INSTRUCTIONS
Answer ALL questions
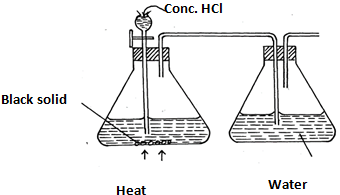
- The diagram shows an incomplete set-up for the laboratory preparation and collection of chlorine gas. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Complete the set-up to show how dry chlorine gas is collected. (2mks)
- Name substance Q.(1mk )
- Give a reason why it is possible to separate nitric (V) acid from sulphuric (VI) acid which is used as one of the reagents in the preparation of nitric (V) acid. (1mks)
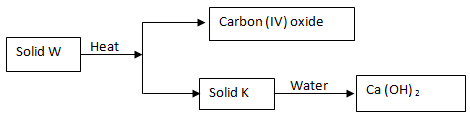
- Study the scheme below and answer the questions that follow
- Identify solids W and K (2mks)
- Write an equation for the formation of Ca(OH)2 from solid K (1mk)
- Write an equation for the decomposition of solid W (1mk)
- The ions M3+ and N2- have identical electronic arrangement. M is in period three.
- Write the electronic arrangement of
M (1mk)
N(1mk) - Write the formula of the compound formed when M and N combine. (1mk)
- Write the electronic arrangement of
- Explain why there is a general increase in first ionization energy of elements in period three of the periodic table from left to right.(1mk)
- When excess magnesium ribbon is burned in air, two products are formed.
- identify the two products (2mk)
- Write the two equations of the reactions that form the products in (i) above (2mks)
-
- State the Boyle’s law. (1mk)
- Calculate the pressure required to compress 12 liters of nitrogen gas at 1 atmosphere to give a volume of 4 liters. (2mks)
- An element W of atomic number 11 and an atom of element Y of atomic number 9 combine to form a compound.
- Write the formula of the compound. (1mk)
- State the type of bond present in the compound formed. (1mk)
- Identify the type of structure formed. (1mk)
- A compound has the following composition by mass:
Carbon =40%, hydrogen=6.7%, oxygen=53.3%
Given that the relative molecular mass of the compound is 180, determine its molecular formula
(C=12, H=1, O=16.0) (3mks) - The melting point of phosphorous trichloride is −910C while that of sodium chloride is 8010C. In terms of structure and bonding, explain the difference in their melting points. (3mks)
- Explain why the following substances conduct an electronic current.
- magnesium metal (1mk)
- Molten magnesium chloride. (1mk)
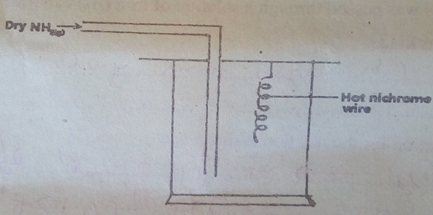
- The apparatus below was a set-up to show the catalytic oxidation of ammonia. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow.
- write an equation for the reaction that takes place in the in the gas jar. (1mk)
- Why is it necessary to have a hot nichrome wire in the gas jar? (1mk)
- When 3.125g of a carbonate, MCO3 was heated completely, the volume of carbon (IV) oxide evolved during the heating is 600cm3 at room temperature and pressure. Calculate the relative atomic mass of M. (Molar gas volume at r.t.p=24dm3) (3mks)
- A sample of river water was suspected to contain zinc and sulphate ions. Describe how the presence of zinc and sulphate ions can be established. (3mks)
- Using dots (.) and crosses(x) to represent electrons, show bonding in carbon (II) oxide(2mks)
- When a burning candle is put into a gas jar of sulphur (IV) oxide gas, it goes off but a burning magnesium ribbon continues to burn. Explain these observations. (2mks)
- Starting with copper metal, describe how pure copper (ii) carbonate can be prepared in the laboratory (3mks)
-
- State the observations that would be made when chlorine gas is bubbled through potassium bromide solution. (1mk)
- Write the ionic equation for the reaction in (a) above (1mk)
- An element M has two isotopes.
And
The relative atomic mass of the naturally occurring M is 63.55. Calculate the percentage abundance of each isotope. (3mks)
- Distinguish between the terms deliquescent and efflorescent as used in chemistry. (2mks)
- 10 cm3 of concentrated sulphuric(vi) acid was diluted to 100cm3. 10 cm3 of the resulting solution was neutralized by 36cm3 of 0.1M sodium hydroxide solution. Determine the mass of the sulphuric (vi) acid that was in the concentrated acid.
(S=32, H=1, O= 16) (3mks) -
- Explain why potassium carbonate cannot be manufactured by the Solvay process. (1mk)
- Write the equation for the reaction that takes place in the Solvay tower (Carbonator) (1mk)
- State one commercial use of soda-ash (1mk)
- What name is given to each of the following?
- Ability of an element to attract electrons (1mk)
- Types of forces that holds the atoms of Neon together (1mk)
- Zinc sulphate was prepared by adding excess Zinc oxide to dilute sulphuric (vi) acid in a beaker. The mixture was wormed until no more effervescence occurred. Excess Zinc oxide was filtered and the filtrate evapourated and then cooled. Fine crystals were obtained.
- Write an equation for the above reaction (1mk)
- Why was excess zinc oxide used (1mk)
- How would you know that the reaction is over (1mk)
- Hydrogen sulphide was passed through a solution of Iron (III) chloride
- State the observation made (1mk)
- Write an ionic equation for the reaction that took place (1mk)
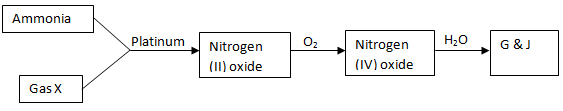
- Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow
- Identify gas X (1mk)
- Write an equation for the reaction between ammonia and gas X (1mk)
- Write an equation to show the formation of G and J (1mk)
- All apparatus used during preparation nitric (V) acid are made of glass. Give a reason. (1mks)
- Sulphur (IV) oxide gas was bubbled through acidified potassium chromate (VI) solution and Iron (III) Sulphate solution chromate. Explain the observations made in each case.
- With Potassium Chromate (VI) solution. (1 ½ mk2)
- Iron (III) Sulphate solution (1 ½ mks)
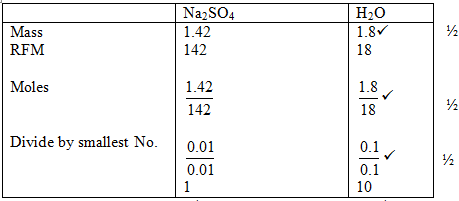
- 3.22g of hydrated Sodium Sulphate, Na2SO4oX H2O were heated to a constant mass of 1.42g, determine the value of X in the formula. (Na = 23, S = 32, O = 16, H=1). (2 mks)
- 20 cm3 of 2 M Sulphuric (IV) acid reacted completely with 3.2 g of WOH (O=16, H=1) Calculate the R.A.M of W in the formula WOH. (3 mks)
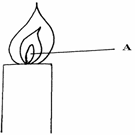
- The figure below shows part of non-luminous flame.
-
- Describe an experiment that would confirm that region labeled A is not suitable for heating. (1 ½ mks
- Explain why luminous flame produce light and soot. (1 ½ mks)
-

MARKING SCHEME
-
- passed through concentrated sulphuric acid; and collected by downward delivery;
- Manganese (IV) oxide;
- Nitric (V) acid is volatile hence turns into vapour while sulphuric (VI) acid is non-volatile.
-
- W – Calcium carbonate
K – Calcium oxide - CaO(s) + H2O(l) → Ca(OH)2(aq)
- CaCO3(s) → CaO(S) + CO2(g)
- W – Calcium carbonate
-
- M: 2.8.3
N: 2.6 - M2N3
- M: 2.8.3
- Due to increased nuclear charge across the period
-
-
- Magnesium oxide (1/2mk)
- Magnesium nitride (1/2mk)
-
- Mg(s) + O2(g) → 2MgO(s)
- 3Mg(s) + N2(g) → Mg3N2(s)
-
-
- Volume of a fixed mass of a gas is inversely proportional to its pressure at a constant temperature.
- P1V1 = P2V2
1×12 = P2×4
4P2=12
P2 =3atm.
-
- WY
- Ionic
- Giant ionic structure
-
Empirical formula is CH2OElements C H O % by mass 40 6.7 53.3 R.A.M 12 1 16 Moles 40/12 =3.3 6.7/1 =6.7 53.3/16 = 3.3 Simplest ratio 3.3/3.3 =1 6.7/3.3 =2 3.3/3.3 =1
Molecular formula (CH2O)n = 180, n = 6
C6H12O6 -
- PCl3 has a simple molecular structure in which molecules are held together by weak van der waals forces of attraction which are easily broken
- NaCl has a giant ionic structure in which ions are held together by strong ionic bonds which are not easily broken.
-
- Presence of mobile/ delocalized electrons.
- Presence of mobile ions, Mg2+ and Cl−
-
- 4NH3(g) +5O2(g) → 4NO(g) + 6H2O(g)
- Acts as a catalyst.
- MCO3(s) → MO(s) + CO2(g)
1mole 1mole 1mole
Moles of CO2 = 600 = 0.025 mole
2400
Moles of MCO3 = 0.025 Moles (mole ratio 1:1)
RFM of MCO3 = 3.125 = 125
0.025
M + 12 + 48 = 125
M = 125-60
=65. -
- Add aqueous ammonia until in excess, formation of a white precipitate which dissolves in excess shows presence of Zn2+ ions
- add aqueous acidified Ba(NO3)2/ BaCl2, formation of white precipitate shows presence of sulphate ions.
-
- The intense heat of burning magnesium decomposes SO2 gas releasing oxygen which supports the burning magnesium while the candle does not have enough heat to decompose SO2
- React excess copper with nitric acid filter and retain the filtrate, add Na2CO3 Or K2CO3 solution to the filtrate filter, wash the residue with distilled water and dry between filter papers
-
- Colourless KBr solution turns red-brown
- Cl2(g) + 2Br−(aq) → 2Cl−(aq) + Br2(l)
- let % abundance of
be x
% abundance of= 100-X
63.55 = (x×63) + (100-x) x 65
( 100 ) ( 100 )
63.55 = 0.6x + 65 + 0.65x
X = 72.5%
% of= 100 – 72.5 = 27.5%
-
- Deliquescent – salt that absorb water from the atmosphere to form solutions
- Efflorescent – salts tat loses their water of crystallization to the atmosphere.
- H2SO4(aq) + 2NaOH(aq) → Na2SO4 (aq) + 2H2O(l)
Moles of NaOH = 36 x 0.1 = 0.0036
1000
Moles of acid = 0.0036(mole ratio 1:2)
2
= 0.0018 moles
Moles of acid in 100cm3 = 100 x 0.0018
10
= 0.018 moles
Mass of acid = RFM of acid x 0.018
=98 x 0.018
= 1.764g -
- K2CO3 is more soluble in water hence cannot be separated from ammonium chloride
- NH3(g) + CO2(g) + H2O(l) + NaCl(aq) → NaHCO3(s) + NH4Cl(aq)
-
- making glass
- making soap
- manufacture of papers
- softening of hard water
-
- Electro negativity
- Van der waals forces
-
- ZnO(s) + H2SO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + H2O(L)
- To ensure all the acid is neutralized
- When effervescence stops
-
- Colour changes from yellow to green
- 2Fe3+(aq) + S2-(aq) → 2Fe2+(aq) + S(S)
OR
2Fe3+(aq) + H2S(g) → 2Fe2+(aq) + 2H+(aq) + S(s)
-
- Oxygen;
- 4NH3(g) + 5O2(g) 4NO(g) + 6H2O(g)
- 2NO2(g) + H2O(l) HNO2(aq) + HNO3(aq)
-
- Nitric acid attacks rubber or cork
-
- Orange ✓½ Potassium chromate VII turns green ✓½ due to reduction process SO2 is a reducing agent where it reduces chlomate VII ions to chloromium III ions ✓½ (1 ½ mk)
- Brown ✓½ iron III sulphate solution turns green ✓½ due to reduction of Fe3+ to Fe2+ ions ✓½ (1 ½ mk)
- H2SO4 + 2 WOH → W2SO4 + 2H2O
Moles of H2SO4 = 20 × 2 = 40 =0.04 ✓½
1000 1000
Mole ratio = 1:2 ✓½
Moles of WOH = 2 × 0.04 ✓½ = 0.08 ✓½
1
RFM of WOH = grams = 5.2 =40 ✓½
Moles 0.08
RAM of W = W +10+1 = 40
= 40 -17 = 23 ✓½ (3 mks) -
-
- Slip a piece of manila paper / wooden ✓½ splint into region A and ✓½ quickly remove before it catches fire. Inner part remains unburnt / Not charred ✓½ or Hold a match stick on a pin and let the head on the head of the match stick in zone A does not light. (1 ½ mk)
- Unburnt carbon ✓½ particles form soot other carbon particles glow ✓½ white hot emitting light ✓½ .
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Chemistry Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Form 3 End Term 3 Exams 2021.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students