Geography Paper 1 Form 3 End Term 2 Exams 2021 with Marking Schemes
SECTION A:
Answer all questions in this section
-
- Give two components of the solar system. (2mks)
- State three effects of the movement of the earth around the sun. (3mks)
-
- How does a land breeze occur? (2mks)
- Name three ocean currents found on the coasts of West Africa. (3mks)
- The diagram below represents a barchans, use it to answer question (a).
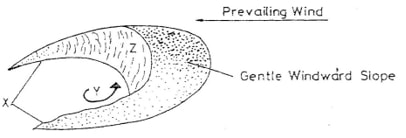
-
- Name the feature marked X. (1mk)
- The air current marked Y. (1mk)
- The slope marked Z. (1mk)
- State two ways in which wind transports its loads. (2mks)
-
- The diagram below shows a composite volcano.
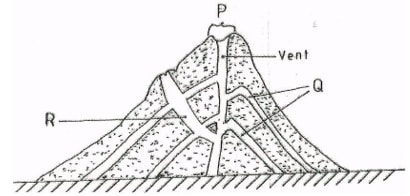
- Name the features marked P, Q, R. (3mks)
- Give two ways in which vulcanicity influences human activities. (2mks)
-
- What is the difference between ice sheet and ice berg? (2mks)
- Name three types of glacier moraine. (3mks)
SECTION B:
Answer question 6 and any other TWO questions from this section.
- Study the map of Oyugis 1:50,000 (sheet 130/1) provided and answer the following questions.
-
- What is the four figure reference of Kokungu dam? (2mks)
- What is magnetic variation of the map? (1mk)
- Calculate the area covered by Kodera forest. Give your answer in square kilometer. (2mks)
- Draw a square 10cm by 10cm to represent the area enclosed by Easting 84 and 94 and Northing 28 and 38. (1mk)
On the square, mark the name;- Forest (1mk)
- Swamp. (1mk)
- District Boundary. (1mk)
- Range. (1mk)
- Describe the relief of the area covered by the map. (6mks)
- Identify three social service of Kamangambo trading centre. (3mks)
- Citing evidence from the map, explain three factors that favour farming. (6mks)
-
-
-
- Apart from the Rift valley, name other relief feature formed as a result of faulting. (3mks)
- With the aid of a well labeled diagram, describe how Rift Valley may have been formed by tensional forces. (8mks)
- Explain three ways in which faulting influences drainage system. (6mks)
- Explain four ways in which features resulting from faulting are of significance to the economy of Kenya. (8mks)
-
-
- What is natural vegetation? (2mks)
- Name the temperate grassland found in the following countries.
- Canada. (1mk)
- Russia (1mk
- Australia. (1mk)
- Explain how precipitation influences distribution of vegetation in an area. (4mks)
- Describe the characteristics of the Savannah vegetation region. (6mks)
- Give two reasons why Tundra region has scanty vegetation. (2mks)
- You are planning to carry out field study in a forest within your district.
- Give four reasons why it is important to seek permission. (4mks)
- Identify four challenges you are likely to encounter during the field study. (4mks)
-
-
- What is underground water? (2mks)
- Explain how the following factors influence the presence of underground water.
- Amount of rainfall. (2mks)
- Vegetation cover. (2mks)
- Slope gradient. (2mks)
-
- What is an artesian basin? (2mks)
- State three conditions leading to the formation of artesian basin. (3mks)
-
- Identify three factors which influence the formation of Karst features. (3mks)
- State four significance of Karst regions. (4mks)
- Your class is planning to carry out field study in a Karst landscape.
- Give two reasons why it is important to seek permission from the school authorities. (2mks)
- Identify three challenges that you are likely to encounter during field study. (3mks)
-
-
- What is a glacier? (2mks)
- Give two reasons why there are no ice sheets in East Africa. (2mks)
- Describe the formation of the following glacial features.
- Hanging valley. (6mks)
- Arête. (6mks)
- Name three erosional features found in glaciated lowland areas. (3mks)
- Explain three positive effects of glaciations in lowland areas. (6mks)

Marking Scheme
SECTION A: (Answer all questions in this section)
-
- Give two components of the solar system. (2mks)
- the sun
- the planets
- Asteroids.
- Meteors.
- Comets. - State three effects of the movement of the earth around the sun. (3mks)
- Change the position of the midday sub at different times of the year.
- Varying length of day and night.
- Causes the four seasons.
- Causes the lunar eclipse.
- Give two components of the solar system. (2mks)
-
- How does a land breeze occur? (2mks)
- This is the movement of the cool air from the land to the sea. - Name three ocean currents found on the coasts of West Africa. (3mks)
- Benguela currents
- Guinea currents
- Cannary currents
- How does a land breeze occur? (2mks)
- The diagram below represents a barchans, use it to answer question (a).
-
- Name the feature marked X. (1mk)
- Horns - The air current marked Y. (1mk)
- Eddy current - The slope marked Z. (1mk)
- The steep concave leeward slopes. - State two ways in which wind transports its loads. (2mks)
- Suspension
- Saltation
- Surface creep
- Name the feature marked X. (1mk)
-
- The diagram below shows a composite volcano.
- Name the features marked P, Q, R. (3mks)
- P – Crater
- Q – Lava layers
- R – Dyke - Give two ways in which vulcanicity influences human activities. (2mks)
- The lower slope are suitable for agricultural activities.
- Scenic beauty, the mountains attracts tourists.
- Expose minerals which are mined.
- Name the features marked P, Q, R. (3mks)
-
- What is the difference between ice sheet and ice berg? (2mks)
- An ice sheet is a large continuous mass of ice covering a vast area of land while an iceberg is a large mass of ice a floating in a large water bodies. - Name three types of glacier moraine. (3mks)
- Laterial moraine
- Medial moraine
- Terminal moraine
- Ground moraine.
- What is the difference between ice sheet and ice berg? (2mks)
SECTION B:
Answer question 6 and any other TWO questions from this section.
- Study the map of Oyugis 1:50,000 (sheet 130/1) provided and answer the following questions.
-
- What is the four figure reference of Kokungu dam? (2mks)
- 7134 - What is magnetic variation of the map? (1mk)
- Oo52’ - Calculate the area covered by Kodera forest. Give your answer in square kilometer. (2mks)
- 14 half square = 14/2 = 7.0km ± 1 km2
- What is the four figure reference of Kokungu dam? (2mks)
- Draw a square 10cm by 10cm to represent the area enclosed by Easting 84 and 94 and Northing 28 and 38. (1mk)
On the square, mark the name;- Forest (1mk)
- Swamp. (1mk)
- District Boundary. (1mk)
- Range. (1mk
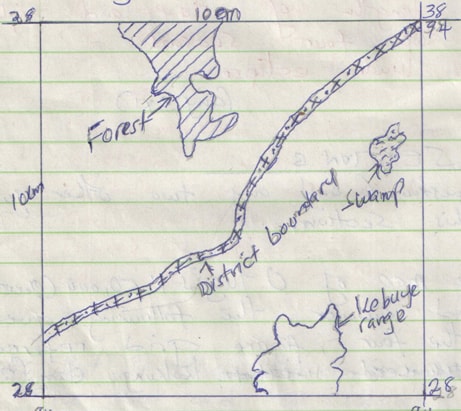
- Describe the relief of the area covered by the map. (6mks)
- The highest point is approximately 6025 feet (6001-6049), while the lowest point is slightly 3750 feet.
- There are many hills in the area.
- There is a pass between Nyatworo and Nyandiere hills.
- The eastern part has many river valleys.
- The south west region is undulating due to widely spaced contours.
- The south eastern part is highly descended due to many river valleys. - Identify three social service of Kamangambo trading centre. (3mks)
- Educational services
- Health services.
- Religious services - Citing evidence from the map, explain three factors that favour farming. (6mks)
- High rainfall evidenced by many rivers offer suitable conditions for growing crops.
- Labour evidenced by dense settlements offering labour during farming of crops.
- Transport evidenced by many roads that facilitate transportation of the crops from the farm to the factory for processing.
-
-
-
- Apart from the Rift valley, name other relief feature formed as a result of faulting. (3mks)
- Fault scarp
- Block/ horst mountain.
- Tilt block. - With the aid of a well labeled diagram, describe how Rift Valley may have been formed by tensional forces. (8mks)

- layers of the rocks are subjected to tensional forces when there is some instability within the earth’s crust.
- Line of weakness occur leading to development of adjacent normal faults.
- The central block eventually sinks as the side blocks are pulled apart.
- Apart from the Rift valley, name other relief feature formed as a result of faulting. (3mks)
- Explain three ways in which faulting influences drainage system. (6mks
- Uplifting landscape which may cause a change of flow of a river.
- Vertical faulting across a river may cause change of the base level resulting in the formation of waterfalls.
- Some rivers may disappear into the ground through fault guided drainage patterns.
- Some rivers may disappear into the ground through a fault forming underground stream.
- Uplift of some rivers may cause river rejuvenation. - Explain four ways in which features resulting from faulting are of significance to the economy of Kenya. (8mks)
- Highlands formed through faulting are sources of rivers which provide water for agriculture, domestic and industrial use.
- Faulting has led to exposure of minerals that are mined to generate income.
- Faulting results to the formation of Lakes that are important fishing grounds.
- Highlands formed through faulting influence formation of relief rainfall on the windward sides which favour farming.
- Faulting has resulted to formation of deep faults which are passage of stream jets that are harnessed to generate electricity.
-
-
- What is natural vegetation? (2mks)
- Natural vegetation is a plant cover that grows wildly on the earth surface without interference from man and his animals. - Name the temperate grassland found in the following countries.
- Canada. (1mk) - Prairies
- Russia (1mk – Steppers
- Australia. (1mk) – Downs
- Explain how precipitation influences distribution of vegetation in an area. (4mks)
- Moisture is an essential commodity for survival of plants.
- It is the various forms of precipitation which provide moisture to plants through the soil.
- The amount of rainfall a region receives determines the type of plants that would grow.
- Heavy rainfall in a region of high temperature would support vegetation grown. - Describe the characteristics of the Savannah vegetation region. (6mks)
- Savannah vegetation is a mixture of trees and grass.
- The dominant type of vegetation is grass.
- Most of the trees are umbrella shaped.
- Most trees are acacia.
- Most of the trees are deciduous.
- Some trees have long roots.
- Most seeds are dominant during the dry season. - Give two reasons why Tundra region has scanty vegetation. (2mks)
- Temperatures are too low to support vegetation.
- The surface is mainly bare rock.
- Water is always in frozen state. - You are planning to carry out field study in a forest within your district.
- Give four reasons why it is important to seek permission. (4mks)
- Is an official requirement.
- Enable the administration arrange for transport.
- Enable the administration to take care of the disruption of school programme.
- Enable the administration to provide entry fee if required. - Identify four challenges you are likely to encounter during the field study. (4mks)
- Attack by wild animals.
- Adverse weather conditions.
- Thick and thorny vegetation.
- Tiredness due to walking long distance.
- Inadequate time for data collection.
- Getting lost or loss of direction to follow.
- Give four reasons why it is important to seek permission. (4mks)
- What is natural vegetation? (2mks)
-
-
- What is underground water? (2mks)
- Body of water found in the pore spaces of a permeable rock layer underground and above the impermeable rock layers. - Explain how the following factors influence the presence of underground water.
- Amount of rainfall. (2mks)
- High rainfall over a long period of time has led to more infiltration leading to a lot of underground water. - Vegetation cover. (2mks)
- Plenty of vegetation cover on the ground reduce surface runoff allowing infiltration causing a lot of underground water. - Slope gradient. (2mks)
- Gentle gradient allow more water infiltration into the ground leading to availability of more underground water.
- Amount of rainfall. (2mks)
- What is underground water? (2mks)
-
- What is an artesian basin? (2mks)
- This is a saucer-shaped shallow depression consisting of a layer of permeable rock layer lying beneath two impermeable layers. - State three conditions leading to the formation of artesian basin. (3mks)
- The Aquifer should be sandwiched between two impermeable rock layers to hold water.
- The Aquifer should out crop in a region of high rainfall.
- The permeable rock must form a syncline for water to have enough pressure.
- What is an artesian basin? (2mks)
-
- Identify three factors which influence the formation of Karst features. (3mks)
- Presence of thick limestone to allow solubility of rain water.
- Hard and well jointed limestone to allow water to percolate.
- Hot and humid climate for chemical weathering.
- Deep water table to form underground Karst features. - State four significance of Karst regions. (4mks)
- Karst region form unique scenery attracting tourist.
- Limestone rocks are raw materials for cement manufacturing industry.
- Karst region have their soil suitable for grazing sheep.
- Limestone rocks are used in building construction industry.
- Identify three factors which influence the formation of Karst features. (3mks)
- Your class is planning to carry out field study in a Karst landscape.
- Give two reasons why it is important to seek permission from the school authorities. (2mks)
- Form official requirement.
- To enable administration arrange for transport.
- To enable administration provide essential tools. - Identify three challenges that you are likely to encounter during field study. (3mks)
- Attack by wild animals such as snake.
- Harsh weather conditions high temperature.
- Rugged terrain makes movement difficult.
- Injuries from sharp rocks.
- Give two reasons why it is important to seek permission from the school authorities. (2mks)
-
-
- What is a glacier? (2mks)
- A glacier is a mass of ice moving outward from an area of accumulation. - Give two reasons why there are no ice sheets in East Africa. (2mks)
- East Africa experiences high temperature.
- Most parts of East Africa have low altitude.
- East Africa is located at low latitude. - Describe the formation of the following glacial features
- Hanging valley. (6mks)
- There exist river valleys, both the main and tributary valley.
- A glacier occupies former river valley.
- Both the main and tributary valley are occupied by the glacier.
- There will be more erosion on the main valley compared to tributary valley.
- The main valley is therefore deepened and widened faster than tributary valley.
- The suspended tributary valley forms a hanging valley. - Arête. (6mks)
- Two adjacent cracks or hollows exist on a mountain side.
- The two hollows or cracks are filled with ice.
- The ice erodes the sides through plucking and deepens the hollow through abrasion.
- Through erosion the back walls of the hollow slowly recedes and eventually the hollows are separated by a knife edged ridge.
- The ridge is called an arête.
- Hanging valley. (6mks)
- Name three erosional features found in glaciated lowland areas. (3mks)
- Crag and tail
- Ice eroded plain.
- Roche montonne - Explain three positive effects of glaciations in lowland areas. (6mks)
- Glacial till provide fertile soil suitable for farming.
- Outwash plains comprises of sand and gravel used as building materials.
- Glacial lakes in low lakes can be exploited for various economic vs such as fishing.
- Glaciations forms features such as drumlins and askers which are tourist attraction.
- What is a glacier? (2mks)
Download Geography Paper 1 Form 3 Questions and Answers - End Term 2 Exams 2021.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

