QUESTIONS ;
- Define the term species. (2mks)
- State the function of the following organelles. (3mks)
- Lysosomes
- Mitochondria
- Chloroplasts
- Distinguish between diffusion and osmosis. (2mks)
- Describe what happens during the light stage of photosynthesis. (3mks)
- State two ways in which root hairs are adapted to their function. (2mks)
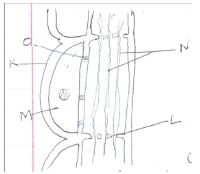
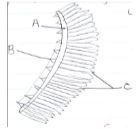
- The diagram below represents a plant tissue.
- Identify the tissue. (2mks)
- Name the structures L and O and the cell labeled K. (3mks)
- State the function of structure labeled N. (1mk)
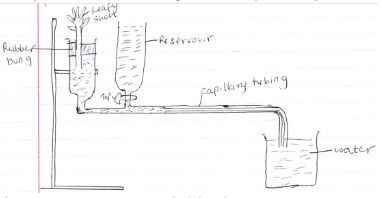
- A setup that was used to investigate a certain process in plants is shown in the diagram below.
- What is this apparatus used for? (1mk)
- Giving reasons state two precautions that should be taken when setting up the experiment. (4mks)
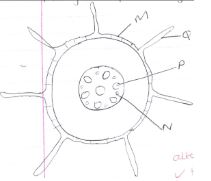
- The diagram below represents a transverse section through a plant organ
- From which plant organ was the section obtained. (1mk)
- Give two reasons for your answer in (a) above. (2mks)
- Name the parts labeled M, N and P. (3mks)
- State two functions of the parts labeled Q. (2mks)
- State two functinal differences between arteries and veins in mammals. (2mks)
-
- A person of blood group O requires a transfusion. Name the blood group of the possible donors. (1mk)
- State the blood group(s) of people who can receive blood from people of all other groups and give the name given to such people. (2mks)
-
- Distinguish between a single circulatory system and a double circulatory system. (2mks)
- Name a class whose members have single circulatory system. (1mk)
- Name the openings to the chamber of the hearts of an insect. (1mk)
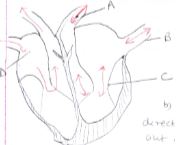
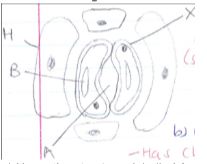
- The diagram below shows a vertical section through a mammalian heart.
- Name the parts labeled A, B, C and D. (4mks)
- Use arrows to show the direction in which blood flows out of the heart. (2mks)
- Account for the difference in the thickness of the walls of the left and right ventricles. (3mks)
- Explain four adaptive characteristics features of respiratory surfaces. (4mks)
- Name three structures through which gaseous exchange takes place in terrestrial plants. (3mks)
-
- Name the structure for gaseous exchange in insects. (1mk)
- The diagram below illustrates the structure of a gill from a bony fish.
- Name the structures labeled A,B, and C and give their functions. (6mks)
- In what way are the structures labeled C adapted for their functions. (3mks)
- Examine the diagram below and answer the questions that follow.
- Name the structures labelled A and B and the cell labeled H. (3mks)
- Give an adaptation of the cell labeled X. (1mk)
MARKING SCHEME
- Define the term species. (2mks)
- Are a group of organisms which can freely interbreed to produce a fertile offspring
- State the function of the following organelles. (3mks)
- Lysosomes - Breakdown of worm out cell organelles or sometimes the whole cell when old and worn out
-Involves in intracellular digestion - Mitochondria - Site of respiration/ ATP or energy production
- Chloroplasts- Site of photosynthesis.
- Lysosomes - Breakdown of worm out cell organelles or sometimes the whole cell when old and worn out
- Distinguish between diffusion and osmosis. (2mks)
- Diffusion is the movement of molecules or ions from a region where they are at a high concentration to a region where they are at a lower concentration.
- Osmosis is the movement of molecules from a region of low concentration thro a semi permiamble membrane
- Describe what happens during the right stage of photosynthesis. (3mks)
- Light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll and used in photolysis of water to split water molecules to form hydrogen ions and oxygen
- Some of the trapped light energy is used to form ATP.
- State two ways in which root hairs are adapted to their function. (2mks)
- Numerous to increase the surface area for absorption of water and mineral salts.
- Have many mitochondria to supply energy for active uptake of mineral salts.
- Are thin walled to allow rapid movement of materials.
- The diagram below represents a plant tissue.
- Identify the tissue. (2mks)
- Phloem tissue
- Name the structures L and O and the cell labeled K. (3mks)
- L - Sieve plate
- O - Plasmodesmata
- K-Companion cell.
- State the function of structure labeled N. (1mk)
- Cytoplasmic filaments along which manufactured food streams.
- Identify the tissue. (2mks)
- A setup that was used to investigate a certain process in plants is shown in the diagram below.
- What is this apparatus used for? (1mk)
- To determine the rate of transpiration.
- Giving reasons state two precautions that should be taken when setting up the experiment. (4mks)
- Cut the shoot under water to avoid blockage of the xylem vessels by air
- Apply petroleum Jelly between the cork/ rubber bung and the glass and between the rubber bung and the shoot to make the apparatus air tight.
- Open the reservoir tap when assembling to remove the air bubbles from the tube.
- Assembles under water to ensure no air bubbles are enclosed.
- What is this apparatus used for? (1mk)
- The diagram below represents a transverse section through a plant organ
- From which plant organ was the section obtained. (1mk)
- Monocotyledonous root
- Give two reasons for your answer in (a) above. (2mks)
- Has root hair
- Xylem and phloem tissues are in groups arranged alternatively in a ring.
- Has a pith
- Name the parts labeled M, N and P. (3mks)
- M - Epidermis
- N-Phloem
- P - Eylem
- State two functions of the parts labeled Q. (2mks)
- Absorption of water and mineral salts
- Anchorage of plant
- From which plant organ was the section obtained. (1mk)
- State two functions differences between arteries and veins in mammals. (2mks)
- Arteries transport blood from the heart to the body tissues while veins transport from body tissues to the heart
- Arteries transport oxygenated blood (other than PA) while veins transport deoxygenated blood other than PV
-
- A person of blood group requires a transfusion. Name the blood group of the possible donors. (1mk)
- 0
- State the blood group(s) of people who can receive blood from people of all other groups and give the name given to such people. (2mks)
- AB, Universal recipients
- A person of blood group requires a transfusion. Name the blood group of the possible donors. (1mk)
-
- Distinguish between a single circulatory system and a double circulatory system. (2mks)
- In single circulation, blood flows through the heart once for a complete circuit while in double circulation blood flows through the heart twice for a complete circuit.
- Name a class whose members have single circulatory system. (1mk)
- Fish / pisces
- Name the openings to the chamber of the hearts of an insect. (1mk)
- ostia
- Distinguish between a single circulatory system and a double circulatory system. (2mks)
- The diagram below shows a vertical section through a mammalian heart.
- Name the parts labeled A, B, C and D. (4mks)
- A -Aorta
- B-Pulmonary vein
- C - Bicuspid valve
- D-Right auricle / Autrium
- Use arrows to show the direction in which blood flows out of the heart. (2mks)
- Account for the difference in the thickness of the walls of the left and right ventricles. (3mks)
- The left ventricles has thicker walls than the right ventricles because it pumps blood a longer distance/ to all parts of the body hence requires to exert more pressure/force
- Name the parts labeled A, B, C and D. (4mks)
- Name three structures through which gaseous exchange takes place in terrestrial plants. (3mks)
- Have thin epithelium for rapid diffusion of gases.
- Have large surface area for rapid diffusion
- Well vascularised to transport the diffusing gases
- Have a moist surface to enhance diffusion.
- Name three structure through which gaseous exchange takes place in terrestrial plant •
- Stomata
- Venticels
- Pheumatophores
-
- Name the structure for gaseous exchange in insects. (1mk)
- Tracheal system/ tracheoles
- The diagram below illustrates the structure of a gill from a bony fish.
- Name the structures labeled A,B, and C and give their functions. (6mks
- A - Gill bar
Function - Holds the gill filament and the gill rakes in position - B-Gill rakers
Function -protects the delicate gill filaments from damage by solid particles - C-Gill filaments
Function - Are the sites for gaseous exchange
- A - Gill bar
- In what way are the structures labeled C adapted for their functions. (3mks)
- Highly folded and very many providing a LSA for gaseous exchange
- Thin epithelical lining thus reducing distance over which gases have to diffuse.
- Richly supplied with blood vessels/ highly vasculated.
- Name the structures labeled A,B, and C and give their functions. (6mks
- Name the structure for gaseous exchange in insects. (1mk)
- Examine the diagram below and answer the questions that follow.
- Name the structures labelled A and B and the cell labeled H. (3mks)
- A- Stoma
- B-Sap vacuole
- C - Epidermal
- Give an adaptation of the cell labeled X. (1mk)
- Has chloroplast
- Their inner wall is thicker and inerastic while the other wall is thinner and elastic.
- Name the structures labelled A and B and the cell labeled H. (3mks)
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Biology Questions and Answers - Form 2 Term 2 Opener Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students