Agriculture Paper 1 Form 3 End Term 1 Exams 2021 with Marking Schemes
INSTRUCTIONS
- This paper contains three sections A, B and C.
- Answer all questions in Section A and B and any two from section C.
- All answers must be written in the spaces provided after the questions
SECTION A (30 MKS)
- Name any two physical characteristics used to classify soil. (2mks)
- Name four types of livestock farming. (2mks)
- State four human factors that affect agriculture. (2mks)
- What is the importance of seed dressing in crop production. (1mk)
- State two conditions that may lead to sub-division of land. (2mks)
- Farmer growing maize on 10 hectares is to dress it with sulphate of ammonia (20% N) at the rate of 120kg of S.A for hectare. AT the local market, S.A is available in 50Kg bag selling at 1500/- per bag. Calculate the amount of S.A the farmer needs to top dress his crop of maize. (3mks)
- Define the following terms. (11/2mks)
- Nursery bed
- Seedling bed
- Seedbed
- State two examples of nitrogenous fertilizers. (2mks)
- State three disadvantages of broadcasting seeds. (11/2mks)
- State four deficiency symptoms of nitrogenous fertilizers. (2mks)
- Give four conditions of the land which may make it necessary to carry out reclamation practices. (2mks)
- State two mechanical methods of separating soil particles according to size during soil analysis. (2mks)
- Give four pieces of information contained in a land title deed. (2mks)
- State four effects of post election violence in 2008 to agriculture production. (2mks)
- State two reasons why shifting cultivation has become unpopular in Kenya. (1mk)
SECTION B
- The diagram labeled E and F illustrate some soil structure. Study them carefully and answer the questions that follow.
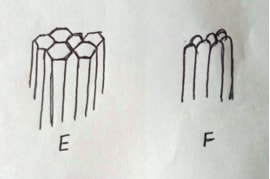
- Identify the soil structure E and F. (1mk)
- List down two field practices which can destroys the structures shown above. (2mks)
- Give two characteristic of a fertile soil. (2mks)
- The diagram below illustrate a compose heap. Study it carefully.
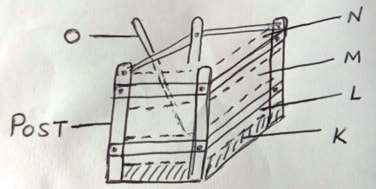
- Name the parts labeled K – N (2mks)
K............................
L............................
M............................
N............................ - State one use of each of the parts labeled K, M, N and O (2mks)
K............................
M............................
N............................
O............................ - List four reasons why compost manure is not popularly used in the farm. (2mks)
- Name the parts labeled K – N (2mks)
- Study the diagrams below.
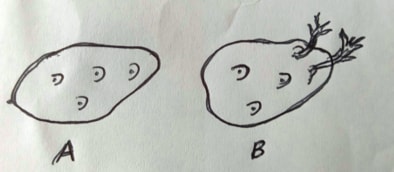
- Name the process used to test Irish potatoes in readiness for planting. (1mk)
- Which of the two is suitable for planting? (1mk)
- Give a reason for your answer in (b) above. (1mk)
- Give two reasons why maize need to be earthed. (2mks)
-
- State the two types of the multiple stem pruning system in coffee. (2mks)
- Name any two carrot varieties planted by farmers. (2mks)
SECTION C (40MKS)
-
- Discuss the factors that should be put into consideration while choosing suitable implements for primary cultivation. (8mks)
- Describe reasons for drainage as a method of land reclamation in crop production. (10mks)
- State two factors that influence mass wasting (2mks)
-
- Discuss ways in which nitrogen is removed from the atmosphere. (8mks)
- Discuss factors to consider in choosing seed rates (10mks)
- State two main methods of planting (2mks)
-
- Mention the procedure involved in harvesting fish. (5mks)
- Discuss four types of soil erosion by water. (8mks)
- Mention various biological measures employed in soil and water conservation. (7mks)
Marking Scheme
SECTION A (30MKS)
- Name any two physical characteristics used to classify soil. (2mks)
- Colour
- Texture
- Structure
- Name four types of livestock farming. (2mks)
- Pastoralism
- Fish farming
- Bee keeping
- Poutry keeping
- State four human factors that affect agriculture. (2mks)
- Level of education and technology
- Human health
- Economy
- Government policy
- Transport and communication
- Cultural practices and religious beliefs
- Market forces.
- What is the importance of seed dressing in crop production. (1mk)
- Prevents attack by pests/diseases
- State two conditions that may lead to sub-division of land. (2mks)
- Purchase/sale of land
- Land sharing
- Government allocation
- Inheritance of land
- Farmer growing maize on 10 hectares is to dress it with sulphate of ammonia (20% N) at the rate. of 120kg of S.A for hectare. AT the local market, S.A is available in 50Kg bag selling at 1500/- per bag. Calculate the amount of S.A the farmer needs to top dress his crop of maize. (3mks)
- 1 hac = 120 kg S.A
10 hac = ?
120 × 10
= 1200kg - 100 kg S.A = 20kg N
1200kg = ?
1200 × 20
100
= 240kg N - 1 bag = 50kg
= 1200kg
1200 × 1
50
= 24 bags
1 bag = 1500/-
24 bags = ?
24 × 1500
1
=36000/=
- 1 hac = 120 kg S.A
- Define the following terms. (11/2mks)
- Nursery bed
- A special seedbed prepared for raising seedlings before transplanting.
- Seedling bed
- A nursery used to raise seedlings after removal from nursery due to overcrowding (after picking out)
- Seedbed
- A piece of land prepared to receive planting materials.
- Nursery bed
- State two examples of nitrogenous fertilizers. (2mks)
- Sulphate of ammonia
- Ammonium sulphate Nitrate
- Calcium Ammonium Nitrate
- Urea (rej symbols)
- State three disadvantages of broadcasting seeds. (11/2mks)
- Uses more seeds
- Seed not spread evenl
- Overcrowding of plants
- Low yields due to competition
- State four deficiency symptoms of nitrogenous fertilizers. (2mks)
- Chlories
- Stunted growth
- Production of purple colour (anthocyanin)
- Premature fall of leaves
- Give four conditions of the land which may make it necessary to carry out reclamation practices. (2mks)
- Swampy/water logged area
- Stony ground
- Steep areas
- Aridity/dryness
- Eroded/bare land
- Tsetse fly infected areas
- Bushy land
- State two mechanical methods of separating soil particles according to size during soil analysis. (2mks)
- Sedimentation
- Sieve method
- Give four pieces of information contained in a land title deed. (2mks)
- Parcel number
- Size of land
- Name/identify of owner
- Date of registration
- Seal
- Conditions if any
- State four effects of post-election violence in 2008 to agriculture production. (2mks)
- Withdrawal of labour
- Insecurity
- Lack of capital to purchase input
- Lack of motivation
- Death of labourers
- Escalation of inputs
- Lack of market
- State two reasons why shifting cultivation has become unpopular in Kenya. (1mk)
- High population pressure
- Change in land ownership
SECTION B
- The diagram labeled E and F illustrate some soil structure. Study them carefully and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the soil structure E and F. (1mk)
- E - prismatic
- F - columnar
- List down two field practices which can destroys the structures shown above. (2mks)
- Filed burning
- Flooding
- Field rolling
- Over cultivation
- Give two characteristic of a fertile soil. (2mks)
- Deep
- Good water holding capacity
- Good pH
- Good drainage/aeration
- Enough materials
- Free from pests and diseases
- Identify the soil structure E and F. (1mk)
- The diagram below illustrate a compose heap. Study it carefully.
- Name the parts labeled K – N (2mks)
K - maize stalks
L - green leaves
M - well decomposed manure
N- Soil - State one use of each of the parts labeled K, M, N and O (2mks)
K – forms foundation of heap
M – Supply nutrients
N- Introduces micro-organism
O- Detect temp of heap - List four reasons why compost manure is not popularly used in the farm. (2mks)
- Lack of technical knowledge
- Scarcity of materials
- Labourious
- Bulky to transport
- Takes time to prepare
- Name the parts labeled K – N (2mks)
- Study the diagrams below.
- Name the process used to test Irish potatoes in readiness for planting. (1mk)
- Chitting/sprouting
- Which of the two is suitable for planting? (1mk)
- B
- Give a reason for your answer in (b) above. (1mk)
- Has produced short healthy sprouts
- Give two reasons why maize need to be earthed. (2mks)
- Provide support to prevent lodging
- Improves drainage
- Name the process used to test Irish potatoes in readiness for planting. (1mk)
-
- State the two types of the multiple stem pruning system in coffee. (2mks)
- Capped multiple stem
- Non-capped multiple stem
- Name any two carrot varieties planted by farmers. (2mks)
- Chartenary
- Nantes
- Oxhast
- State the two types of the multiple stem pruning system in coffee. (2mks)
SECTION C (40MKS)
-
- Discuss the factors that should be put into consideration while choosing suitable implements for primary cultivation. (8mks)
- The condition of the land. land with stones and stumps require a disc plough. a land with couch grass
- type of tilth required: fine tilth require different types of implements
- Depth of cultivation heavy implement is necessary when deep cultivation is needed. light implements are needed in shallow cultivation.
- Capital availability: with enough money, a suitable implement can be bought
- Source of the power on the form includes animals, tractor hand
- Describe reasons for drainage as a method of land reclamation in crop production. (10mks)
- to increase soil aeration
- To increase soil volume
- To raise soil temperature relevant explanation to be given 2x5
- To increase micro-bial activities
- To reduce soil erosion
- To remove toxic substances
- State two factors that influence mass wasting (2mks)
- slope of the land
- Nature of materials
- Climate
- Vegetation cover
- Human activities
- Forces within earth’s crust
- Discuss the factors that should be put into consideration while choosing suitable implements for primary cultivation. (8mks)
-
- Discuss ways in which nitrogen is removed from the atmosphere. (8mks)
- nitrogen fixation by lightening: lighting helps to combine nitrogen with oxygen to form nitric oxide. Further reaction’s occur to form nitrates
- Fixation by nitrogen fixing bacteria. Involves symbiotic and non-symbiotic fixation where bacteria convert free nitrogen into nitrates.
- Nitrification: involves conversion of ammonium compounds are converted into nitrites and nitrates
- Discuss factors to consider in choosing seed rates (10mks)
- Seed purity: pure seeds have a high germination percentage hence less required
- Germination percentage. Less seed is used when germination percentage is higher
- Spacing: closer spacing require more seeds than wider spacing
- Number of seeds per whole: more seeds per hole increase the seed rate
- Purpose of the crop. Crop for silage making is spaced closely than that meant for grain production. (2 x5)
- State two main methods of planting (2mks)
- row planting
- Broad casting
- Discuss ways in which nitrogen is removed from the atmosphere. (8mks)
-
- Mention the procedure involved in harvesting fish. (5mks)
- inflow of water from the river is stopped by closing the channel
- Normal cropping is done to remove all large fish
- The outlet is then opened to allow water to flow out
- A scoop net is used to catch the fingerlings which are kept in a holding pond.
- Water is completely drained for the pond to dry
- Discuss four types of soil erosion by water. (8mks)
- splash/raindrop erosion. Involves soil splash from the impact of water drops directly on soil particles. The kinetic energy in the rain drop detaches and transfer soil particles.
- Sheet erosion: involves uniform removal of soil in the layer from flat or gently sloping land.
- Rill erosion. Removal of soil from small but well defined channels (Streamlets). It’s common on slope with little vegetation
- Gulley erosion: An advanced stage of rill erosion. Channels get progressively deeper and wider until they become gullies. (2 x 4)
- Mention various biological measures employed in soil and water conservation. (7mks)
- grass/filter strips
- cover cropping
- contour farming
- mulching
- cross systems
- slip cropping
- grassed/vegetated waterways
- afforestation/reforestation
- agroforestry
- Mention the procedure involved in harvesting fish. (5mks)
Download Agriculture Paper 1 Form 3 Questions and Answers - End Term 2 Exams 2021.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

