INSTRUCTIONS
- Answer ALL questions
-
- Give the name of reagent which when reacted with concentrated hydrochloric acid produce
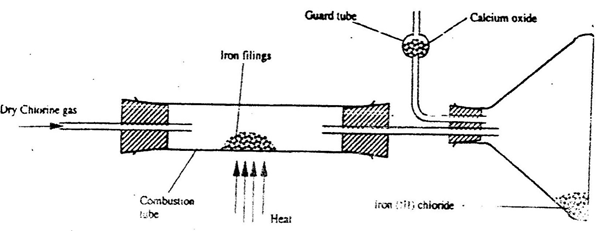
chlorine gas. (1mk) - A student set out to prepare iron III chloride using the apparatus shown in the diagram below.
- Explain why:
- It is necessary to pass chlorine gas through the apparatus before heating begins. (1mk)
- Calcium oxide would be preferred to calcium chloride in the guard tube. (2mk)
- What property of iron (III) chloride makes it possible to be collected as shown in the diagram? (1mk)
- Write an equation for one chemical reaction that took place in the guard tube. (2mk)
- The total mass of iron (III) chloride formed was found to be 0.5g.
Calculate the volume of chlorine gas the reacted with iron.
(Fe - = 56.0, Cl = 35.5 and Molar gas volume at 298K is 24,000cm (2mks)
- Explain why:
- When hydrogen sulphide gas was passed through a solution of iron (III) chloride, the following observation were made:
- The colour of the solution changed from reddish – brown to green and
- a yellow solid was deposit. Explain these observations. (2mks)
- One of the industrial uses of chlorine gas is manufacture of Hydrochloric acid.
- Give one source of chlorine gas. (1 mk)
- Give the name of reagent which when reacted with concentrated hydrochloric acid produce
- Study the table below and answer the questions that follow.
Element A B C D E F G Atomic radius (nm) 0.156 0.136 0.125 0.110 0.110 0.104 0.099 Ionic radius (nm) 0.095 0.065 0.050 - - 0.184 0.181 1st Ionization energy KJ/mol 492 743 790 791 1060 1063 12.54 Mpt (0C) 97.8 650 660 1410 44.2 119 –101 Atomic number 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 - Explain why
- A has a larger atomic radius than its ionic radius? (1 mk)
- G has a smaller atomic radius than its ionic radius? (1 mk)
- Comment on the trend of melting points from A to C. Explain. (2 mks)
- What is the general trend of the 1st ionization energies for elements A – F. Explain? (2 mks)
- Explain why D has the highest melting point. (2 mk)
- Explain why
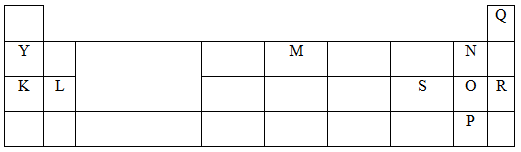
- The grid below is a section of the periodic table. The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
- How does electro negativity vary from N to P? Explain (2 mks)
- Give the formula of the compound formed between L and P. (1 mk)
- An oxide of Y was dissolved in water to form a solution. How would you distinguish between this solution and a solution made by dissolving an oxide of S in water. Explain. (2 mks
-
- The table below gives formulae and volumes occupied by 1g of some gases at STP, study it and answer the questions that follow:
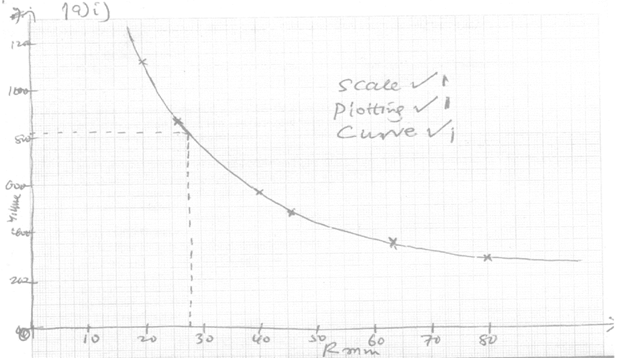
Formulae of gas Ne C2H2 Ar NO2 SO2 SO3 Relative molecular mass 20 26 40 46 64 80 Volume occupied by 1g (cm3) 1120 861 560 485 350 280 - Plot a graph of volume of gas (Y-axis) against the relative molecular mass (3mks)
- Use the graph to predict the volume occupied by 1g of Carbon (ii) oxide and use your answer to calculate the molar gas volume at STP (C = 12, 0 = 16) (3 mks)
-
- State Graham’s law of diffusion? (1mk)
- Apart from density or mass of a gas state one other factor that affects the rate of diffusion (lmk)
- Calculate the relative molecular mass of gas V (RMM of X = 34) Gas V takes 60 seconds to diffuse through a porous plug. A gas X diffuses through the same plug in 90 second (2mks)
- The table below gives formulae and volumes occupied by 1g of some gases at STP, study it and answer the questions that follow:
-
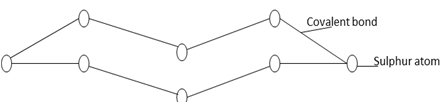
- Study the structure below and answer questions that follow
- What observation is made when the molecule above is heated to a temperature of 1130C? (2mks)
- Write an equation for the reaction of atom of the above structure with hydrogen. (2mk)
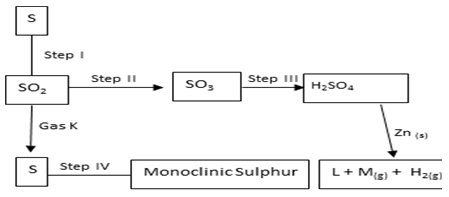
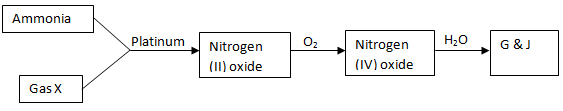
- Study the scheme below and answer questions that follow.
-
- Name
Gas K (1mk)
Gas M (1mk) - State the observation made in
Step I (1mk)
Step II (1mk) - State the conditions necessary for step II to occur. (2mks)
- Name
- Write an equation to show how pollution effect of sulphur (IV) oxide is controlled in contact process. (2mks)
-
- Study the structure below and answer questions that follow
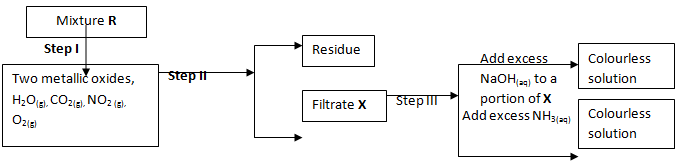
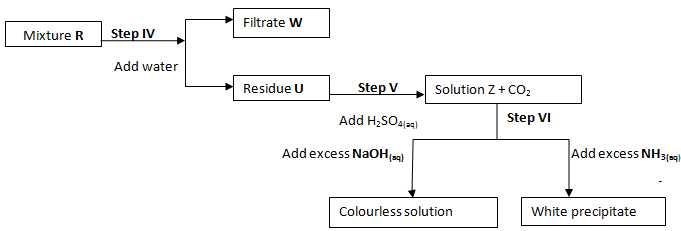
- The flow charts below show an analysis of a mixture R that contains two salts. Study the analysis and answer the questions that follow:
-
- State:-
- The condition in step I (1 Mark)
- The process in step II (1 Mark)
- A small portion of mixture R is added to dilute nitric (V) acid in a test-tube. What would be observed? (1 Mark)
- Write an equation for the reaction between the cation in filtrate X and sodium hydroxide Solution (1 Mark)
- Explain how water vapour in step I could be identified (1 Mark)
- State:-
- State and explain the conclusion that can be made from step IV only (2 Mark)
- Name the anion present in residue U. Explain (2 Mark)
- From the flow chart in (a) and (b);
Write the formulae of cations present in mixture R (2 Mark)
-
- The flow chart below shows the preparation of carbon (II) oxide and its reactions
-
- Name the type of reaction taking place between H2C204 and Conc. H2S04 ( 1mk )
- Why is gaseous mixture passed through Conc. KOH? ( 1mk )
- Write an equation for the production of B and C ( 1mk )
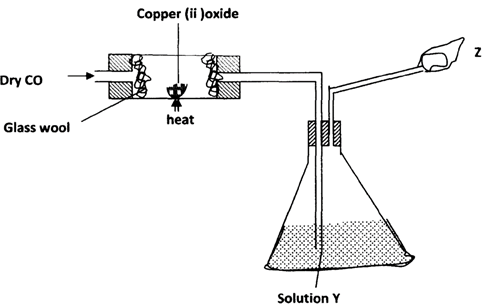
- The figure below is used to investigate the effect of carbon (ii) oxide on copper (ii) oxide. Study it and answer the questions that follow Copper (ii) oxide
- What will be observed in the combustion tube at the end of the experiment? (1mk)
- Identify Y and give its use (2mks)
- Why is it necessary to burn the excess gas at Z (2mks)
- Write the equation for the reaction taking place at Z (lmk)
- What is the use of glass wool? (lmk)
- Give two uses of carbon (II) oxide (2mks)
-
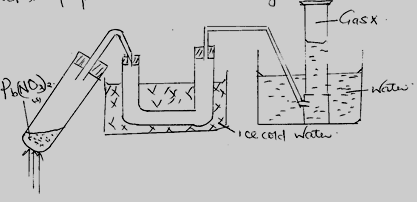
- The diagram below represents a set up that can be used to prepare and collect nitrogen (iv) oxide.
- Write a chemical equation for the reaction that takes place in the boiling tube. (1 mk)
- Name gas x. (1 mk)
- What observations are made on final residue in the boiling after reaction on heating and cooling the residue. (1mk)
- When a piece of burning magnesium is lowered into a gas jar containing gas x it continues to burn.
- Explain the observation 2mks
- Write a chemical equation for the reaction.(1mk)
- What precaution should be taken when preparing gas x
- Explain why it is not advisable to use copper (II) nitrate instead of lead (II) nitrate. (1mk)
- What property of gas x makes it possible to be collected by the method above.(1mk)
- State one use of gas x. (1 mk)

MARKING SCHEME
-
- Potassium permanganate, Manganese (IV) oxide, Lead (IV) oxide
KMnO4 or MnO2 or PbO2 √1 -
- to remove all oxygen or air which would form iron (III) oxide √1
- CaO absorbs both Cl2(g) and moisture. CaCl2 can only absorb Moisture √
- It sublimes or changes directly from solid to gas √ 1
- CaO(s) + H2O(g) → Ca(OH)2 or /
CaO(s) + Cl2(g) → CaOCl2 +(s) or/
Ca (OH)2 + Cl2(g) → CaOCl2 + H2O either √ 1 - (Fe = 56.0, Cl = 35.5 and molar gas volume at 298K is 24,000cm3)
2fe(s) + 3Cl2(g) 2FeCl3(s) or mole ratio 2:3
R.F.M of Fe = 0.5 = 0.003 √½
162.5
Moles of Cl2 = 3 x 0.003 = 0.0045 √½
2
Vol of gas = 0.0045 x 24000 √½
= 110.76cm3 – 111cm3 √½
OR / Alternative method
2Fe(s) + 3Cl2(g) 2FeCl3(s)
= 3 x 24000 x 0.5
162.5 x 2
= 110.76cm3>111cm3
-
- Fe3+(aq) is reduced to Fe2+(aq) or Fe2+ (aq) ions formed √1
- H2S(g) is oxidized to sulphur or sulphur is formed √1
NB/ (contradiction of the process subtract ( ½ mk)
-
- From electrolysis of brine √1
Hydrogen√
- From electrolysis of brine √1
- Potassium permanganate, Manganese (IV) oxide, Lead (IV) oxide
-
-
-
- A reacts by losing electron √½ hence the ion formed has fewer energy levels than that of its atoms √½
- G reacts by gaining electrons √½ increasing the negative charge hence more repulsion. √½
- Increases from A to C √½ The strength of metallic bonds increases √½ from A to C as the number of valency electrons increase √½ and nuclear increases √½
- It increases due to √½ increase in the nuclear charge. √½
- D has giant covalent or atomic structure √½ with strong covalent bonds √½
-
-
- It decreases from N to P √½ The atomic radius increases from N to P √½ and the ability of the nucleus to attract electrons is thus reduced. √1 or / Electron affinity decreases with increase in atomic radius.
- LP2√
- Using litmus paper the solution of oxide of y turns red litmus paper blue √½ Oxide of S change blue litmus to red.√½ Y oxide is basic √½ while S oxide is acidic. √½
-
-
-
-
- CO 12+16= 28g √ ½
volume occupied by 1g of CO = 820cm3 √ 1
molar gas volume = 820x 28J√ ½ = 22960cm3√ 1 (read from the graph )
1
-
-
- The rate of diffusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of its density at a constant temperature and pressure. √ 1
- temperature √ 1
-
√ 1
M1 = 34 × 9 =76.5
4 √ 1
-
-
-
- Yellow solid melts into amber liquid.(2mks)
- H2(g) + S(s) → H2S(g) (2mk) Penalise ½ for wrong state symbol / penalize fully for unbalanced eqn.
-
-
- K – Hydrogen sulphide 1 reject H2S(1mk)
M – sulphur (IV) oxide 1 reject SO2(1mk) - Step I -Blue flames ½ misty fumes ½ chocking smell.(1mk)
Step II-a vigorous reaction that produces white fumes.(1mk) -
- Temp of 450oC. (1mk)
- Pressure of 2 to 3 atmosphere.(½mk)
- V2O5 finely divided platinum or silica(½mk)
- K – Hydrogen sulphide 1 reject H2S(1mk)
- Ca(OH)2(aq)+ SO2(g) → CaSO3(s)+ H20(l) (2mks)
-
-
-
-
-
- Heating √1
- Filtration. √1
- Effervescence √1 / Bubbles.
- Zn2+(aq) + 2OH−(aq) → Zn(OH)2(s) √1
- Pass the water vapour over white anhydrous√1 Copper (II) suplhate. It turns blue. √½
-
-
- R is a mixture of sulphur √½ and insoluble√½ salt. It forms √1 a filtrate and residue in filtration of mixture
- Carbonate √1 / CO32- √1
It produces CO2 on reaction with H+ - Zn2+√1 and Al3+ √1
-
-
-
- Dehydration
- So that CO2 is absorbed (eliminated) √1
- PbO(s) + CO(g) → CO2(g) + Pb(s)
-
- Black solid √ 1
- NaOH or KOH √ 1
To absorb C02 - It is poisonous √ 1
- 2C0(g) + 02(g) → 2C02(g)
- Prevents heat from burning the cork/bung √ 1
-
- Fuel √ 1
- Reducing agent’J
-
-
- 2Pb(NO3)2(s) → 2PbO(s) + 4NO2(g) + O2(g) (1 mk)
- Gas = Oxygen (1 mk)
-
- On cooling is yellow (½ mk)
- On heating is Reddish brown (½mk)
-
- Magnesium ribbon continues to burn (1 mk), forming white fume. Burning magnesium is exothermic, therefore decompose nitrogen(iv)oxide to nitrogen and oxygen. Oxygen produced support burning. (1 mk)
- 4Mg(s) + 2NO2(g) → 4MgO + N2(g)
- Reaction should be carried in a fume chamber on open space, since the gas is poisonous. (1 mk)
- Cu(NO3)2 contains water of crystallisation or it is hydrated (1 mk)
- Nitrogen (iv) oxide easily liquedify. (1 mk)
- Manufacture of Nitric(v)acid. (1 mk)
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Chemistry Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Form 3 End Term 3 Exams 2021.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students