/size of the pipe;
- Durability;
- Colour of the pipes;
- State two advantages of plastic pipes. (1mk)
- Resistance to corrosion. Corrosion is one of the biggest problems associated with metal piping systems.
- Energy saving.
- Smaller risk of leakage.
- Easier installation.
- Recyclable.
- A word from an expert.
- List four factors that determine the choice of a particular irrigation system. (2mks)
- Topography:
- Climate
- Means of Irrigation
- Crops:
- Water Conservation:
- Economic Factors and Labour:
- State two problems associated with farm yard manure. (1mk)
- odour issues
- cost
- Give three characteristics of goats that make them perform better in dry parts of the country. (3mks)
- When is opportunity cost equal to zero? (1mk)
The formula for calculating opportunity cost is to compare the net benefit of one choice with the benefit of another option. If the difference between those benefits is zero, then the opportunity cost is zero, meaning you'd get the same benefit from either choice. - State two effects of applying excess nitrogen to crops. (2mks)
- List four methods of fertilizer application. (2mks)
Excessive N causes "luxuriant" growth, resulting in the plant being attractive to insects and/or diseases/pathogens. The excessive growth can also reduce stem strength resulting in lodging during flowering and grain filling. Excessive use of N also has negative implications for the environment and lowers farm profits. - A maize farmer has a plot measuring 40m by 60m. Calculate the number of maize plants he will have on his plot if he used a spacing of 75cm x 75cm. (3mks)
1 m = 100 cm
40m = 4000 cm
60 m = 6000cm
= 4000 x 6000 = 24000000
= 75 x 75 = 5625
= 24000000
5625
=4266 maize plants - The diagrams below represent two methods used in soil sampling study them carefully and answer the questions that follow.
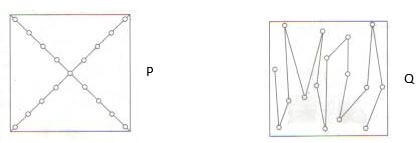
- Name methods (2mks)
P diagonal/transverse method
Q zigzag method - State two precautions observed when carrying out the above two methods. (2mks)
avoid contamination/use sterilized contained
avoid sampling soil from unusual sites e.g ant hills
avoid mixing top soil with sub soil
- Name methods (2mks)
- The following is a list of plant nutrients copper, calcium, nitrogen, molybdenum, zinc, phosphorous, carbon, sulphur, iron and magnesium which of the above plant nutrients are: (4mks)
- Macro-nutrient - nitrogen, calcium, magnesium, phosphorous, sulphur
- Micro-nutrients - copper, iron, zinc, molybdenum
- Fertilizer elements - nitrogen, potassium
- Liming elements - calcium, magnesium
- State two methods of breaking seed dormancy. (2mks)
Scarification, hot water, dry heat, fire, acid and other chemicals, mulch, and light are the methods used for breaking seed coat dormancy - Differentiate between oversowing and undersowing. (2mks)
Undersowing is the establishment of a pasture under a cover crop usually maize/nurse crop. Oversowing is the establishment of a pasturelegume/grass on an existing grass pasture. - State three factors to consider in choosing seed rates. (3mks)
Purity - should be clean / free from impurities. Maturity - should be of correct maturity stage. Age/storage period: - seeds stored for long periods have low viability/germination percentage hence should not be selected. Size of the seed, should be of correct size. - The diagrams labeled A,B,C below illustrate materials and methods used in crop propagation. Study them and use them for to answer questions that follow.
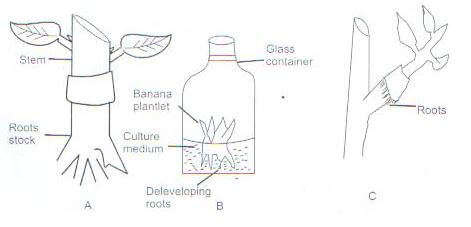
- Identify the methods (3mks)
A cutting
B
C budding - State two importance of carrying out method B. (2mks)
- Identify the methods (3mks)
-
- Define crop rotation. (1mk)
Crop rotation is defined as a “system of growing different kinds of crops in recurrent succession on the same land” (Martin et al., 1976). Rotating different crops year after year adds various economic and environmental benefits. In addition, crop rotation is helpful in long-term soil and farm management. - State four advantages of carrying out crop rotation. (2mks)
- Outline four factors to consider before designing a crop program. (2mks)
A crop rotation can help to manage your soil and fertility, reduce erosion, improve your soil's health, and increase nutrients available for crops.
- Define crop rotation. (1mk)
- Differentiate the following terms.
- Inter cropping and mixed cropping
Mixed Cropping alludes to a method of cropping in which two or more crops are grown simultaneously in the same piece of land. Intercropping refers to process of cultivating crops wherein different types of crops are cultivated together in a specified pattern - Thinning and rogueing. (2mks)
Thinning is removal of excess seedlings from the seedbed while rogueing is removal and destruction of diseased or infected plants. - The diagram below shows a routine management practice carried out in tomato production.
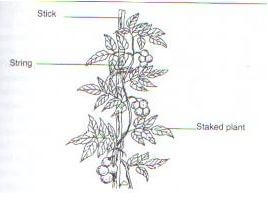
- Identify the routine management practice. (1mk)
String trellis/Trllising/ trellis system - State two importance of carrying out the practice mentioned in c (i) above. (2mks)
Not only do trellises keep vining plants off the ground, protecting them from a variety of pests, diseases and foot traffic, they also ensure plants receive adequate circulation and sunlight—two necessities to help reduce disease and hasten ripening.
- Identify the routine management practice. (1mk)
- Inter cropping and mixed cropping
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Agriculture Questions and Answers - Form 2 Mid Term 2 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

