SECTION A.
Answer all the questions in this section.
-
-
- Define the term atmosphere. (2mks)
- State three components suspended in free atmosphere. (3mks)
-
- Apart from the troposphere, name two other main zones of the atmosphere. (2mks)
- Give THREE characteristics of the troposphere. (3mks)
-
-
- Differentiate between primary data and secondary data. (2mks)
- Apart from conducting interview state three other methods of collecting statistical data. (3mks)
-
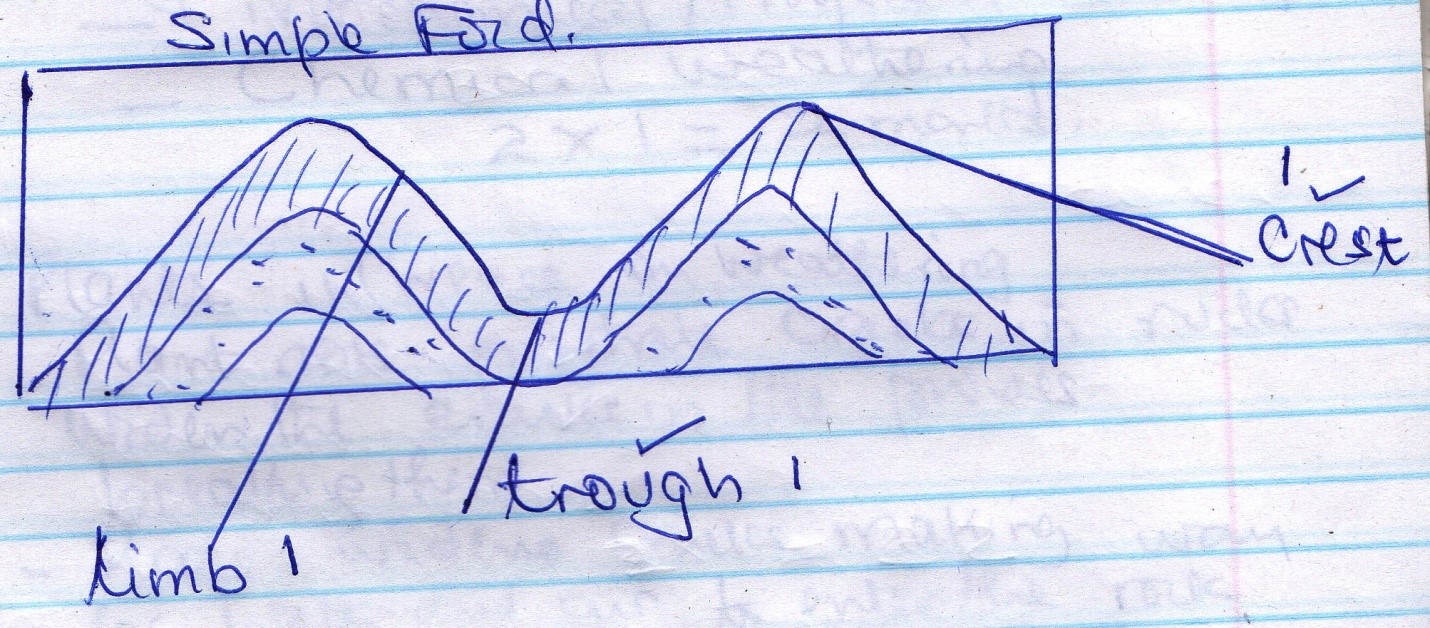
- Draw a simple fold. On it indicate the following
- Crest
- Trough
- Limb
- State two negative effects of folding on human activities. (2mks)
- Draw a simple fold. On it indicate the following
-
- Below is a diagram showing parts associated with faulting. Name the parts U, V, W. (3mks)
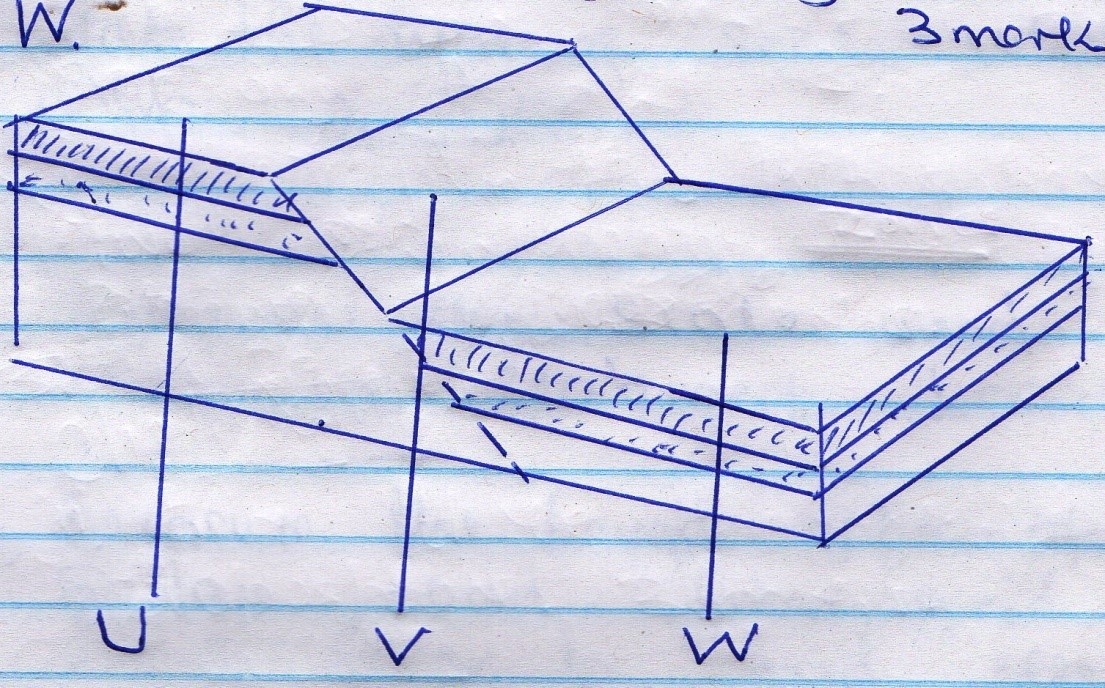
- State two forces which cause faulting. (2mks
- Below is a diagram showing parts associated with faulting. Name the parts U, V, W. (3mks)
-
- Apart from biological weathering, name two other types of weathering. (2mks)
- State three ways in which plants influence weathering. (3mks)
SECTION B
ANSWER QUESTIONS 6 AND ANY OTHER TWO QUESTIONS FROM THIS SECTION
- Study the map of Oyugis 1:50,000 (sheet 130/1) provided and answer the following questions.
-
- State the types of scale used in the map. (2mks)
- Express the scale used in the map in statement. (1mk)
- Measure the length of the loose surface road from grid square 6731 to grid reference 77 0186. Give your answer in kilometers. (2mks)
- Calculate the area covered by Kodera forest. Give your answer in Kilometers square. (2mks)
-
- Identify the methods used to represent relief of the area covered by the map. (2mks)
- Identify two features found in grid square 6737. (2mks)
-
- Apart from forest, identify two other types of vegetations found in the area covered by the map. (3mks)
- State the general direction of flow of river Maugo. (1mk)
- Citing evidence from the map give five economic activities carried out in the area covered by the map. (10 mks)
-
-
-
- Define the term mineral . (2mks)
- Name three fossil fuels. (3mks)
- State threeforms in which minerals occur. (3mks)
-
- State SEVEN factors which influence the exploitation of minerals. (7mks)
- Explain five significance of minerals to the economy of Kenya (10mks)
-
-
-
- Define the term earthquakes. (2mks)
- Name two types of earthquake waves. (2mks)
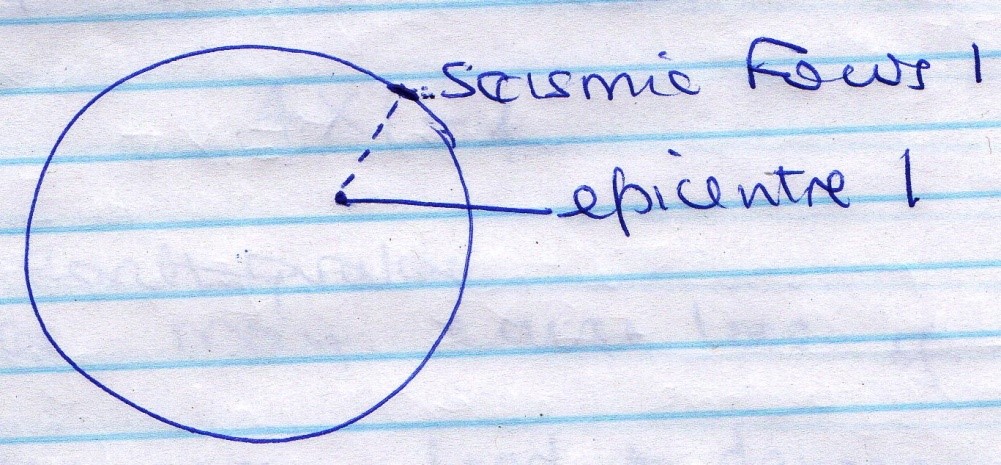
- Draw a simple diagram of the earth. On it indicate
- Seismic focus (1mk)
- Epicenter (1mk)
-
- Name four human activities which cause earthquakes. (4mks)
- State three earthquake zones of the world. (3mks)
- State four effects of earthquake on crustal rocks. (4mks)
- Explain four negative effects of earthquakes. (8mks)
-
-
- Define the following terms.
- Agro forestry. (2mks)
- Afforestation 2mks)
- Re- afforestation (2mks)
- Name three examples of each of the following.
- Hardwood tree species in Kenya forests (3mks)
- Exotic tree species planted in Kenya. (3mks)
- State three factors that favour the growth and development of softwood forests in Canada. (3mks)
- Explain five measures being taken by the government of Kenya to conserve forest. (10mks)
- Define the following terms.
-
-
- Define the term mass wasting. (2mks)
- Differentiate between weathering and mass wasting. (2mks)
-
- State four factors which influence mass wasting. (4mks)
- Apart from soil creep, state three other processes of slow mass wasting. (3mks)
- You intend to carry out a field study on the processes of mass wasting within the local environment.
- State three preparations you would carry out before the field study. (3mks)
- List three methods you would use to record the data. (3mks)
- State five effects of soil creep to the human and physical environment. (5mks)
- Give three reasons why it is important to study mass wasting through field study. (3mks)
-
MARKING SCHEME
-
-
- Define the term atmosphere,
- This is the mixture of gases, solid particles and liquid droplets suspended above the earth’s surface and held to it by gravitational force. 1 x 2 = 2
- Three components suspended in free atmosphere
- Smoke particles
- Salt particles
- Dust particles
- Water droplets 3 x 1 = 3
- Define the term atmosphere,
-
- Main layers of the atmosphere zones of the atmosphere
- Stratosphere
- Mesosphere
- Thermosphere 2 x 1 = 2
- Characteristics of the troposphere.
- It is the lowest layer above the earth’s surface
- It contains 75% of the total gases in the atmosphere.
- It has 90% of the water vapour
- Temperature decreases with increase in altitude
- Pressure decreases upwards
- Wind speed increases with increase of altitude. 3 x 1 = 3
- Main layers of the atmosphere zones of the atmosphere
-
-
-
- Primary data are facts and figures collected directly from the field while secondary data is stored information. 1 x 2 = 2
- Methods of collecting statistical data apart from interview
- Observation
- Administering questionnaire
- Taking measurements
- Carrying out-experiments
- Content analysis 3 x 1 = 3
-
-
- Simple Fold

- Negative effects of folding
- Fold mountains are a barrier to transport and communication
- Folding may bury valuable minerals deep making mining expensive.
- Folding cause a shadow effect on the leeward side. 2 x 1 – 3
- Simple Fold
-
- U – Upthrow 1
V –Fault plane 1
W – Down throw 1 - Compressional Force
Tensional Force
Tear Force 2 x 1 = 2
- U – Upthrow 1
-
- Types of weathering apart from biological
- Mechanical/Physical weathering
- Chemical weathering 2 x 1 = 2.
- Plants influence on weathering
- Plants roots penetrate cracks in rocks widen the cracks in the process breaking them.
- Rooks widen cracks to enter the rock them aiding chemical weathering.
- Plants roots absorb minerals from rocks and make them decay easily.
- Some plants growing on rocks keep the surface moist hence encouraging chemical weathering
- Some plants during decay produce humic acids which react with rode minerals in the process encouraging chemical weathering. 3 x 1 = 3
- Types of weathering apart from biological
Mapwork
-
-
-
- Types scale used on the map
- Representative fraction/Ratio
- Linear 2 x 1 = 2
- One centimeter represents ½ kilometer 1 x 1 = 1
- 17km 1 x 2 = 2mks
-
- Number of full squares 0
- Number of half squares = 15 ÷ 2 = 7.5
- Area= 7.5 km2 1 x 2 = 2
-
-
- Contour lines
Trigonometrical station 2 x 1 = 2 - Features in grid square 6737
- Dam
- Footpath/track
- Settlements 2 x 1 = 2mks
- Contour lines
-
- Apart from forest
– Scrub vegetation
- Scattered trees
-Woodland vegetation 3 x 1 = 3mks - General directions of River Mango is South East to North West 1 x 1 = 1mk
- Apart from forest
- Economic activities
- There is transport evidence roads e.g Kisii – Kehancha
- There is maize growing evidence flour mill grid square 9040.
- There is brick-making evidence brick making factory in grid square 8843.
- There is trade evidence market
- There is livestock keeping evidence veterinary office grid square 7533.
NB: Economic activity must be tied to evidence. 5 x 2 = 10mks
-
-
-
- Meaning of mineral
- This is naturally occurring inorganic substance on or below the earth surface 1 x 2 = 2mks - Fossil fuels
- Coal
- Petroleum
- Natural gas 3 x 1 = 3mks
- Forms in which minerals occur
- Weathering products
- Alluvial deposits
- Veins and lodes
- Seams 3 x 1 = 3mks
- Meaning of mineral
-
- Factors which influence exploitation of minerals.
- Mode of occurrence of the mineral
- Economic value of the mineral
- Size of the mineral deposit
- Quality of the Ore
- Transport cost
- Availability of labour
- Methods of extraction
- Government policy
- Technological advancement
- Availability of market for the mineral. 7 x 1 = 7mks
- Significance of minerals to economy of Kenya
- Mining has created employment enabling Kenyans to earn.
- Some minerals are exported earning the Country foreign exchange
- Minerals have led to growth of some urban centres e.g. Magadi
- Money earned from minerals is used infrastructure development.
- Money that have been used in importing some raw materials is saved.
- Minerals have uplifting living standards for those employed. 5 x 2 = 10mks
- Factors which influence exploitation of minerals.
-
-
-
- Meaning of earthquake.
- This is a sudden earth movement which causes vibrations within the crust. 1 x 2 = 2
- Types of earthquake waves
- Primary waves
- Secondary waves
- Longitudinal waves 2 x 1 2
-
- Meaning of earthquake.
-
- Human activities which cause earthquakes.
- Explosives used in mining
- Moving locomotives
- Testing of nuclear bombs underground.
- Construction of large water reservoirs 4 x 1 = 4mks
- Earthquake zones
- The circum – pacific belt
- The Mediterranean belt
- The Rift valley
- Boundaries of tectonic plates
- Himalayas belt 3 x 1 = 3mks
- Effect of earthquakes on crustal rocks
- Earthquakes cause crustal rocks to fracture/crack/break.
- Earthquakes make crustal rocks to more horizontally, vertically or past each other
- Earthquakes cause crustal rocks to band upwards or downwards.
- Earthquakes cause the uplift on canaling crystal rocks 4 x 1 = 4
- Human activities which cause earthquakes.
- Effects of earthquakes
- Earthquakes may cause loss of lives.
- Earthquakes may lead to damage/destruction of property
- Earthquakes may lead to tsunamis leading to drowning of wasted land
- Earthquakes can lead to disruption of transport and communication line. 4 x 2 = 8mks
-
-
-
- Define
Agro-forestry- This is the farming on trees in the same field with crops 1 x 2 = 2
- Afforestation
- This is the planting of trees where forests did not exist 1 x 2 = 2
- Re-afforestation
- This is the planting of trees to create forest where the vegetation existed but destroyed. 1 x 2 = 2
- Define
- Examples of
- Hardwood
-Meru Oak
-Teak
-Mvule 3 x 1 = 3 - Exotic softwood
- Cyprus
- Pine
- Eucalyptus 3 x 1 = 3
- Hardwood
- Softwood in Canada.
Factors favouring- Favourable climate
- Sparse population
- Availability of different tree spices
- Availability of market for softwood 5 x 2 = 10mks
-
- Mass wasting
- The movements of weathered materials down a slope under the influence of gravity.1 x 2 = 2mk
- Mass wasting is the movement of weathered material down slope by gravity while weathering is the breakdown of rocks in situ. 1 x 2 = 2mks
- Mass wasting
-
- Factors which influence mass wasting.
- Angle of slope
- Human activities
- Climate
- Nature of material
- Tectonic movements 4 x 1 = 4mks - Processes of slow mass wasting other than soil creep
-Rock creep
-Talus creep
-Solifluction
- Factors which influence mass wasting.
-
- – Seek for permission
- Carry re-visits
-Do research on the topic 3 x 1 = 3mks - -photographing -Tape recording
- Sketching -Taking notes 3 x 1 = 3mks - Effects of soil creep
-Walls bend
-Tree trunks bend
-Soil material collects at the base of slope
-There is slope retreat
-Displacement of soil part holes upper parts leaving it bare
-Accumulation of soil on roads which interferes with transport. 5 x 1 = 5mks - Importance of studying mass wasting through field study
-Removes class monotony
-Makes geography real
-A learner is able to use skills learnt in class. 3 x 1 = 3mks)
- – Seek for permission
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download GEOGRAPHY - FORM 3 END TERM 1 EXAMS 2020.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

