GEOGRAPHY
PAPER 1
TERM 2 OPENER EXAM
INSTRUCTIONS
- This paper has two sections A and B
- Answer all the questions in section A.
- Answer questions 6 and any other two questions from section B.
SECTION A
-
- What is the relationship between Geography and Mathematics? (2mks)
- State four reasons why it is important to study Geography. (4mks)
-
- Name the two layers of discontinuity that are part of the interior structure of the earth. (2mks)
- State three characteristics of the outer core in the interior structure of the earth. (3mks)
-
- Name two forms of precipitation that commonly occur in Kenya. (2mks)
- What is a steveson’s Screen? (2mks)
-
- Identify two causes of earth movements. (2mks)
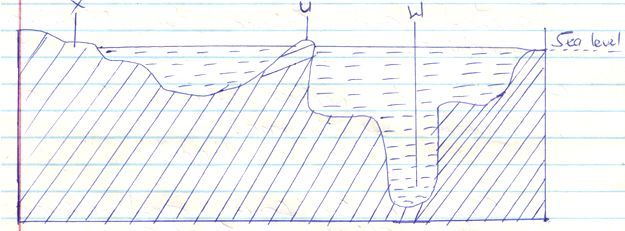
- The diagram below represents the relief of the ocean floor, use it to answer questions
- Name the features marked U, W and X. (3mks)
X
W
U - Give three reasons why ocean are saline. (3mks)
- Name the features marked U, W and X. (3mks)
-
- State one characteristic of Rift Valley lakes. (1mk)
- Name one salt water lake that lies north of the equator in Kenya. (1mk)
SECTION B.
Answer questions 6 and any other two questions from this section.
- Study the map of Busia 1:50,000 (sheet 101/1) provided and answer the following questions.
-
- What is the vertical interval of the area covered by the map? (1mk)
- Give the six figure grid reference of the chiefs house. (2mks)
- What was the magnetic variation of the area when the map was drawn? (1mk)
- What is the height of Odiado hill? (2mks)
-
- Measure the distance of the international boundary from point where it crosses Northing 41 to Northing 50 (Give your answer to the nearest 100 metres) (2mks
- Calculate the area enclosed by river sio, south of Northing 50, West of all weather road, loose surface ( B8/3) and East of the international boundary. (2mks)
-
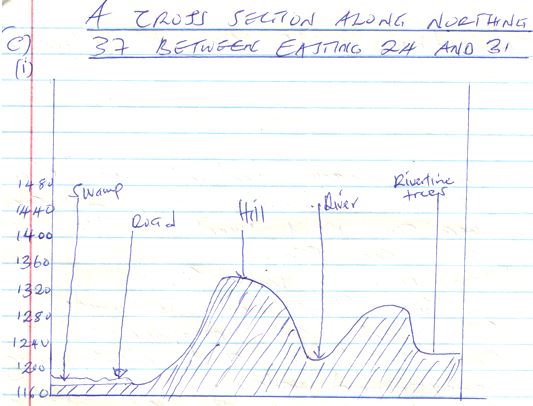
- Using a vertical scale of 1cm to represent 40metres, draw a cross section along Northing 37 from Easting 24 to Easting 31. On the cross-section mark and name. (7mks)
- All weather road, loose surface
- River
- Swamp
- Hill
- Riverine trees
- Calculate the vertical exaggeration of the cross section. (2mks)
- Determine the intervisibility of the section you have drawn. (1mk)
- Using a vertical scale of 1cm to represent 40metres, draw a cross section along Northing 37 from Easting 24 to Easting 31. On the cross-section mark and name. (7mks)
- Describe the drainage of the area covered by the map. (5mks)
-
-
- Define chemical weathering. (2mks)
- Explain how crystal growth leads to weathering. (5mks)
- Geography students in your school are planning to carry out a field study on rock weathering around your school.
- Apart from crystal growth, name five other mechanical weathering processes they are likely to study in the area. (5mks)
- State five importance of each of the following for your study.
- Reconnaissance (5mks)
- Working schedule (5mks)
- Which three problems are you likely to experience while collecting the data in the field? (3mks)
-
- Describe how a river erodes its channel through the following processes. (6mks)
- Abrasion
- Solution
- Hydraulic action
- Explain four ways through which a river transports its load. (8mks)
-
- State three factors that determine a river ability to transport its load. (3mks)
- Highlight four ways through which a gorge may be formed. (4mks)
- State four significance of rivers in Kenya. (4mks)
- Describe how a river erodes its channel through the following processes. (6mks)
-
-
- What is an earthquake? (2mks)
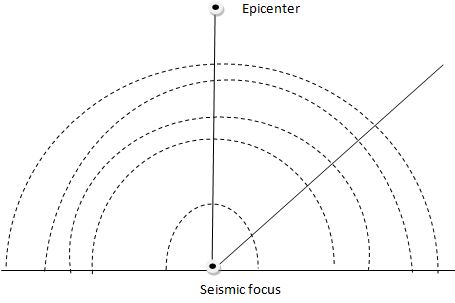
- Using a simple diagram explain the following terms. (5mks)
Epicenter
Seismic focus
Shockwaves travel outwards
-
- Explain four human causes of Earthquake. (8mks)
- Name the two types of Earthquake waves. (2mks)
- Differentiate between:
- Deep focus earthquake and shallow focus Earthquake. (2mks)
- Richter scale and mercallic scale. (2mks)
- List four regions of the world where earthquakes are likely to occur. (4mks)
-
-
-
- Distinguish between an ocean and a sea. (4mks)
- State three types of submerged coasts. (3mks)
- Explain two ways in which water moves in an ocean. (4mks)
- Explain four significance of oceans, coasts and coastal features. (8mks)
- Describe the formation of the following features due to wave erosion. (6mks)
-
MARKING SCHEME
-
- What is the relationship between Geography and Mathematics? (2mks)
- Mathematics being a science that deals with numbers, quantity and space, it is an important instrument in handling various numerical data in geography.
- Mathematics helps geography to simplify and interpret numerical data. Example calculation of averages, population sizes and densities.
- State four reasons why it is important to study Geography. (4mks)
- Study of geography encourages international awareness, interaction and cooperation for it teaches interdependence among people and geographical phenomena at local, national and international levels.
- Able to acquire basic skills and knowledge which contribute to national development.
- Geography is a career subject.
- Through the study of field work, one is able to manage time properly by drawing a time schedule.
- Helps learners to develop the skills of observing, reading, analyzing and interpretation of maps, photographs, charts, diagrams and statistical data.
- What is the relationship between Geography and Mathematics? (2mks)
-
- Name the two layers of discontinuity that are part of the interior structure of the earth. (2mks)
- mohorovicic / moho discontinuity
- Gutenberg discontinuity
- State three characteristics of the outer core in the interior structure of the earth. (3mks)
- Composed of molten rock materials
- Made up of iron and nickel
- Has very high temperatures
- Name the two layers of discontinuity that are part of the interior structure of the earth. (2mks)
-
- Name two forms of precipitation that commonly occur in Kenya. (2mks)
- Rainfall
- Dew
- What is a steveson’s Screen? (2mks)
- Refers to an wooden box where some instruments are placed in a weather station.
- Name two forms of precipitation that commonly occur in Kenya. (2mks)
-
- Identify two causes of earth movements. (2mks)
- Magma movement
- Gravitational force
- Convectional currents
- Isostatic Adjustment
- The diagram below represents the relief of the ocean floor, use it to answer questions.
- Name the features marked U, W and X. (3mks)
X – Continental shelf
W – Ocean deep
U – Oceanic island /island - Give three reasons why ocean is saline. (3mks)
- Volcanic activity adds salt in the ocean.
- Rivers bring in some salts into ocean
- Ocean beds contain salts which dissolves in the water
- Name the features marked U, W and X. (3mks)
- Identify two causes of earth movements. (2mks)
-
- State three characteristics of Rift Valley lakes. (3mks)
- They are very deep
- They are long in shape
- They are narrow in diameter
- Name one salt water lake that lies north of the equator in Kenya. (1mk)
- Lake Bogoria
- State three characteristics of Rift Valley lakes. (3mks)
SECTION B.
Answer questions 6 and any other two questions from this section.
- Study the map of Busia 1:50,000 (sheet 101/1) provided and answer the following questions.
-
- What is the vertical interval of the area covered by the map? (1mk)
- 20 metres
- Give the six figure grid reference of the chiefs house. (2mks)
- 255 - 315
- What was the magnetic variation of the area when the map was drawn? (1mk)
- 2O21’
- What is the height of Odiado hill? (2mks
- 1568m
- What is the vertical interval of the area covered by the map? (1mk)
-
- Measure the distance of the international boundary from point where it crosses Northing 41 to Northing 50 (Give your answer to the nearest 100 metres) (2mks
- 9700 metres / 9800m /9900m
- Calculate the area enclosed by river sio, south of Northing 50, West of all weather road, loose surface ( B8/3) and East of the international boundary. (2mks
- Complete square – 3
- Incomplete square – 2
- Total square 46
- Measure the distance of the international boundary from point where it crosses Northing 41 to Northing 50 (Give your answer to the nearest 100 metres) (2mks
-
- Using a vertical scale of 1cm to represent 40metres, draw a cross section along Northing 37 from Easting 24 to Easting 31. On the cross-section mark and name. (7mks)
- All weather road, loose surface
- River
- Swamp
- Hill
- Riverine trees
- Title ½ m
- Labeling V.A 1mk
- Features 5mks
- s.p & ep ½ mk
- trend ½ mk
- total 7mks)
- Calculate the vertical exaggeration of the cross section. (2mks)
- V.E = V.S
H.S
= 1/400 X 50,000
= 12.5 / 12 ½
- V.E = V.S
- Determine the intervisibility of the section you have drawn. (2mks)
- The two points are not intervisible.
- Using a vertical scale of 1cm to represent 40metres, draw a cross section along Northing 37 from Easting 24 to Easting 31. On the cross-section mark and name. (7mks)
- Describe the drainage of the area covered by the map. (5mks
- Main drainage features are rivers
- There are many rivers in the are
- Rivers are permanent
- Main river is river sio
- River sio flows south westwards
- Some rivers are meandering
- Some rivers are short / disappearing underground / vanishing
- Some rivers originate from highlands around Samia hills.
-
-
- Define chemical weathering. (2mks)
- Decomposition of rocks and disintegration due to reaction between them water and air.
- Explain how crystal growth leads to weathering. (5mks)
- Rain falls and percolates into the ground carrying with it dissolved minerals.
- In the dry season ground water is evaporated into the atmosphere.
- It carries with it the dissolved minerals from the rocks.
- Minerals accumulate the surface rock pores and cracks as water evaporates into the atmosphere.
- The accumulating minerals cause stress in the rocks leading to rock breakup.
- Geography students in your school are planning to carry out a field study on rock weathering around your school.
- Apart from crystal growth, name five other mechanical weathering processes they are likely to study in the area. (5mks)
- Pressure release / unloading / sheetin
- Slaking
- Exfoliation
- Granular disintegration
- Block disintegration
- State five importance of each of the following for your study.
- Reconnaissance (5mks)
- Enable them to prepare a work schedule
- To seek permission from the authorities
- Enable them to draw a route map
- Identify likely problems and prepare how to solve them.
- To familiarize with the route to follow to save time on the day to travel
- To acquaint themselves with some residents to extract information from them.
- Working schedule (5mks)
- Plan all activities such that none are forgotten.
- Give ample time to each item to ensure thoroughness
- Help to evaluate the work done while it is still in progress
- Estimate cost of study
- Estimate time required for study
- Reconnaissance (5mks)
- Which three problems are you likely to experience while collecting the data in the field? (3mks)
- Trouble in identifying some weathering processes.
- Fatigue due to too much working on rocky places
- Attack from animals commonly found on rocks
- Apart from crystal growth, name five other mechanical weathering processes they are likely to study in the area. (5mks)
- Define chemical weathering. (2mks)
-
- Describe how a river erodes its channel through the following processes. (6mks)
- Abrasion
- The river uses its load (gravel,boulders) as erosive tool.
- The load is hurled by the river water against the banks and dragged along the bed thereby chipping off the rocks on the bank and bed.
- Solution
- Running river may dissolve minerals found in the rocks in which they flow.
- The material is carried down the river channel in solution form.
- Hydraulic action
- The force of the moving water sweep away loose materials in the river channel or water is forced into cracks on the river banks.
- When water is hurled against the riverbank, air in the cracks is compressed creating pressure, which widens the cracks.
- As water retreats, pressure in the cracks is suddenly released. The compression and widening of cracks repeatedly shatter the rocks; which are then carried away by the retreating water.
- Abrasion
- Explain four ways through which a river transports its load. (8mks)
- Suspension; involves transportation of light insoluble materials like mud and clay down stream floating or partially submerged.
- Saltation/hydraulic lift; involves the transportation of large materials through a series of short jumps/hops. Material are pushed up by force of water and back by force of gravity.
- Traction; heavy materials are pushed and rolled along the riverbed by force of moving water.
- Solution; involves the transportation of materials already dissolved in water.
-
- State three factors that determine a river ability to transport its load. (3mks)
- Volume of water
- Gradient and velocity
- Nature and amount of load
- Highlight four ways through which a gorge may be formed. (4mks)
- River flows along a line of weakness
- Waterfall retreats upstream
- River flows across a plateau
- As a result of river rejuvenation
- State two significance of rivers in Kenya. (2mks)
- Provide water for domestic use industrial and irrigation purposes.
- Provision of hydroelectric stations (HEP)
- Features like waterfalls are site for tourist attraction.
- State three factors that determine a river ability to transport its load. (3mks)
- Describe how a river erodes its channel through the following processes. (6mks)
-
-
- What is an earthquake? (2mks)
- An earthquake is the rapid and sudden shaking of parts of the earths crust.
- Using a simple diagram explain the following terms. (3mks)
- Epicenter
- Seismic focus
- Shockwaves travel outwards
- What is an earthquake? (2mks)
-
- Explain four human causes of Earthquake. (8mks)
- Underground nuclear tests; when nuclear bombs are detonated below the surface, they cause a lot of vibrations which are felt on the earth’s surface.
- Construction of large reservoirs; water on dams or man made lakes exert a lot of weight on the ground. This can trigger earthquakes.
- During quarrying; rocks are blasted using explosives in order to reduce their sizes. This cause vibrations to be felt in surrounding areas.
- Movement of heavy trains; when they pass by, they vigorously shake the ground and these vibrations are felt as tremors nearby.
- Name the two types of Earthquake waves. (2mks)
- Body waves
- Surface waves
- Explain four human causes of Earthquake. (8mks)
- Differentiate between:
- Deep focus earthquake and shallow focus Earthquake. (2mks)
- Deep focus earthquakes occurs between 300-700 km below the surface while shallow earthquakes occur at a depth of 0-7km below the surface.
- Richter scale and mercallic scale. (2mks)
- Richter scale measures magnitude while mercalli scale measures the intensity of an earthquake.
- List four regions of the world where earthquakes are likely to occur. (4mks)
- Mid ocean ridges
- Ocean deeps and volcanic islands
- Regions of crustal compressions
- Within the Rift valley
- In areas of volcanic activities
- Deep focus earthquake and shallow focus Earthquake. (2mks)
-
-
-
- Distinguish between an ocean and a sea. (2mks)
- An ocean is an extensive mass of saline water occupying a large basin between continents while a sea is a large body of saline water on the margins of continents.
- State three types of submerged coasts. (3mks)
- Ria coasts
- Longitudinal coasts
- Ford coast
- Explain two ways in which water moves in an ocean. (4mks)
- Horizontally; water moves from ocean to other on the surface and via the ocean floor.
- Vertically; ocean water move from the surface to the bottom.
- Explain four significance of oceans, coasts and coastal features. (8mks)
- Provide water transport which is cheaper especially for bulky goods.
- Used for sporting ground.
- Mangrove trees that grow on coastal marshes provide timber for construction and furniture.
- Ocean modify the climate of the coastal lands through land and sea breezes.
- Features along the coastline, provided sceneries for tourists.
- Oceans are rich source of salts
- Some ocean waves are harnessed to produce tidal and wave energy.
- Raised coral platforms have been exploited to provide limestone used in cement making.
- Describe the formation of the following features due to wave erosion. (6mks)
- Wave cut platform and cliff.
- The breaking of waves at the same point on a lowland coast may form a notch.
- Further erosion deepens the notch to form a cliff.
- Waves undercut the cliff face at the bottom to form a hanging cliff face which eventually collapses.
- This force the cliff face to retreat further inland leaving behind a rock floor which is known as a wake-cut platform
- Geo
- As waves break in the cave, the roof of the cave may become thinner and weaker as it is slowly eroded, causing it to collapse.
- This leaves a long and wide opening od the cave roof to form a geo.
- Distinguish between an ocean and a sea. (2mks)
-
Download Geography Paper 1 Questions And Answers - Form 3 Term 2 Opener Exams 2021.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students