QUESTIONS
- During an ecological study, form three students encountered three plant species: X, Y and Z. The students recorded the main features of each plant species, as shown below
X: - Leaves with broad lamina and with large air spaces
- Many stomata on the upper epidermis
Y: - Leaves with broad lamina
- Long flexible stems with tendrils
Z: - Large buttress roots
- Pneumatophores- State the possible habitat of each plant
X...................................................................................................................................... (1 mark)
Y...................................................................................................................................... (1 mark)
Z...................................................................................................................................... (1 mark) - State the significance of the following:
- Numerous stomata on the upper epidermis in plant X (1 mark)
- Broad leaves in plant Y (1 mark)
- Buttress roots in plant Z (1 mark)
- Give two problems faced by plant X in its habitat (2 marks)
- State the possible habitat of each plant
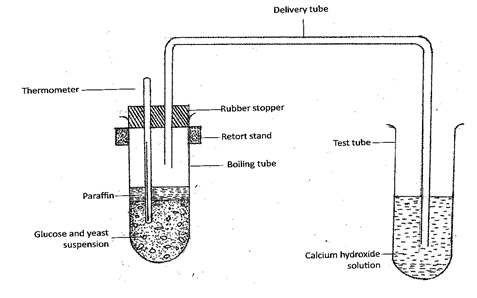
- The set up below illustrates an experiment to demonstrate a certain biological process, before the addition of the yeast suspension the glucose solution was first boiled and then cooled at 40oC.
- What was the aim of the experiment? (1mk)
- What observations would you make in the tubes a few minutes after the experiment begun (2mks)
- Explain the observations made in (b) above (2mks)
- Why was glucose solution boiled before cooling at 40oC (1mk)
- How can you set up a control experiment for the above (1mk)
- Use the photograph of mammalian digestive system and associated organs to answer the questions that follow.
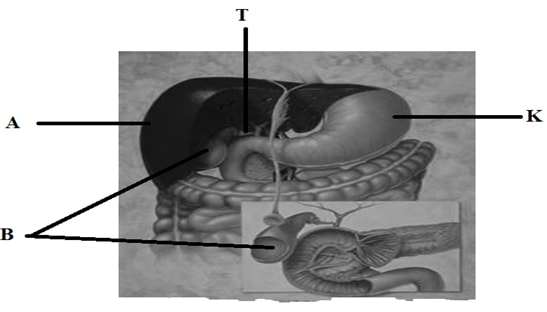
- Name the structures marked A, B, K andT. (4marks)
A……………………………………………………………………………………………….
B……………………………………………………………………………………………….
K……………………………………………………………………………………………….
T……………………………………………………………………………………………….. - Name an acid found in the structure labelled K. (1mark)
- Name the juice stored in the structure labelled B and give its function. (2marks)
Juice…………………………………………………………………..…………………..
Function…………………………………………………………………………………… - Label with letter D part where function named in (iii) above takes place. ( 1 mark)
- Name the structures marked A, B, K andT. (4marks)
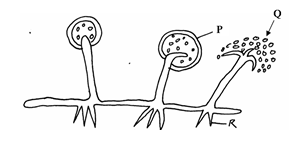
- The diagram below represents a mature bread mould (Rhizopus)
- Name the structures P, Q and R (3mks)
- What is the function of the structure P? (1mk)
- State two economic importances of moulds (2mks)
-
- Name the kingdom to which bread mould belong (1mk)
- List down one general characteristic of member of the kingdom named in d (i) above.
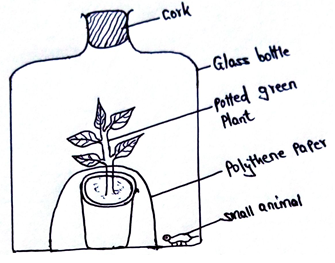
- An experiment was set up to investigate a factor in autotrophism in green plants.
Vaseline was applied at joint between the cork and the mouth of glass bottle and set up was left under sunlight for 6 hours.- Why was it necessary;
- To apply Vaseline (1mk)
- To cover the pot with polythene paper (1mk)
- What was the purpose of including the small animals? Give two reasons. (2mks)
-
- What would happen to the small animal if the set up was left over night in darkness
- Account for the answer in b (i) above (1mk)
- State the respiratory surface of the following organism (2mks)
- Amoeba
- Fish
- Why was it necessary;
SECTION B (40MARKS)
Answer question 6 (compulsory) then choose any between question 7 and 8
- A research was carried out to determine the trend of growth of some boys and girls. Their average mass in kilograms was taken separately for a period of 20 years and tabulated as shown in the table below.
Age Average mass of boys (Kg) Average mass of girls (Kg) 0 2.5 2.5 2 11.5 11.5 4 15.0 16.0 6 18.5 19.3 8 22.1 27.1 10 25.1 27.1 12 27.5 30.5 14 37.0 35.5 16 44.0 44.0 18 46.9 52.0 20 48.5 55
On the same axis draw a graph of the average mass of the girls and boys against age (7mks)
- From graph, determine the:
- Mass of boys at the age of 11 years (1mk
- Growth rate of girls between ages 13 and 15 (3mks)
- Account for the change in the mass of girls during the age stated in ( ii) above (2mks)
- Explain the trend observed in the curves for both boys and girls (2mks)
- Why do girls above 10 years require intake of food that richer in iron than boys of the same age (2mks)
- Apart from using average mass to estimate growth in human beings name two other parameters that can be used (2mks)
- From graph, determine the:
-
- Describe the mechanism of inhalation and exhalation in mammals (14mks)
- Explain three factors that affect rate of breathing (6mks)
-
- Describe the process of double fertilization in flowering plants. (15 mks)
- Describe what happens to the various parts of a flower after fertilization. (5 mks)
MARKING SCHEME
-
- X Fresh water body/ river/ lake/ pond; Reject: Wet/ Aquatic habitat (1 mark)
Y Tropical rain forest; Accept: Forest/ Rain forest; (1 mark)
Z Estuary/ Salt marsh;
Reject: Sea/ Ocean
Reject: Marsh alone: marsh is a wetland that is dominated by herbaceous rather than woody
plant species(Cf. Swamp: a wetland dominated by trees) -
- Many stomata on the upper epidermis in plant X
Speed up loss of excess water (through transpiration); (1 mark) - Broad leaves in plant Y
Offer large surface area for absorption of sunlight (for photosynthesis)/ gas exchange;
Reject: Offer large surface area for transpiration (1 mark) - Buttress roots in plant Z
Bind the soft mud, prevent the plant from being swept away by (strong) waves/ water currents; Accept: Anchor the plant firmly into the ground; (1 mark)
- Many stomata on the upper epidermis in plant X
- Give two problems faced by plant X in its habitat
- Excessive intake of water by osmosis resulting in low osmotic pressure of its tissues;
- Low (sun)light intensity (and thus reduced levels of photosynthesis);
- Low concentration of dissolved carbon (IV) oxide (and thus reduced levels of photosynthesis) and oxygen (and thus reduced levels of respiration);
- Strong water currents/ waves which may dislodge/ uproot the plant from its substratum;
(Mark the first two. 1 mark x 2 = 2 marks)
- X Fresh water body/ river/ lake/ pond; Reject: Wet/ Aquatic habitat (1 mark)
-
- To show that carbon (IV) oxide is produced during anaerobic respiration;. (1mark)
- There is production of bubbles in the boiling tube of carbon (IV) oxide leading to the formation of a white precipitate in the test tube containing calcium hydroxide solution;.
There is raise in temperature as of result to heat production (2marks) - Yeast cells undergo anaerobic respiration producing carbon (IV0 oxide gas which dissolves in calcium hydroxide solution forming a white precipitate; production of the gas results in bubbles; (2marks)
- To kill other micro-organisms present in glucose solution thus eliminating microbial respiration; (1 mark)
Elimination of air/oxygen - Through the use of glucose solution without yeast cells;
Through use of glucose solution with boiled yeast (1 mark)
-
- A-Liver;
B-Gall bladder;
K-stomach;
T-Pancreatict duct; - hydrochloric acid;
- bile
Emulsification of fats;
Neutralize acidic chime;
- A-Liver;
-
- P – sporangium;
Q – spore;
R – rhizoids; - Formation of spores;
-
- Causes decomposition of dead matter thus releasing nutrients to the soil to increase it’s fertility.
- Destroy old cloths/ shoes/ timber;
- Causes food spoilage; (mark first two)
-
- Fungi;
- They lack chlorophyll;
- Has cellwall made up of chitin instead of cellulose; (chitinous cellwall)
- Store carbohydrates as glycogen; (mark first one)
- P – sporangium;
-
-
- Prevent entry of respiratory gases. (1mk)
- To ensure soil microbes do not interfere with gas volumes in glass bottle. (1mk)
- – To consume oxygen released from photosynthesizing plant.
- To release carbon (IV) oxide from it respiration for photosynthesis by plant (2mks)
-
- Small animal would die. (1mk)
- Lack oxygen gas for respiration (1mk)
-
- Cell membrane
- Gill filament
-
SECTION B (40MKS)
-
-
- 26kgs±0.5
- Girls 15yrs – girls 13yrs =39 − 33=6
6÷2=3.0kg/year - Girls at adolescence grow faster: there is an increase in the size of hips and breasts.
- Girls generally grow faster than boys /boys grow slowly compared to girls: but later after puberty they grow more steadily.
- Girls above 10 years begin the menstruation cycle they need more iron to replace the blood lost during menstruation.
- -Height of the body
-Volume of the body
-
-
- Inhalation-External intercostal muscles contract ;internal intercostal muscles relax ; ribcage is raised upward and outwards;diaphragm muscles contract ,causing it to flatten;volume of throrarcic cavity increases;,while pressure decreases;,due to higher atmosphere pressure Air is drawn in through nostrils ;making the lungs to inflate
- Exhalation –External intercostal muscles relax ;internal intercostal muscles contract ;rib cage is lowered downward and inward ;diaphragm muscles relax and it arches upward/resumes dome shape; Volume of chest cavity decreases/reduces;pressure increases above that of atmosphere; and air is forced out of the lungs;
- Exercise /Activities
- During vigorouse physical activities the rate of breathing increases so as to meet oxygen demand .
- Age -Young people have higher demand of oxygen since they are more active.
- Emotions –body emotions such as fear ,anxiety and fright increases the breathing rate.
- Temperature – whne temperature is high ,there is tendency to increase the breathing rate.
- Healthy –in health increases body temperature which tend to increase body metabolic rate hence increased breathing rate.
- Altitude –high altitude has low oxygen concentration leading to increase breathing rate.
-
- Pollen grains lands and sticks/adheres onto the stigma;
- It absorbs nutrients/sugary substances and germinates to develop a pollen tube
- Pollen tube penetrates the stigma and grows down through the styles
- It obtains nutrient from the style (tissues)
- (As the pollen tube grows down the style), the pollen tube nucleus is located behind the tip as it directs the growth of the pollen tube while the generative nucleus follows behind it.
- The generative nucleus divides by mitosis (mitotically) into two male nuclei;
- When pollen tube reaches the ovary, it enters the ovule through the Micropyle; it enters the embryo sac; its tip bursts open/ruptures;
- The pollen tube nucleus disintegrates creating a clear passage for the male nuclei; (into the embryo sac)
- One male nucleus fuses with the (two/both) polar nuclei; to form a triploid endosperm nucleus;
- Total 16 max
- Max 15
Rej. Degenerates for disintegrates
NB. If an illustration is used mark:- Landing of pollen grains on stigma
- Germination of pollen grains
- Formation of pollen tube
- Position of correctly labelled generative nucleus behind the tube nucleus in pollen tube.
- Growth of pollen tube down the style
- Entry of pollen tube into the ovule
- (Max 6 marks)
- The stamens/petals/sepals/calyx/style wither and drop off/fall off
- The zygote (divides by mitosis to) form the embryo
- The endosperm nucleus (divides by mitosis) to form the endosperm. (Accept primary endosperm for endosperm)
- The integuments develop into a seed coat/testa
- The ovary develops into a fruit
- The ovary wall develops into a fruit wall/pericarp
Total 6 marks
Rej. Legmen for Testa/seed coat Max. 5
- Pollen grains lands and sticks/adheres onto the stigma;
Download Biology Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Form 3 Term 3 Opener Exams 2021.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students