QUESTIONS.
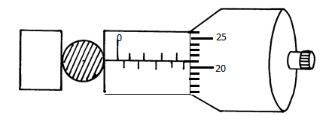
- A spherical ball bearing of mass 0.0024kg is held between the anvil and spindle of a micrometer screw gauge. Use this information and the position of the scale in the figure below to answer the questions (a) and (b) below:
- What is the diameter of the ball bearing? (1 mk)
- Find the density of the ball bearing correct to 3 significant figures (3 mks)
- Explain why it is dangerous for a bus to carry standing passengers. ( 2 mks)
- Differentiate between cohesive and adhesive forces. (2mks)
- Explain the cause of random motion of smoke particles as observed in Brownian motion experiment using a smoke cell. (2mks)
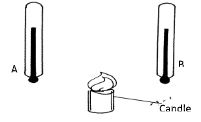
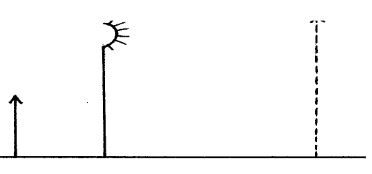
- The Figure 2 shows two identical thermometers.Thermometer A has a blackened bulb while thermometer B has a silvery bulb. A candle is placed equidistant between the two thermometers
State with a reason the observations made after sometime (2 mks) - Give a reason why water is not suitable as a barometric liquid. (1 mk)
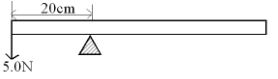
- A uniform metre rule is balanced as shown below.
- Find the weight of the metre rule (3mrks)
- State the difference between a soft magnetic material and a hard magnetic material.(1 mk)
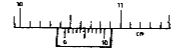
- The Figure shows a scale of part of a vernier calliper.
.
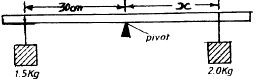
What is the actual reading indicated by the scale if the vernier caliper has a zero of +0.02cm.(2mks) - A uniform plank of wood is pivoted at its centre. A block of wood of mass 2kg is balanced by a mass of 1.5kg placed 30cm from the pivot as shown in the diagram below
.
Calculate the distance X. (3mks) - A highly negative charged rod is gradually brought close to the cap of a positively charged electroscope. It is observed that the leaf collapses initially and the leaf diverges. Explain this observation (2mks)
- State the right hand grip rule.(2maks)
- The figure below shows an object O and its image I formed by a concave mirror.
Using suitable rays, to locate the focal length of the mirror. (3mks) - The figure below shows a uniform rectangular lamina.
Locate and indicate the centre of gravity of lamina. (3mks) -
- Use the information below to answer questions below
-
- In an experiment to determine the density of a liquid, the following readings were made.
- Mass of empty density bottle = 20g
- Mass of bottle filled with water = 70g
- Mass of bottle filled with a liquid = 695g
-
- Find the density of the liquid,given that density of water is 1000kgmˉ³. (4mks)
- Find the mass of the liquid. (2mks)
- Use the information below to answer questions below
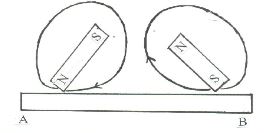
- In an attempt to make a magnet, a student used the double stroke method as shown below.
State the polarities at the ends A and B (2mks)\ - An object is placed 30cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 20cm. Determine
- Size of the image. (3mks)
- Magnification (2mks)
- Name two applications of concave mirrors (2mks)
- A metre rule is balanced by masses 18g and 12g suspended from its ends. Find the position of its pivot. (3mks)
- Explain the function of constriction present in a clinical thermometer. (1mrk)
- Define the term moment of force. (2mrks)
- State the two laws of reflection (4mks)
- Give that the diameter of an oil drop is 0.15cm and the diameter of a circular patch formed by the same drop on water is 35.35cm.Calculate the thickness of the oil molecule. (4mks)
- State two differences between mass and weight.(2mks)
- Name two factors that affect stability of a body(2mrks)
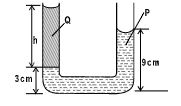
- The figure 2, below, U-tube contains two immiscible liquids P and Q. If the density of Q is 900kg/m³ and that of P is 1200kg / m³, Calculate the height of liquid Q. (3 marks)
- State two defects of a simple cell (2mks)
MARKING SCHEME
- A spherical ball bearing of mass 0.0024kg is held between the anvil and spindle of a micrometer screw gauge. Use this information and the position of the scale in the figure below to answer the questions (a) and (b) below:
- What is the diameter of the ball bearing? (1 mk)
- 4.71mm
- Find the density of the ball bearing correct to 3 significant figures (3 mks)
D = ??
??
= 0.0024
4/3 × 22/7 × (2.3 × 10−3)3
= 47, 091.13 kg??3
= 47100 kg/m3 (3 s.f)
- What is the diameter of the ball bearing? (1 mk)
- Explain why it is dangerous for a bus to carry standing passengers. ( 2 mks)
- The position of CoG will be raised making the bus unstable
- Differentiate between cohesive and adhesive forces. (2mks)
- Cohesive force is the force of attraction between molecules of the same kind
- Adhesive force is the force of attraction between molecules of the differnt kind
- Explain the cause of random motion of smoke particles as observed in Brownian motion experiment using a smoke cell. (2mks)
- Air molecules are in constant random motion they bombard the smoke particles randomly
- The Figure 2 shows two identical thermometers. Thermometer A has a blackened bulb while thermometer B has a silvery bulb. A candle is placed equidistant between the two thermometers
State with a reason the observations made after sometime (2 mks)- Thermometer a will record a high value. Dull surfaces are good absorbers of heat energy
- Give a reason why water is not suitable as a barometric liquid. (1 mk)
- It gives a long measurable column of about 10m
- A uniform metre rule is balanced as shown below.
Find the weight of the metre rule (3mrks)- W= 3.333N
- State the difference between a soft magnetic material and a hard magnetic material.(1mk)
- Soft magnetic materials are materials which are easily magnetized and they don’t retain they magnetism for so long.
- Hard magnetic materials are materials which are not easily magnetized and they retain they magnetism for so long.
- The Figure shows a scale of part of a vernier calliper.
What is theactual reading indicated by the scale if the vernier caliper has a zero of +0.02cm. (2mks)- 10.44 – 0.02 = 10.42cm
- A uniform plank of wood is pivoted at its centre. A block of wood of mass 2 kg is balanced by a mass of 1.5 kg placed 30 cm from the pivot as shown in the diagram below. Neglect the mass of the plank
Calculate the distance X. (3mks)- X = 22.5g
- A highly negative charged rod is gradually brought close to the cap of a positively charged electroscope. It is observed that the leaf collapses initially and the leaf diverges. Explain this observation (2mks)
- The initial collapse and subsequent divergence of the leaves of the electroscope is due to the interplay between the positive and negative charges in the electroscope and the negatively charged rod. The negative rod first repels positive charges towards the leaves, causing them to collapse. Then, the negative rod induces a separation of charge in the leaves, causing them to become positively charged and diverge.
- State the right hand grip rule.(2maks)
- The right hand grip rule states that if a coil carrying a current is grasped in the right hand such that the fingers point in the direction of current in the coil, then the thumb points in the direction of North Pole.
- The figure below shows an object O and its image I formed by a concave mirror.
Using suitable rays, to locate the focal length of the mirror.(3mks) - The figure below shows a uniform rectangular lamina.
Locate and indicate the centre of gravity of lamina. (3mks) - Use the information below to answer questions below
In an experiment to determine the density of a liquid, the following readings were made.- Mass of empty density bottle = 20g
- Mass of bottle filled with water = 70g
- Mass of bottle filled with a liquid = 695g
- Find the density of the liquid, given that density of water is 1000kgmˉ³. (4mks)
- 13.5g/cm3
- Find the mass of the liquid. (2mks)
- 675g
- Find the density of the liquid, given that density of water is 1000kgmˉ³. (4mks)
- In an attempt to make a magnet, a student used the double stroke method as shown below.
State the polarities at the ends A and B (2mks)- A - South Pole
- B - North Pole
- An object is placed 30cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 20cm. Determine
- Position of the image (3mks)
- 60cm
- Magnification (2mks)
- 2
- Name two applications of concave mirrors (2mks)
- Shaving mirrors
- By dentist in examining teeth
- In telescopes for astronomical observations
- Solar concentrators
- Position of the image (3mks)
- A metre rule is balanced by masses 18g and 12g suspended from its ends. Find the position of its pivot. (3mks)
- Explain the function of constriction present in a clinical thermometer. (1mrk)
- Prevent backflow of mercury before the nurse record the temperature
- Define the term moment of force. (2mrks)
- Moment of a force is the product of the force (F) and the perpendicular distance from the line of of the force and the point of support
- State the two laws of reflection (4mks)
- The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal at the point of incidence all lie on the same plane.
- The angle of incidence, i, equals the angle of reflection, r.
- Give that the diameter of an oil drop is 0.15cm and the diameter of a circular patch formed by the same drop on water is 35.35cm.Calculate the thickness of the oil molecule.(4mks)
thickness of oil molecule = (4/3 × diameter of oil drop)
(diameter of oil patch)Substituting the given values, we get:
thickness of oil molecule = 4/3 × 0.15 cm
35.35 cm
= 0.0016 cm
= 1.6 × 10-5 mTherefore, the thickness of the oil molecule is 1.6 × 10-5 m.
- State two differences between mass and weight.(2mks)
Mass Weight 1. Its a quantity of matter on a body 1. It is a pull of gravity on a body. 2. It's measured in kg. 2. It is measured in (N) 3. Same everywhere. 3. Varies from one place to another. 4. Measuresd using a beam balance. 4. Measured using spring balance. 5. Has magnitude only (scalar quantity) 5. Has both magnitude and direction. (vector quantity) - Name two factors that affect stability of a body(2mrks)
- The area of the base
- The position of the centre of gravity
- The figure 2, below, U-tube contains two immiscible liquids P and Q. If the density of Q is 900kg/m³ and that of P is 1200kg / m³, Calculate the height of liquid Q. (3 marks)
h1p1g = h2p2g ii1h × 900 = 0.06 × 1200 ii1
900h = 72
900 900
h = 0.08 - State two defects of a simple cell (2mks)
- Polarisation
- Local action
Download Physics Questions and Answers - Form 2 End Term 1 Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students