- Answer ALL questions in the spaces provided.
- All working must be clearly shown. where necessary
- Candidates should answer the questions in English
-
- Define the following terms as used in Chemistry.
- Compound (1 mark)
- Catalyst (1 mark)
- Why is it important to observe the following laboratory rules.
- Label all chemicals. 1 mark)
- Do not eat anything in the laboratory. (1 marks)
- Fill in the blank spaces in the table below. (3 marks)
Apparatus U To separate immiscible liquids Measuring cylinder Scooping solid substances
- Define the following terms as used in Chemistry.
-
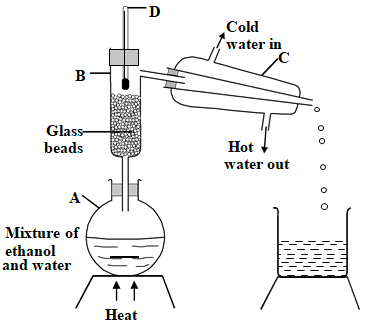
- Below is an apparatus used in the laboratory. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the parts labelled. (2 marks)
- A
- B
- C
- D
- What is the purpose of the parts: (2 marks)
- A
- B
- Identify the parts labelled. (2 marks)
- State two differences between luminous and non luminous flame (2 marks)
- Why are most laboratory apparatus made of glass? (1 marks)
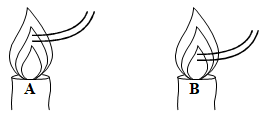
- In an experiment, a hollow glass tube was placed in different regions of a non-luminous flame a shown below.
If a burning wooden splint / match stick was introduced at the tip of glass tubes in A and B, in which set up would a frame be formed. Explain. (2 marks)
- Below is an apparatus used in the laboratory. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
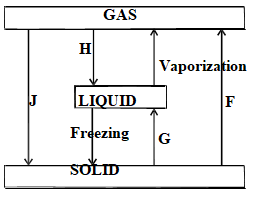
- The diagram below shows the changes that take place between states of matter.
- Give the names of the processes.(1 ½ mk)
- H
- G
- J
- Name one substance that undergoes process F. ( ½ mark)
- Give the names of the processes.(1 ½ mk)
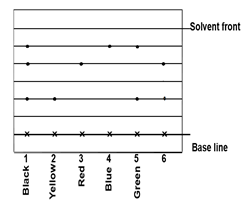
- A piece of chromatography paper was spotted with coloured inks obtained from pens labelled 1 to 6. The diagram below shows the spots after chromatogram was developed.
- Which two pigments are contained in pen 5? (1 mark)
- According to the chromatogram which pigments are present in the ink of pen number 6. (1 mark)
- Write the chemical symbols for the following elements. (2 marks)
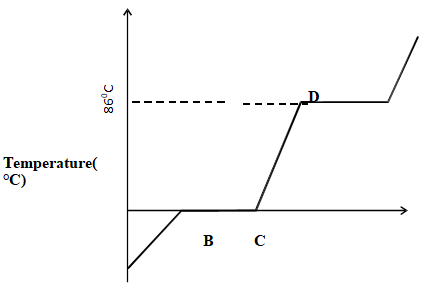
Element Symbol Sulphur Copper Helium Sodium - The diagram below shows changes in physical states when a typical solid is heated. Study and answer the questions that follows.
- On the same graph, sketch a curve that would be obtained if the solid was impure. (1 mark)
- What name is given to the curve above? (1 mark)
- Name process taking place at (1marks)
- BC
- DE
- Study the set up below and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify one mistake in the set up. (1 mark)
- Name the parts labelled (1mk)
- B
- C
- What is the purpose of the parts labelled (2mk)
- C
- D
- Ethanol has a boiling point of 78°C and water 100°C. Which will be the first distillate? (1 mark)
- Give one industrial use of the above method of separating mixtures. (1 mark)
-
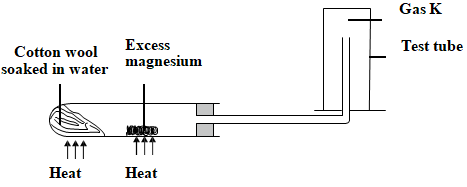
- A student set up the experiment below to collect gas K. The glass wool was heated before heating the magnesium coil.
- Explain why is it necessary to heat the moist cotton wool before heating the magnesium (1 marks)
- Identify gas K. ( ½ mark)
- What property of gas K make it possible to be collected as shown. ( ½ mk)
- Give one use of gas K. ( 1 mark)
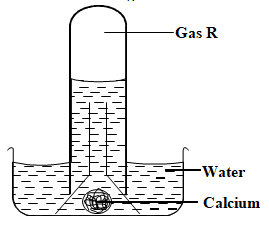
- The diagram below was used to investigate the action of water on calcium metal.
-
- Identify gas R. (1 mark)
- The remaining solution in the beaker changed red litmus paper to blue. What does this suggest about the nature of solution.(1 mark)
- Write a word equation for the reaction. (1 mark)
- What would be observed if:
- Phenolphthalein indicator is added to the solution? ( ½ mark)
- Methyl orange indicator is added to the solution? ( ½ mark)
-
- A student set up the experiment below to collect gas K. The glass wool was heated before heating the magnesium coil.
- The table below shows the pH values of certain solutions. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
Which of the solutions is most likely to be:Solution A B C D E F pH Values 13.5 12.0 6.5 7.0 10.0 1.0 - Lime water (calcium hydroxide)? ( ½ mark)
- Common table salt? ( ½ mark)
- Wood ash ? ( ½ mark)
- Weakly basic? ( ½ mark)
- Orange juice? ( ½ mark)
- Strongly acidic? ( ½ mark)
- The diagram below is a set up for the laboratory preparation of oxygen gas.
- Name substance at (1mk)
- A
- R
- Write down a word equation for the reaction taking place in the flask. (1 mark)
- What property of oxygen makes it possible to be collected as shown above? (1 mark)
- Give two commercial uses of oxygen gas. (1 marks)
- Name substance at (1mk)
-
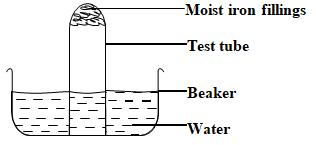
- The set up below was used to study some properties of air.
- Why was the iron fillings moistened? (1 mark)
- State one observation made after 48 hours. (1 marks)
- Explain the observations made. (1 marks)
-
- What is the chemical name for rust? (1 mark)
- Name two methods that can be used to prevent rusting. (1 mark)
- Explain why it is not advisable to wash vehicles using sea water. (1 marks)
- Explain why galvanized iron objects are better protected even when scratched. (1 mark)
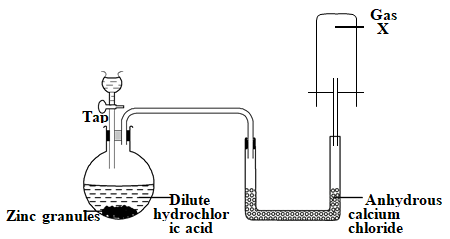
- The set up below was used to study some properties of air.
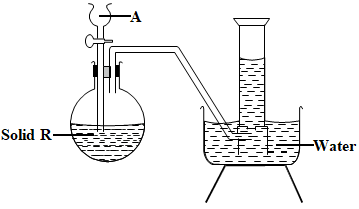
- Study the set up below and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify gas X (1 mark)
- Write a word equation for the reaction liberating gas X. (1 mark)
- Why is it not advisable to use calcium in this method of preparing hydrogen? (1 mark)
- What is the purpose of anhydrous calcium chloride in the U-tube? (1 mark)
- Name another compound that could serve the same purpose as anhydrous calcium chloride.(1 mark)
- Name the method used to collect the gas and give one property of the gas that enables it to be collected using this method. (1 marks)
- Why is it necessary to discard the first few bubbles of gas that is produced? (1 mark)
- Give 2 differences between a physical change and a chemical change(2mk)
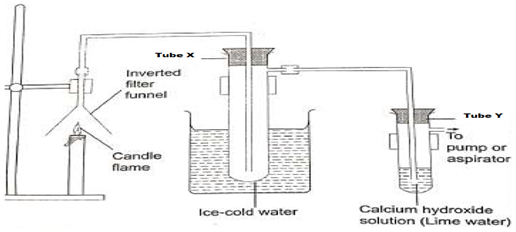
- The set up below was used to investigate the products formed when candle wax burns in air
- What observation are made in:-
- Test –tube X (1mk)
- Test – tube Y. (1mks)
- Explain why test-tube A is dipped in ice-cold water (1mk)
- What is the effect of contest of test-tube X on anhydrous copper (ii) sulphate (1mk)
- Identify the products formed when candle wax burns in air (1mks)
- What observation are made in:-
- Name the method used to separate the following mixture (2mks)
- Salt from sea water (both salt and water needed)
- Copper (ii) Sulphate crystals from its aqueous solution
- Metal S removes oxygen combined with P. Q reacts with an oxide of R and not with an oxide of P. P reacts with cold water but Q does not.
- Which is the most reactive metal ? (1 mark)
- Which is the least reactive metal ? (1 mark)
- Arrange the metals in order of reactivity starting with most reactive to the least reactive. (1 mark)
- Differenciate between the following terms:-
- proton and electron (2mks)
- atomic number and mass number (2mks)
- An atom X can be represented as
.
- write the electronic configuration of X. (1mk)
- To what group and period does element X belong? Give a reason for each. (2mks)
- Element T has two isotopes, 35T with relative abundance of 75% and 37T with relative abundance of 25%.
- Define the term isotope (1mk)
- Calculate the relative atomic mass of element T (2mks)

MARKING SCHEME
-
- Define the following terms as used in Chemistry.
- Compound (1 mark)
- pure substance made up of two or more elements chemically combined
- Catalyst (1 mark)
- a substance which alters the reaction rate but remain unchanged
- Compound (1 mark)
- Why is it important to observe the following laboratory rules.
- Label all chemicals. (1 mark)
- to avoid confusion
- Do not eat anything in the laboratory. (1 marks)
- avoid poisoning
- Label all chemicals. (1 mark)
- Fill in the blank spaces in the table below. (3 marks)
Apparatus Use Separatinig funnel To separate immiscible liquids Measuring cylinder Scooping solid substances
- Define the following terms as used in Chemistry.
-
- Below is an apparatus used in the laboratory. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the parts labelled. (2 marks)
- A - chimey
- B – collar
- C - air hole
- D - base
- What is the purpose of the parts: (2 marks)
- A - allows air and laboratory gas to mix.
- B - regulate the amount of air entering the chimney
- Identify the parts labelled. (2 marks)
- State two differences between luminous and non luminous flame (2 marks)
Luminous flame Non-luminous flame Bright yellow in colour Blue in colour Produces a lot of light Produces less light Large and unsteady Small and steady Produces soot ;Does not produce soot Has four mzones Has three zones Burns quietly Burns noisily Moderately hot Very hot - Why are most laboratory apparatus made of glass? (1 marks)
- its transparent
- easy to clean
- don’t react with most chemicals
- In an experiment, a hollow glass tube was placed in different regions of a non-luminous flame a shown below.
If a burning wooden splint / match stick was introduced at the tip of glass tubes in A and B, in which set up would a frame be formed. Explain. (2 marks)- B - contains unburnt gases that burn in air
- Below is an apparatus used in the laboratory. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
- The diagram below shows the changes that take place between states of matter.
- Give the names of the processes.(1 ½ mk)
- H - Condensation
- G - Melting
- J - Deposition
- Name one substance that undergoes process F. ( ½ mark)
- ammonium chloride
- Iodine
- aluminium chloride
- Iron(iii) chloride
- benzoic acid
- Give the names of the processes.(1 ½ mk)
- A piece of chromatography paper was spotted with coloured inks obtained from pens labelled 1 to 6. The diagram below shows the spots after chromatogram was developed.
- Which two pigments are contained in pen 5? (1 mark)
- yellow and blue
- According to the chromatogram which pigments are present in the ink of pen number 6. (1 mark)
- Red and yellow
- Which two pigments are contained in pen 5? (1 mark)
- Write the chemical symbols for the following elements. (2 marks)
Element Symbol Sulphur S Copper Cu Helium He Sodium Na - The diagram below shows changes in physical states when a typical solid is heated. Study and answer the questions that follows.
- On the same graph, sketch a curve that would be obtained if the solid was impure. (1 mark)
- What name is given to the curve above? (1 mark)
- Heating curve
- Name process taking place at (1marks)
- BC - Melting
- DE - Evaporation
- Study the set up below and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify one mistake in the set up. (1 mark)
- flow of water in the condenser is interchanged
- Name the parts labelled (1mk)
- B - fractionating column
- C - liebig condenser
- What is the purpose of the parts labelled (2mk)
- C - to condense ethanol vapours
- D – to identify the fractions coming out
- Ethanol has a boiling point of 78°C and water 100°C. Which will be the first distillate? (1 mark)
- ethanol
- Give one industrial use of the above method of separating mixtures. (1 mark)
- separating crude oil component
- separating liquid air component
- Identify one mistake in the set up. (1 mark)
-
- A student set up the experiment below to collect gas K. The glass wool was heated before heating the magnesium coil.
- Explain why is it necessary to heat the moist cotton wool before heating the magnesium(1 marks)
- to generate steam that reacts with magnesium
- Identify gas K. ( ½ mark)
- Hydrogen
- What property of gas K make it possible to be collected as shown. ( ½ mk)
- It is less dense/lighter than air
- Give one use of gas K. ( 1 mark)
- manufacture of ammonia in the Haber process
- manufacture of margarine/hardening oils to fats
- In weather balloons (any other correct use)
- Explain why is it necessary to heat the moist cotton wool before heating the magnesium(1 marks)
- The diagram below was used to investigate the action of water on calcium metal.
-
- Identify gas R. (1 mark)
- Hydrogen
- The remaining solution in the beaker changed red litmus paper to blue. What does this suggest about the nature of solution (1 mark)
- it is basic/ base
- Write a word equation for the reaction. (1 mark)
Calcium + water = Calcium hydroxide + Hydrogen
- Identify gas R. (1 mark)
- What would be observed if:
- Phenolphthalein indicator is added to the solution? ( ½ mark)
- Turns pink
- Methyl orange indicator is added to the solution? ( ½ mark)
- Turns pink/red
- Phenolphthalein indicator is added to the solution? ( ½ mark)
-
- A student set up the experiment below to collect gas K. The glass wool was heated before heating the magnesium coil.
- The table below shows the pH values of certain solutions. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
Which of the solutions is most likely to be:- Lime water (calcium hydroxide)? ( ½ mark)
- B
- Common table salt? ( ½ mark)
- D
- Wood ash ? ( ½ mark)
- E
- Weakly basic? ( ½ mark)
- D
- Orange juice? ( ½ mark)
- C
- Strongly acidic? ( ½ mark)
- F
- Lime water (calcium hydroxide)? ( ½ mark)
- The diagram below is a set up for the laboratory preparation of oxygen gas.
- Name substance at (1mk)
- A – Hydrogen peroxide OR A - Water
- R - Manganese(iv) oxide R - Sodium peroxide
- Write down a word equation for the reaction taking place in the flask. (1 mark)
Hydrogen peroxide manganese (iv) oxide → Water + Oxygen
OR
Sodium peroxide + Water → Sodium hydroxide + Oxygen - What property of oxygen makes it possible to be collected as shown above? (1 mark)
- It is slightly soluble in water
- Give two commercial uses of oxygen gas. (1 marks)
- used in hospitals for patients with breathing problems
- in oxy –acetylene flame used for welding and cutting of metals
- used by mountain climbers and deep sea divers
- burning rocket fuels
- a reactant in fuel cells
- to remove impurities of iron in steel making
- Name substance at (1mk)
-
- The set up below was used to study some properties of air.
- Why was the iron fillings moistened? (1 mark)
- to ensure that iron filings stick on to the wet surface
- State one observation made after 48 hours. (1 marks)
- iron filings turned brown
- level of water in the test tube rose
- Explain the observations made. (1 marks)
- iron filings reacted with oxygen and water to form rust (brown)
- water rose in the test tube to occupy/replace the volume of air/oxygen used
- Why was the iron fillings moistened? (1 mark)
-
- What is the chemical name for rust? (1 mark)
- Hydrated iron(iii)oxide
- Name two methods that can be used to prevent rusting. (1 mark)
- painting
- oiling and greasing
- galvanising
- Alloying
- Coating with other metals
- Sacrificial protection
- What is the chemical name for rust? (1 mark)
- Explain why it is not advisable to wash vehicles using sea water. (1 marks)
- salt speeds up/accelerates the rate of rusting
- Explain why galvanized iron objects are better protected even when scratched. (1 mark)
- Zinc being more reactive than iron corrodes preferentially, protecting iron.
- The set up below was used to study some properties of air.
- Study the set up below and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify gas X (1 mark)
- Hydrogen
- Write a word equation for the reaction liberating gas X. (1 mark)
Zinc + Hydrochloric acid = Zinc chloride + Hydrogen - Why is it not advisable to use calcium in this method of preparing hydrogen? (1 mark)
- reaction between calcium and hydrochloric acid is explosive
- What is the purpose of anhydrous calcium chloride in the U-tube? (1 mark)
- Drying agent/ drying hydrogen gas
- Name another compound that could serve the same purpose as anhydrous calcium chloride.(1 mark)
- concentrated sulphuric acid
- calcium oxide/ Quick lime
- Name the method used to collect the gas and give one property of the gas that enables it to be collected using this method. (1 marks)
- Upward delivery, hydrogen is less dense than air
- Why is it necessary to discard the first few bubbles of gas that is produced? (1 mark)
- They are mixed with air that was initially in the apparatus
- Identify gas X (1 mark)
- Give 2 differences between a physical change and a chemical change(2mk)
Physical change Chemical change 1. No new substance is formed 1. New substance is formed 2. Not accompanied by change in mass 2. Accompanied by change in mass 3. Not accompanied by heat changes 3. Heat energy is released or absorbed 4. Reversible 4. Irreversible - The set up below was used to investigate the products formed when candle wax burns in air
- What observation are made in:-
- Test –tube X (1mk)
- Colourless liquid condensed/water was formed
- Test – tube Y. (1mks)
- calcium hydroxide turned into a white precipitate.
- Test –tube X (1mk)
- Explain why test-tube A is dipped in ice-cold water (1mk)
- To condense any vapour produced by the burning candle
- What is the effect of contest of test-tube X on anhydrous copper (ii) sulphate (1mk)
- Turn white anhydrous copper (ii) sulphate blue
- Identify the products formed when candle wax burns in air (1mks)
- water
- carbon (iv) oxide
- What observation are made in:-
- Name the method used to separate the following mixture (2mks)
- Salt from sea water (both salt and water needed)
- simple distillation
- Copper (ii) Sulphate crystals from its aqueous solution
- crystallisation
- Salt from sea water (both salt and water needed)
- Metal S removes oxygen combined with P. Q reacts with an oxide of R and not with an oxide of P. P reacts with cold water but Q does not.
- Which is the most reactive metal ? (1 mark)
- S
- Which is the least reactive metal ? (1 mark)
- R
- Arrange the metals in order of reactivity starting with most reactive to the least reactive. (1 mark)
- R, Q, P, S
- Which is the most reactive metal ? (1 mark)
- Differenciate between the following terms:-
- proton and electron (2mks)
- proton is positively charged while electron is negatively charge
- proton are located in the nucleus while electrons are located in the energy levels
- proton has mass of 1 a.m.u while electron has a negligible mass of 1/1840
- atomic number and mass number (2mks)
- Atomic No. is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom while mass number is the sum of proton and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom.
- An atom X can be represented as
.
- write the electronic configuration of X. (1mk)
- 2:8:2
- To what group and period does element X belong? Give a reason for each. (2mks)
- Group: 2
- Period: three
- Reason: Has 2 electrons in the outermost energy level. Reason: has 3 occupied energy levels
- write the electronic configuration of X. (1mk)
- proton and electron (2mks)
- Element T has two isotopes, 35T with relative abundance of 75% and 37T with relative abundance of 25%.
- Define the term isotope (1mk)
- atoms of the same element with different mass numbers
- Calculate the relative atomic mass of element T (2mks)
relative atomic mass is the weighted average of all the isotopes of that atom present.
Isotope 35T 35 percentage - 75%
Isotope 37T percentage - 25%RAM = (75×35) + (25×37)
100
RAM = 142/4 = 35.5 amu
Thus, the relative atomic mass number of chlorine is 35.5.
- Define the term isotope (1mk)
Download Chemistry Questions and Answers - Form 2 Mid Term 1 Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students