INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES:
- Answer ALL the questions
- Answers should be written in the spaces provided
SECTION A ( 30MARKS)
- Name three types of dairy goats reared in Kenya (1½)
-
- What is raddling in sheep management
- Give two reasons for raddling in sheep management (1mk)
- Give three advantages of contemporary comparison method in selection of livestock (1½)
- Give two reasons for spreading a polythene paper (pvc) on the slab of a permanent farm building (2mks)
- Name three types of Fresh warm water fish reared in Kenya (1½ mks)
-
- Give three disadvantages of inbreeding in cattle production (1½mks)
- Give three advantages of embryo transplant in cattle (1½mks)
- Name the farm tools used for each of the following operations listed below.
- Tightening barbed wire during fencing........(½ mark)
- Smoothening of concrete floors.........(½ mark)
- Giving liquid drugs to livestock through the mouth ......(½ mark)
- Sharpening the teeth of across-cut saw..........(½ mark)
- List four factors considered when making a choice of building materials. (2 marks)
- What is cropping in fish farming? (½ mark)
- State three methods of disbudding young calves. (1½marks)
- State two reasons why calves should be housed singly . (1 mark)
- Name one intermediate hosts for each of the following.
- Tapeworm(Taenia spp).......(½ mark)
- Liver fluke(Fasciola spp)..........(½ mark)
- Name four disease predisposing factors outside an animal’s body. (2 marks)
- State four factors that determine the amount of water a beef animal can take .
(2 marks) - State the function of any six parts of a zero grazing unit in dairy farming. (2 marks)
-
- Name the tool used for shearing wool sheep. ..........(½ marks)
- State three practices carried out during tupping season in sheep management. (1½ marks)
- State three functions of carbohydrates in livestock nutrition. (1½ marks)
SECTION B 20 MARKS
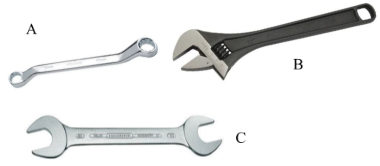
- Below are illustrations of farm tools and equipment.
- Identify the tool labelled A and B
A (1 mark)
B (1 mark) - State the advantage of tool B over tool C (1 mark)
- State two maintenance practices carried out on tool labelled B. (2 marks)
- Identify the tool labelled A and B
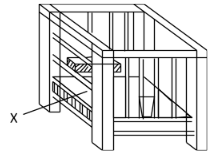
- Below is a farm structure. Study it carefully and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the farm structure above ................(1 mark)
- State the requirement of the part labelled X (1 mark)
- State three maintenance practices that should be carried on the structure.
(3 marks)
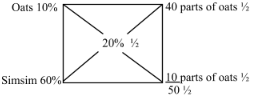
- A dairy farmer prepared 1000kg of feed (20%DCP) from the following feedstuffs:
Oats – 10% DCP , Simsim seedcake 60% DCP- Calculate the amount of each feedstuff used using Pearson’s square method. (3marks)
- Classify the following feedstuffs as either roughage or concentrate. (2marks)
- Bone meal
- Silage
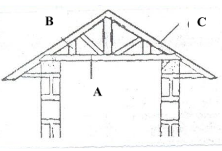
- Study the diagram below of a farm structure and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the parts labelled A, B, and C. (3 marks)
- Name two chemical preservatives that can be used to treat the wooden part of the above structure against fungi and insect attack. (2marks)
SECTION C 40 MARKS
Answer any two questions from this section in the spaces provided.
-
- Describe six signs of farrowing in a sow. [6mks.]
- Explain six benefits of the Kenya top bar hive. [6mks.]
- Explain eight factors considered when siting farm structures. [8mks.]
-
- State and explain five reasons for keeping livestock. (10 marks)
- Describe factors considered when selecting a gilt for breeding. (6 marks)
- Name four systems of breeding used to improve livestock. (4 marks)
-
- Describe ten general methods of disease control in livestock. (10marks)
- Describe the advantages of fences. (10 marks)

Marking Scheme
SECTION A (30 MARKS)
-
- Saanen
- Toggen burg
- Anglo-Nubian
- Jamnapari
- British Alpine
( ½ x3= 1 ½ mks)
-
- A Practice of flitting the rams with breeding chutes which are painted in different colours during breeding/application of coloured dye on the brisket of the rams during breeding,(1mk)
- Reasons for raddling
- Helps to identify ewes that have been served by individual/specific ram.
- Helps to identify ewes and rams which are infertile
- Helps to identify active rams.
( ½ x2=1mk)
-
- It is possible to compare animals with different age group since heifer locations are used
- It eliminates difference brought about by the environment since average performance of the herd is used.
- It is possible to make direct comparision of bulls and different artificial insermination centres since the environmental differences are removed.
- It is accurate method that can be used accurately in large herds of animals.
- ( 1 x ½ =1 ½ mks)
-
- To prevent moisture from rising up
- To prevent coldness from ascending to the floor surface.
- To control termites from rising up and damaging the floor. ( ½ x 2 =1mk)
-
- Tilapia
- Carps
- Black bass
- Cat fish
- Blue gill
- Nile perch
( 3 x ½ = 1 ½ )
-
-
- It brings loss of hybrid vigour
- May lead to decline in fertility which leads to species extinctions.
- Proving about reaction in performance
- Leads to high rates of parental mortality
( ½ x 3=1 ½ mks)
-
- It is possible to implant embryo from a high quality female to less valuable female hence improve performance of offspring.
- It stimulates milk production in a female that was not ready to produce milk.
- A highly productive female can be spread over a large area to benefit many females.
- It is easy to transport embryo in test tubes than the whole animal.
- Embryos can be stored for long period awaiting availability of recipient female
( 3 x ½ = 1 ½ mks)
-
- Farm tools used for each of the following operations listed below
- Tightening barbed wire during fencing
- Wire strainer /monkey winch
- Smoothening of concrete floors
- Steel float
- Giving liquid drugs to livestock through the mouth
- Drenching gun
- Sharpening the teeth of across-cut saw
- Triangular file
4x ½ = 2 marks
- Triangular file
- Tightening barbed wire during fencing
- Factors considered when making a choice of building materials
- Availability of the material
- Durability of the material
- Workability of the material
- Suitability of the prevailing weather
- Use of the structure in relation to the material
- Strength of the material (2marks)
- Cropping-removal of marketable size/mature fish from the pod (1mark)
-
- Use of dehorning iron
- Dehorning collodion
- Use of caustic potash stick
3 x ½ = (1½ marks)
-
- Prevent calves licking each other leading to formation of hair balls in the lumen
- Reduces risks of worms and disease spread
- Reduce risk of injury
2 x ½ = (1mark)
-
- Tape worm-intermediate host –Cattle or pig
- Liver fluke - Fresh water snail
2 x ½ = (1mark)
- Disease predisposing factors outside an animal’s body
- Contact with sick animals
- Poor housing / overcrowding
- Attack by external parasites
- Poor nutrition
- Unfavorable climatic factors e.g. extreme temperatures. Any 4x½ = 2mark
- Factors determining amount of water a beef animal should take
- Ambient temperature (rej.‘temperature’ alone or body temperature)
- Type of food eaten.
- Body size or weight.
- Physiological status e.g. pregnancy, health condition.
4x ½ = 2marks
- The various parts of a zero grazing unit in dairy farming are:
- Milking stall - restraining cows during milking
- Calf pen - rearing calf up to weaning
- Sleeping cubicles - provide shelter and warmth
- Loafing area/walking area -dunging, feeding, exercise and sunning.
- Feed and water troughs – feeding and watering the animals
- Feed preparation room – preparing feed rations and chopping fodder.
- Store - storing/keeping dairy equipments/feeds
- Manure storage area and storage of manure
- Milk recording room – recording manure individual milk production.
-
- Wool shears. (rej. Shears alone)
-
- Ringing-removal of wool around the penis sheath.
- Crutching-Removal of wool around the anus and vulva.
- Flushing-providing high quality feeds/concentrates of sheep a few days to mating.
- Raddling-Application of colored paste/tupping paste on the underside of the ram so that it leaves the color on the ewe it mounts.
-
- Metabolized to release energy.
- For synthesis of products such as milk, meat, eggs.
- Excess carbohydrates are converted into fat and stored for later production of energy.
3x ½ = 1½marks
SECTION B 20 MARKS
-
- A-Ring spanner
B-Open ended spanner - Has an adjusting nut which is used to close/open the jaws depending on the size of the nut to be opened or tightened. (1x1=1mk)
-
- Apply grease to rotating part
- Store properly in a tool rack
- A-Ring spanner
-
- Calf pen
- Have slatted floor (1x1=1)
-
- Should be clean.
- Leaking roof repaired
- Walls to be white washed to prevent lead poisoning
- Keep dry and warm by placing dry litter. (any 3x1=3mks)
-
Amount of oats = 40/50 x 1000kg
= 800kg of oats ½mk
Amount of simsim = 10/50 x 1000kg
= 200kg of simsim ½mk- Classifying feedstuffs as either roughage or concentrate
- Bone meal - Concentrate(1mk)
- Silage - Roughage( 1mk)
-
- Parts labelled as A, B, and C
- A- Cross tie
- B- Strut
- C- Rafter
(3x1=3mks)
-
- old engine oil
- copper sulphate
- sodium dichromate
- arsenic pentoxide
- Parts labelled as A, B, and C
SECTION C (40 MARKS)
Answer any TWO questions from this section in the spaces provided.
-
- Signs of farrowing in a sow
- Restlessness of a sow
- Enlarged vulva
- Muscles slacken on either side of the tail
- Loss of appetite
- Enlarged udder and teats
- Making a nest at a corner
- Presence of milk in the teats. [6marks]
- Benefits of top bar hive
- Bars can be removed for inspection
- Honey combs can be removed without disturbing the brood
- High quality honey is achieved without combs
- More wax is harvested
- Easy to construct and repair
- Queen excluder separates the brood from honey
- Cheap to construct .[6mks]
- Factors considered when siting farm strucutres
- Location of the farmstead should be at the central position of the farm
- All the farm structures should be accessible
- All structures should be well drained
- Stenchy enterprises like piggery, compost pit, poultry unit, silo should be on the leeward of the homestead
- Structures that are related should be close to one another for the efficiency of labour
- Farmers tastes and preferences should be considered like sheltering the homestead or improving the panorama
- Amenities like water and electricity should be close to the homestead
- All structures should be constructed on a gently sloping piece of land
- Structures should be constructed on infertile land so that crops are established on fertile ground .
- Structures should be secure by being built close to the homestead. [8marks]
- Signs of farrowing in a sow
-
- uses of livestock
- source of food-animal products like meat and milk, are used as food
- source of energy-Animal dung is used to generate biogas used for domestic activities e.g lighting and cooking
- source of income-when products of animals are sold or livestock themselves, they create income
- provision of raw materials —products like skin/hide can be used in leather industries
- provision of farm power- animal like oxen can be used to provide power in the farm
- provision of organic manure
- cultural uses such as payment of dowry or slaughtered during ceremonies 5x2=10mks
- Factors considered in selecting a gilt for breeding
- maturity-should be of appropriate age of 6-7 months
- Good mothering ability
- Should be fast growing to reach maturity early
- Should have good body conformation
- Should be free from physical defects
- Should be healthy
- Should have ability to withstand various stresses eg during heat 6x 1=6mks
- systems of breeding
- Cross breeding
- Upgrading
- Inbreeding
- Out crossing
(4 x 1 = 4 marks)
- uses of livestock
-
- General methods of disease control in livestock.
- Use of prophylactic drugs – Animals are given drug routinely to control certain diseases e.g. chicken are given.
- Use of antiseptic and disinfectants: They contain germicidal chemicals e.g. elecauning poultry or calf pen with disinfectant help control certain diseases/maintain hygiene’s.
- Quarantine – during an outbreak of certain notifiable disease like foot and mouth disease. Livestock movement is restricted to avoid spread of diseases.
- Isolation – Animals suffering from certain dangerous disease e.g. scours and brucullosis are isolated to prevent the spread of the disease to the healthy ones.
- Mass slaughter/culling: Animals suffering from certain dangerous diseases e.g. zoonotic disease like anthrax should be slaughtered in mass to eliminate the disease.
- Vaccination: Animals are usually vaccinated against certain diseases e.g. lumpy skin disease/black quarter.
- Control of vectors – Diseases carrying parasites e.g. Tsetse fly are controlled by spraying with appropriate chemicals or bush clearing to control diseases like nagana.
- Use of healthy breeding stock/AI healthy breeding stock or use AI help to prevent breeding diseases like brucellosis.
- Proper nutrition – well nourished animals are healthy and do not suffer from nutritional diseases like anaemia in piglets.
- Drenching/control of internal parasite. Internal parasites may cause diseases.
- Keeping resistant breeds of livestock. By keeping Zebu cattle occurrence E.C.F is reduced.
- Proper housing – this prevent diseases like pneumonia.
- Foot trimming – to minimize occurrence of foot rot.
(1 x 10 = 10mks)
- Advantages of fences
- Marking boundary/border.
- Keeps off thieves/intruders.
- Prevent damages of crops by crops.
- Control grazing in paddocks.
- Control breeding by separating males and females.
- Live fences act as windbreak.
- Fences help to control pests and diseases by controlling wild animals.
- Add aesthetic value.
- Live fence may provide livestock feeds or human fruit or firewood.
- Add value to the farm.
(1 x 10 = 10mks)
- General methods of disease control in livestock.
Download Agriculture Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Form 3 End Term 1 Exams 2021.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students