QUESTIONS;
-
- State two functional differences between arteries and veins in mammals.(2mks)
- Differentiate between Arteriosclerosis and Atherosclerosis.(2mks)
- Distinguish between active and passive natural acquired immunity.(2mks)
- Name the antigens and antibodies in human blood groups.(2mks)
- Explain why people with blood group O are referred to as universal donors while people with blood group AB are universal recipients.(2mks)
- Outline two functions of each of the following structures of a cell
- plasmalemma.(2mks)
- Golgi bodies(2mks)
- Centrioles (2mks)
- State the functions of the following parts of a light microscope.
- Condenser (1mk)
- Diaphragm (1mk)
- Course adjustment knob (1mk)
- Fine adjustment knob (1mk)
- Eye piece (1mk)
-
- Name the compound formed when carbon (II) oxide combines with haemoglobin: (1mk)
- Why would the compound named in (a) above lead to death? (2mks)
- Name the substance that transports carbon (iv) oxide
- Plasma (1mk)
- Red blood cells (1mk)
-
- Distinguish between a single circulatory system and double circulatory system. (2mks)
- Name a class whose members have a single circulatory system. (1mk)
- Name the openings to the chamber of the hearts of an insect. (1mk)
- Outline two functions of lipids. (2 mks)
-
- How are leucocytes adapted to their functions. (2 mks)
- Name the blood vessel with highest concentration of:
- Glucose (1 mk)
- Carbon (Iv) oxide (1 mk)
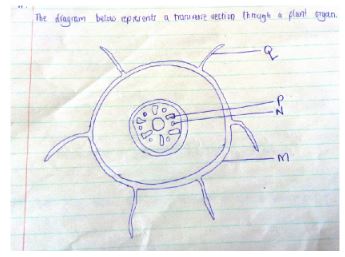
- The diagram below represents a transverse section through a plant organ.
- From which plant organ was the section obtained.(1mk)
- Give two reasons for your answer in (a) above.(2mks)
- Name the parts labeled M, N, P AND Q.(4 mks)
- M –
- N –
- P –
- Q –
- State two functions of part labeled Q.(2mks)
- Howe is part Q adapted to its function?(3mks)
- State three factors that cause decrease in rate of transpiration from leaves.(3mks)
- A student observed a row of 16 epidermal cells in a microscopic field that was 8mm in diameter. Calculate the average length of each cell in micrometers.(2mks)
-
- Give the formula of working out the magnification of a microscope.(1mk)
- Calculate the magnification that is obtained when an object is viewed with a X20 eyepiece and x80 objective. (2 mks)
- Name the organelles that are involved in the following:-
- forms secretory vesicles (1mk)
- Involved in cell division and formation of cilia and flagella.(1mk)
- formation of ATP (1mk)
- fixation of carbon (Iv) oxide to form sugars (1mk)
- detoxification (1mk)
- Differentiatebetween Active transport and Osmosis. (2mks)
- State three roles of active transport in human body. (3mks)
-
- Define gaseous exchange. (1mk)
- Explain four adaptive characteristic features of respiratory surfaces.
MARKING SCHEME
- State two functional differences between arteries and veins in mammals. (2 mks)
Arteries Veins Transport blood froom ,heart to body tissues Transports blood from body tissues to the heart Transports oxygenated blood except pulmonary artery Tranport deoxygenated blood except pulmonary vein - Differentiate between Arteriosclerosis and Atherosclerosis. (2 mks)
- Arteriosclerosis – hardening and narrowing of arteries due to deposition of calcium deposits on walls
- Atherosclerosis – narrowing of arteries due to accumulation of cholesterol
- State two functional differences between arteries and veins in mammals. (2 mks)
- Distinguish between active and passive natural acquired immunity. (2 mks)
- Active natural acquired immunity – arises as a response to natural infection by a pathogen
- Passive natural acquired immunity – are passed from mother to foetus through placenta or to newborn through colostrums.
- Name the antigens and antibodies in human blood groups. (2mks)
- Antigens: A and B
- Antibodies a and b
- Explain why people with blood group O are referred to as universal donors while people with blood group AB are universal recipients. (2 mks)
- Blood group O − They do not have antigens, which would react with recipient antibodies
- Blood group AB – They don’t produce antibodies to react with donors antigens
- Outline two functions of each of the following structures of a cell
- plasmalemma. (2 mks)
- Encloses all the cell organelles
- Gives shape to the cell
- protects the cell organelles
- Golgi bodies (2 mks)
- Transport and package the glycoproteins
- Forms the lysosomes
- Centrioles (2 mks)
- Involved in cell division
- Formation of cilia and flagella
- plasmalemma. (2 mks)
- State the functions of the following parts of a light microscope.
- Condenser - Concentrates light onto the stage (1 mk)
- Diaphragm- Regulates the amount of light passing through the condenser (1 mk)
- Course adjustment knob – Brings the image into rough focus by raising and lowering the body tube. (1 mk)
- Fine adjustment knob – Brings the image into sharp focus by raising or lowering the body tube (1 mk)
- Eye piece- Contains a lens which contributes to the magnification of the image of the specimen under view (1 mk)
- Name the compound formed when carbon (II) oxide combines with haemoglobin: (1 mk)
- Caboxyhaemoglobin
- Why would the compound named in (a) above lead to death? (2 mks)
- Caboxyhaemoglobin does not dissociate hence lowers the efficiency of haemoglobin to carry oxygen.
- Name the substance that transports carbon (iv) oxide
- Plasma – Hydrogen carbonate (1 mk)
- Red blood cells - Haemoglobin (1 mk)
- Name the compound formed when carbon (II) oxide combines with haemoglobin: (1 mk)
- Distinguish between a single circulatory system and double circulatory system. (2 mks)
- Single circulation – blood flows through the heart once for a complete circulation while in Double circulation blood flows through the heart twice for a complete circulation
- Name a class whose members have a single circulatory system. (1mk)
- Class Insecta: Class pisces
- Name the openings to the chamber of the hearts of an insect. (1mk)
- Ostia
- Distinguish between a single circulatory system and double circulatory system. (2 mks)
- Outline two functions of lipids. (2mks)
- Oxidized to release energy
- Insulation
- Source of metabolic water
-
- How are leucocytes adapted to their functions. (2mks)
- They are amoeboid which enables them to engulf pathogens and move through the capillary wall
- Name the blood vessel with highest concentration of:
- Glucose – Hepatic portal vein (1mk)
- Carbon (Iv) oxide - Pulmonary artery (1mk)
- How are leucocytes adapted to their functions. (2mks)
- The diagram below represents a transverse section through a plant organ.
- From which plant organ was the section obtained. (1mk)
- Monocotyledon root
- Give two reasons for your answer in (a) above. (2mks)
- Has root hairs
- Xylem and phloem tissues are in groups alternatively in a ring
- Has a pith
- Name the parts labeled M, N, P and Q. (4mks)
- M – Epidermis
- N – Phloem
- P – Xylem
- Q – Root hair (reject root)
- State two functions of part labeled Q. (2mks)
- Absorption of water and mineral salts
- Anchorage
- How is part Q adapted to its function? (3mks)
- Are numerous to increase SA for absorption of water and mineral salts
- Many mitochondria to supply energy for active upstate of mineral salts.
- Thin walled to allow rapid movement of materials
- From which plant organ was the section obtained. (1mk)
- State three factors that cause decrease in rate of transpiration from leaves.(3mks)
- Low temperature
- low light intensity
- high humidity
- high atmospheric pressure
- decrease in soil water
- A student observed a row of 16 epidermal cells in a microscopic field that was 8mm in diameter. Calculate the average length of each cell in micrometers. (2 mks)
Diameter of field of view = 8mm × 1000μm = 8000μm
Length of a cell = Diameter = 8000
Number of cells 16
= 500μm -
- Give the formula of working out the magnification of a microscope. (1 mk)
- Eye piece magnification x objective lens magnification
- Calculate the magnification that is obtained when an object is viewed with a X20 eyepiece and x80 objective. (2 mks)
= X20 × X80
= X1600
- Give the formula of working out the magnification of a microscope. (1 mk)
- Name the organelles that are involved in the following:-
- forms secretory vesicles
- Golgi bodies/apparatus (1 mk)
- Involved in cell division and formation of cilia and flagella. (1 mk)
- centrioles
- formation of ATP
- Mitochondrion (1 mk)
- fixation of carbon (Iv) oxide to form sugars
- Chloroplasts (1 mk)
- detoxification
- smooth Endoplasmic reticulum (1 mk)
- forms secretory vesicles
- Differentiate between Active transport and Osmosis. (2 mks)
- Osmosis – movement of water molecules from a region of high concentrated area to low concentrated are across a semi permeable membrane.
- Active transport – movement of molecules /ions from a region where they are at a lower concentration to a region of higher concentration with help of energy/ATP.
- State three roles of active transport in human body. (3 mks)
- Re-absorption of sugars and salts in kidney tubules
- Absorption of digested food from ileum to the bloodstream
- Pumping of ions by the Na+ /K + across nerve cell membrane.
- State three roles of active transport in human body. (3 mks)
-
- Define gaseous exchange. (1 mk)
- Is the process by which the respiratory gases are passed across the respiratory surface eg O2 (Oxygen and carbon (iv) oxides)
- Explain four adaptive characteristic features of respiratory surfaces. (4 mks)
- Have a thin epithelium for rapid diffusion of gases
- Have large surface area for rapid diffusion of gases
- well vascularised to transport diffusing gases
- Have a moist surface to enhance diffusion.
- Define gaseous exchange. (1 mk)
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Biology Questions and Answers - Form 2 End Term 1 Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students