SECTION A
Answer all question
- The figure below shows a diagram of part of a vernier caliper that has zero error of −0.02cm. Determine the length of the object using vernier caliper (2mks)
- A block measuring 20cm x 10cm x 5cm rests on a flat surface. The block has a weight of 3N. Determine the maximum pressure it exerts on the surface (3mks)
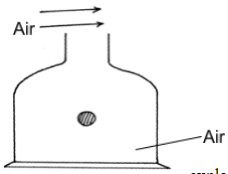
- The figure below shows a light body floating in a container
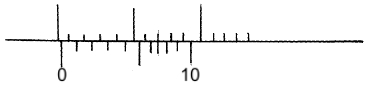
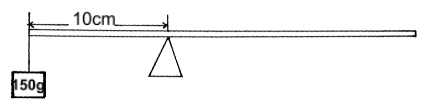
State and explain the observation when a stream of air is blown over the month of the container as shown (2mks) - A uniform half-metre rule pivoted at the 10cm mark, balances when a mass of 150g is suspended at the 0cm mark as shown below. Determine the mass of the half-metre role. (2mks)
- A person of mass 60kg stands on a spring weighing machine inside a lift. The lift is accelerated upwards at 3m/s2, calculate the reading of the weighing machine (3mks)
- A motorcycle accelerates from 8m/s to 20m/s in 10seconds. What distance does it cover in this time (3mks)
- Explain why a hole in a ship near the bottom is more dangerous than one nearer the surface (2mks)
- Xcm3 of substance A which has density of 800kg/m3 is mixed with 100cm3 of water with a density of 1000kg/m3. The density of the mixture is 960kg/m3. Determine the value of X (3mks)
- Explain in terms of the arrangement of particles the kinetic theory of matter. (3mks).
- A hippo of mass 500kg is able to walk on a muddy river bank while a car of mass 220kg is not able. Explain (2mks)
SECTION B: (55MARKS)
ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS
-
- The table below shows the values of extensions of a spiral spring when various forces are applied to it.
Force F, (N)
0
1.2
2.0
3.0
4.0
5.0
6.0
Extension R, (cm)
0
0.8
1.5
2.3
3.1
3.8
4.6
- On the grid provided, plot a graph against the extension. (5 mks)
- From the graph, determine the work done in stretching the spring by 4cm. (3mks)
- The table below shows the values of extensions of a spiral spring when various forces are applied to it.
- The mass of density bottle is 20.0g when empty. 70g when full of water and 55g when full of a second liquid. Calculate the density of the liquid
(take density of water to be 1000kgm−3) (4mks) -
- Explain why it is easier to ride a bicycle round a bend on a road if the surface is dry than when it is wet (2mks)
- Give one difference between limiting and dynamic forces of friction (2mks)
- Mercury on a clean glass slide collects into small spherical balls as shown in figure below. Explain why (2mks)

- State Pascal’s principle of transmission of pressure (2mks)
- A helical spring extends by 1 cm when a force of 1.5N is applied to it. Find the elastic potential energy stored in it. (2mks)
-
- State Hooke’s law (1mark)
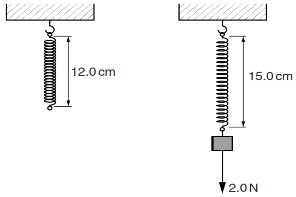
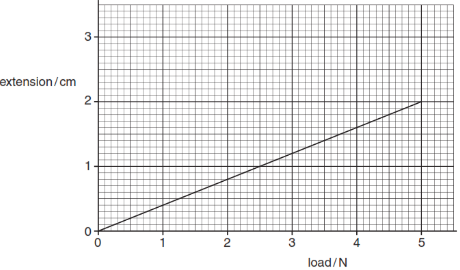
- A student hangs a spring vertically from a hook, as shown in Figure below.
With no load, the spring is 12.0 cm long. With a load of 2.0 N on the end of the spring, its length is 15.0 cm. Calculate the extension of the spring. (2 marks) - When the graph of extension against load is drawn for the spring, the result is the line shown below.
The unstretched length of the spring is 9.0 cm.- Calculate the total length of the spring when a 5.0 N load is hanging from the spring. (2 marks)
- Calculate the energy stored in the spring when it stretches through 2cm
(2 marks) - Calculate the spring constant from the graph (3 marks)
- A burette is filled with oleic acid drop upto the 15.5cm3 ark. After 50 drops of the oil were let out of the burette the level of the oil dropped to 22.5cm3.
- Determine the volume of one drop of the oleic oil. (3 mks)
- One drop of the oleic oil is carefully introduced onto a clean surface of a trough. It spread to a patch. Determine the thickness of each oleic oil molecules in metres. (Assuming the radius of drop = radius of patch). (5 mks)
- State two assumptions made in part (b) above.
-
- What is diffusion? (1 mark)
- A smoke cell contains a mixture of trapped air and smoke. The cell is brightly lit and viewed through a microscope. State and explain what is observed. (3 marks)
- A beaker is filled completely with water. A spoon full of common salt is added slowly. The salt dissolves and the water does not overflow.
- Why is salt added slowly? (2 mark)
- Why doesn’t the water overflow? (2 mark)
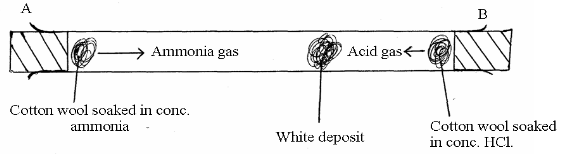
- In the figure below, ammonia gas and an acid gas diffuse and react to form a white deposit on the walls of a long glass tube as shown.
- What conclusion can be made from the result of this experiment? (2mark)
- How does the size and mass of a gas affect its rate of diffusion? (2 marks)
- The experiment is performed at a lower temperature. Explain how the time taken to form the white deposit would be affected. (2 marks)

Marking Scheme
- Main scale 20.00cm
vernier scale 0.07cm
20.07cm
Error + 0.02
20.09cm (2mks) - Pressure (max) = Force
Area (min)
= 3 = 3
0.1 x 0.05 0.005
= 600N/m2 (3mks) - High speed of air reduced pressure above the mouth of the container . Higher pressure below the body pushes it up. (2mks)
- Clockwise moments = Anticlockwise moments
1.5 x 1.0 = W x 0.15
W = 0.15
0.15
W=1N (2mks) - W = m(g+a)
= 60(10+3) = 780N (3mks) - a = v−u
t
a =20−8
10
a =1.2m/s2
S = ut + ½ at2
S = 8 x 10 + ½ x 1.2 x 102
S = 80 + 60
S = 140m (3mks) - Pressure in liquids increases with depth; hence water will enter the ship at a higher rate making it to sink. (2mks)
- Total mass = m1 + m2
m1 = 0.8 x x =0.8x g
m2= 1x100 = 100g
total = (0.8x + 1000)g
total volume = (x +100) = 0.96
x+100
x = 4
0.16
= 25cm3 (3mks) - Solid – particles very close, hence low kinetic energy
Liquids – particles fairly free, moderate kinetic energy
Gases – particles very free, high kinetic energy (2mks) - The fact of a hippo have a large area of contact which reduces pressure. For a car area of contact is small which leads to greater pressure. (2mks)
-
-
- Work done = ½ ke2 (where k is the spring constant)
K = F/e = gradient = 130N/m (from the graph) (1 mk)
= ½ x 130 x 0.042 (1 mk)
W = 0.104J (1 mk)
-
- R.D = mass if substance
Mass of equal volume of water
= 55-20
70-20
R.D= 35
50
Density = 35 x Density of water
50
= 35 x 1000 = 700kg/m3 (4mks)
50 -
- When the surface is dry, the frictional force between the tyres and the surface is higher than when wet, hence there is less skidding
- Limiting friction is friction between objects just before moving while dynamic friction is friction between surfaces in relative motion.
- Cohesive force between mercury molecules is stronger than the adhesive force between mercury molecules and the glass side;
- Pressure at one point in a liquid is transmitted equally to all other parts of the enclose liquid
- Elastic PE = ½Fe
=½ × 1.5 × 0.01
= 7.5 × 10−3J
-
- Hooke’s law states that “the extension of a spring is proportional to the applied force, provided that the force is not large enough to deform the spring permanently”.
- 15.0cm -12.0cm = 3.0cm
-
- F= Ke
5 = K × 2
100
2k=500
k=250N/m - PE = ½Ke2
=½ × 250 × 0.01 × 0.02
=0.05J - F/e = K
(5, 2), (3, 1.2)
∆ = ∆y = 2 − 1.2 = 0.8
∆x 5−3 2
e/F = 0.4
F/e = 1/0.4 = 10/4 × 100
=250N/m
- F= Ke
-
- 50 drops = 22.5
−15.5 (1 mk)
7.0
1 drop = 7.0
50 (1 mk)
= 0.14cm3 (1 mk) - Vol of the drop = vol of the patch
∴ 4/3πr3 = πr2×t (1 mk)
But 4/3πr3=0.14 (1 mk)
r3 = 0.14×3
4π
= 0.322 cm (1 mk)
Hence 0.14 = π x 0.3222 x t (1 mk)
t = 0.14
π x 0.3222
= 0.4298 cm (1 mk) -
- Oil spread to one molecule thick. (1 mk)
- No evaporation took place. (1 mk)
- 50 drops = 22.5
-
- Spreading of particles from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration.✔ (2mks)
- Bright specks of light in constant random motion are seen. ✔ (1mk)
Smoke particles collide with air particles that are in constant motion which make them change their direction of motion and hence move randomly.✔ (1mk) -
- To give enough time for the salt to dissolve to prevent displacement of water.✔ (1mk)
- Particles of salt enter into spaces between larger water particles. ✔ (1mk)
-
- Ammonia gas particles diffuse faster than acid gas particles.✔ (1mk)
- The smaller the size of particles and the smaller the mass, the faster the rate of diffusion. ✔ (1mk)
- It takes longer time because the kinetic energy of particles is reduced i.e particle move at a lower speed
Download Physics Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Form 3 End Term 1 Exams.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students