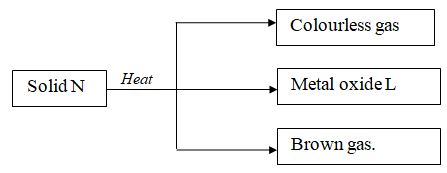
- Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow.
- Write the formula of the anion present in solid N. (1mk)
- Metal oxide L is black in colour. Identify:
- Cation present in solid N. (1mk)
- Metal oxide L. (1mk)
-
- State the mathematical expression of Boyle’s Law. (1mk)
- In an experiment, 375cm3 of gas P have a pressure of 800mmHg at 25°C. what will be the volume if pressure is reduced to 720mmHg under the same temperature? (3mks)
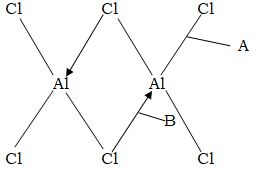
- Below is a structure of Aluminium chloride.
- Identify the bonds labeled A and B. (2mks)
- When aluminium chloride is dissolved in water, the resultant solution has a pH of 3. Explain. (2mks)
- Lithium has two isotopes with mass numbers 6 and 7. If the relative atomic mass of Lithium is 6.94, determine the percentage abundance of each isotope. (3mks)
- A mixture of magnesium powder and lead oxide will react vigorously when heated but no reaction occurs when a mixture of magnesium oxide and lead powder are heated.
- Explain the observation. (2mks)
- Which of the two substances, magnesium or lead oxide is:
- Oxidized in the reaction? (1mk)
- The oxidizing agent? (1mk)
- Give two reasons why hydrogen is not commonly used as a fuel. (2mks)
- Using dots(•) and crosses (x), show the type of bonding in the following compounds
- Sodium oxide (1mk)
- Silicon (IV) chloride. (1mk)
- An ion T3- has an electronic arrangement of 2.8
- What is the atomic number of the element? (1mk)
- To which group and period does the element belong to:
Group …………………………………………………………. (1mk)
Period ………………………………………………… ( (1mk)
- Air was passed through several reagents shown in the flow chart below.
- Write an equation for the reaction which takes place in the chamber with magnesium powder. (1mk)
- Name another solution that can be used in place of conc. KOH solution. (1mk)
- Name one gas, which escapes from the chamber containing magnesium powder. Give a reason for your answer. (2mks)
- Give the name of each of the following properties as described.
- When anhydrous copper sulphate is exposed to air for some time, it becomes wet. (1mk)
- Lead oxide can react with both dilute nitric (V) acid and sodium hydroxide solutions. (1mk)
- Magnesium metal can be hammered into sheets. (1mk)
- A mass of 3.6g of magnesium reacts in excess chlorine to form a chloride. If the mass of the chloride is 14.25g, find the formula of the chloride formed (Mg=24, Cl=35.5) (3mks)
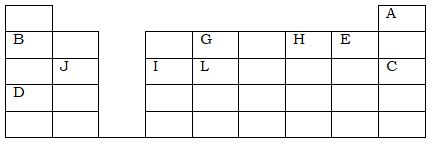
- The grid below represents part of the periodic table. Study it and answer the questions that follow. The letters are not actual symbols of the elements.
- What name is given to the family of elements to which A and C belong? (1mk)
- Write the formula of the sulphate of element D. (1mk)
- Which letter represents the most reactive; (2mks)
- Metal
- Non-metal
- Name the bond formed when B and H react. Explain your answer. (2mks)
- Select one element that belongs to period 4. (1mk)
- Explain why the ionic radius of element E is bigger than the atomic radius. (2mks)
- The electron configuration of a divalent anion of element N is 2.8.8. Indicate the position of element N on the periodic table above. (1mk)
- The oxide of G has a lower melting point than the oxide of L. Explain. (2mks)
- How do the atomic radii of I and C compare. Explain. (2mks)
- Explain the trend in the 1st ionization energies of the elements J, I and L. (1mk)

Marking Scheme
-
- NO-3
-
- Copper (II) or Cu2+
- Copper (II) oxide or CuO.
-
- P1V1 = P2V2
- P1 = 800mmHg P2 = 720mmHg
V1 = 375 cm3 V2 = ?
P1V1 = P2V2
V2 = P1V1=(800 × 375)=416.7cm3
P2 720
-
- A – Covalent
B – Dative or co-ordinate - Aluminium chloride undergoes hydrolysis with production of hydrated ions which are responsible for the PH of 3.
- A – Covalent
- R.A.M = (Mass.no ×Abundance)
(Total abundance)
Let the abundance of Li-6 be x
Relative abundance of Li-7 will be 100−x.
∴ 6.94 = (6 × x)+ 7(100−x)
100
6x + 700 – 7x = 694
X = 6%
Li-6 has 6%, Li-7 has 94% -
- Magnesium is more reactive than lead hence removes oxygen from lead oxide while lead cannot remove oxygen from magnesium oxide hence no reaction.
-
- Magnesium.
- Lead oxide.
- A mixture of hydrogen and air explodes when ignited Hydrogen is not readily available hence expensive.
-
-
-
- 7
- Group V
Period 2
-
- 3Mg(s) + N2(g) → Mg3N2(s)
- Sodium hydroxide.
- Argon/Neon/ Xenon /Krypton
It’s stable hence does not react under normal conditions.
-
- Hygroscopy
- Amphoterism.
- Malleability.
- Mass of chloride used = 14.25 – 3.6g = 10.65g.
Element Mg Cl
Mass (g) 3.6 10.65
R.A.M 24 35.5
Moles 3.6 10.65
24 35.5
0.15 0.3
0.15 0.15
Mole ratio 1:2
Formula MgCl2 -
- Noble gases
- D2SO4
-
- D
- E
- Ionic bond. It involves transfer of electrons from B to H.
- D
- During ionization, an extra electron is added to the energy shell which reduces the effective nuclear force of attraction.
- Placed in group VI and period 3.
- G forms a simple molecular structure with oxygen while L forms a giant atomic (covalent) structure with strong covalent bonds which require more heat to break.
- I is larger than C. I has a lower effective nuclear charge due to smaller number of protons hence weaker attraction between the outermost energy level and the nucleus.
- It increases across from J to L due to increase in the effective nuclear charge from J to L.
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Chemistry Questions and Answers - Form 3 Term 1 Opener Exams 2021.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students