INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES:
- Write your name and Admission number in the spaces provided.
- Answer all the questions in Section A in the spaces provided.
- In section B answer questions 6 (compulsory) and either question 7 or 8 in the spaces provided.

QUESTIONS
SECTION A (40 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section in the spaces provided.
-
- The figure below shows the effect of pH on an enzyme catalysed reaction.
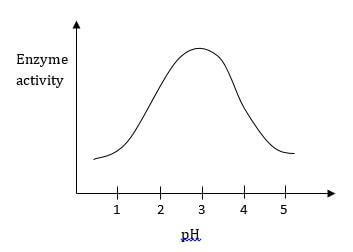
- State the pH at which the enzyme is most active……………………………………. (1 mark)
- Name one enzyme likely to be the one in the figure above and suggest the part of the alimentary canal where it is found. (2 marks)
Name...............................................................................................................................
Location in the alimentary canal...................................................................................... - Name the digestive juice that contains the enzyme. (1 mark)
- Explain how temperature affects the rate of enzyme controlled reactions (3 marks)
- What is enzyme specificity? (1 mark)
- The figure below shows the effect of pH on an enzyme catalysed reaction.
- The figures below represent mammalian tissue as seen under a light microscope.
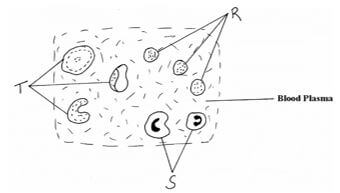
- Identify the tissue ……………………………………………………… (1 mark)
- Name the cells represented by (3 marks)
R…………………………………………………………………………….
S…………………………………………………………………………….
T……………………………………………………………………………. - State the function of structure S and R. (2 marks)
S ……………………………………………………………………………………………….
R……………………………………………………………………………………………….. - Explain one adaptations of structure T to its function. (1 mark)
- Name one defect of the circulatory system. (1 mark)
-
- Define the term photosynthesis (1 mark)
- State two raw materials of photosynthesis (2 marks)
- State two factors that affect the rate of photosynthesis (2 marks)
- Describe briefly the light stage of photosynthesis (3 marks)
- The diagram below represents the nitrogen cycle.
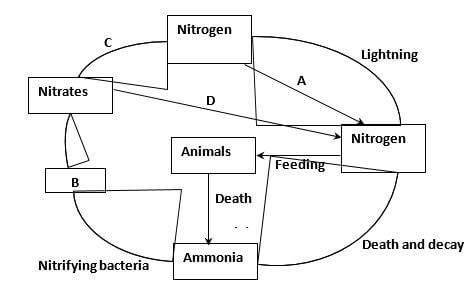
- Identify the processes labelled A and D. (2 marks)
A ………………………………………………………
D ……………………………………………………… - Name the compound represented by B. ………………………………………………… (1 mark)
- Name the group of organisms labelled C. ………………………………………………. (1 mark)
-
- Name the group of plants that promote process A………………………. (1 mark)
- In which part of the plant does process A take place? (1 mark)
- How would excess pesticides in the soil interfere with process A (2 marks)
- Identify the processes labelled A and D. (2 marks)
- Below is a diagram of a plant a student collected while carrying out an ecological study.
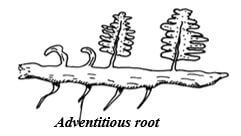
- With reasons identify the division into which the students classified the plant.
Division ………………………………………………………………………… (1mark)
Reasons ……………………………………………………………………….. (2marks) -
- Name the structure that produces spores in this plant. (1mark)
- State two differences between the plant division above and that of the division spermatophyta. (2 marks)
Spermatophyta
- Give two distinguishing features of class Amphibia (2 marks)
- With reasons identify the division into which the students classified the plant.
SECTION B (40 marks)
Answer question 6 (compulsory) and either question 7 or 8 in the spaces provided.
- The table below shows how the quantities of sweat and urine vary with external temperature
External temperature °C
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
Urine cm³/hr
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
Sweat cm³/hr
5
6
10
20
30
60
120
200
- On the same graph, plot the quantities of urine and sweat produced against the external temperature. (7 marks)
- At what temperature are the amounts of sweat and urine produced equal? (1 mark)
- What happens to the amount of sweat produced as the temperature rises? Explain the observation. (3 marks)
- Explain the observation made on the amount of urine produced as the temperature increases. (3 marks)
- How does the skin regulate temperature? (6 marks)
- On the same graph, plot the quantities of urine and sweat produced against the external temperature. (7 marks)
-
- What is meant by the term digestion (2 marks)
- Describe how mammalian small intestine is adapted to its function (18mks)
-
- Explain how xerophytes are adapted to their habitats (10 marks)
- Describe how insect pollinated flowers are adapted to pollination. (10 marks)

MARKING SCHEME
-
-
- State the pH at which the enzyme is most active. 2.5 (1 mark)
- Name one enzyme likely to be the one in the figure above and suggest the part of the alimentary canal where it is found. Name - Pepsin/Rennin; Location in the alimentary canal - Stomach. (2 marks)
- Name the digestive juice that contains the enzyme. Gastric juice (1 mark)
- Enzymes work best at optimum temperatures; At very low temperature enzymes are inactivated thus the rate of enzyme reaction decreases;at very high temperatures above optimum enzymes are denatured thus the rate of enzyme reaction decreases (3mks)
- Enzyme specificity – a particular enzyme only acts on a specific substrate. (1mk)
-
-
- blood
- R – Platelets S - White blood cells T - Red blood cells
- S – Engulf and destroy foreign micro – organism R – Involved in clotting of blood.
-
- Biconcave disc to create a large surface area through which oxygen diffuses into cell.
- Lack nucleus to create more space for packing of haemoglobin
- Contain haemoglobin which has high affinity for oxygen.
-
- Thrombosis
- Arteriosclerosis
- Hypertension
- Varicose veins
-
- Photosythesis is the process by which plants manufacture food substances from carbon (IV)oxide and water using energy from sunlight. (1mk)
- Carbon (IV) oxide and water.(2mks)
-
- Temperature
- carbon (IV) oxide
- light intensity .
- Availabilty of water (3mks)
-
- Occurs in the grana of chloroplasts
- The light trapped is used to split water molecules into hydrogen atom and oxygen gas i.e photolysis.
- Some of the light energy is used in the formation of ATP.(3mks)
-
- A – Nitrogen fixation; D – Absorption; (2mks)
- Nitrites; (1mk)
- Denitrifying bacteria/Pseudomonas denitrificans/Thiobacillus denitrificans/ Denitrifiers; (1mk)
-
- Leguminous plants/legumes/e.g. beans, peas, covers, cashew nuts, groundnuts, accassia (accept a correct example). (1mk)
- Root nodules; rej root Acc. Root tubercles. (1mk)
- Reduction/killing of decomposers; Reduction/killing of nitrogen fixing bacteria; Destruction of leguminous plants/killing of leguminous plants; (2mks)
-
- Division Pteridophyta;
Reasons: Leaves are compound with leaflets/Pinna/frond; Presence of sori; Presence of horizontal underground stem/Rhizome (2mks) -
- Sporangia (1mk)
-
(2mks)Pteridophyta
Spermatophyta
fertilization is dependent on water
fertilization is mainly independent of water
Does not produce seeds
Seed bearing
- Gaseous occurs through the skin, mouth and lungs /Hind limbs are longer and more muscular than the forelimbs. (2mks)
- Division Pteridophyta;
-
- Labeling of axis; (1mk) Scale ; (1mk) Curves; (2mks) Plotting points; (2mks) Curve labelling; (1mk)
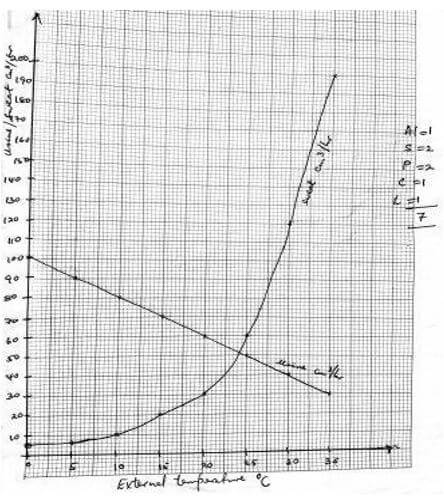
- 24ºC;
- Sweat production increases with increase in temperature; because high temperatures increase the evaporation rate, hence more sweat is converted to water vapour; This uses latent heat of vapourization from the body causing cooling; (3mks)
- An increase in temperature decreases the amount of urine produced; This is due to increased sweating which raises the osmotic pressure of blood; A lot of water is reabsorbed into blood in the kidney tubules resulting in the production of little, concentrated urine; (3mks)
- Hair - When hot, the erector pili muscle relax; the hair lies that on the skin surface; to reduce insulation and encourage heat loss; When cold, the erector pili muscles contract; causing hairs to stand and trap a layer of warm air which insulated the body; (3mks)
Blood vessels - When cold blood vessel; constrict (vasoconstriction); Less blood flows near skin surface; reducing heat loss by radiation and convection; When hot, blood vessels dilate (vasodilatation); more blood flows on the skin surface; increasing heat loss by radiation and convection thus cooling the body; (3mks)
Sweat glands - When hot, sweat is released; it evaporates, taking latent heat of vapourisation from the body; hence cooling it; When cold, sweat glands release less sweat; there is less evaporation; and hence less heat loss; Total = (9mks; Max = 6mks)
- Labeling of axis; (1mk) Scale ; (1mk) Curves; (2mks) Plotting points; (2mks) Curve labelling; (1mk)
-
- Digestion is the breakdown of complex food sustances(by enzymes) to simpler compounds which can be absorbed.
-
- The small intestine has two functions i.e final stage of digestion takes place here and so does absorption of soluble products of digestion.
- Is long to provide a large surface area for absorption of digested food.
- Is narrow so as to to bring digested food into close contact with the walls of the ileum for easier absorption.
- Is highly folded/coiled to slow down the movement of food to allow more time for digestion and absorption and also to increase surface area for digestion and absorption.
- Inner surface of the ileum has alarge number of villi and micro villi which increase surface area for absorptionof end products of digestion.
- The wall of the ileum is thin/thin epithelium which is one cell thick to reduce distance over which digested foood has to diffuse into the blood.
- Villus/villi are highly vascularised/have a rich blood supply/rich network of blood capillaries,into which amino acids,glucose,vitamins etc diffuse into and this helps to maintain a steep concentration gradient.
- Villi have lacteal for absorption of fatty acids and glycerol and channels them to lymphatic system.
- Cells of the ileum have a large number of mitochondria to release energy that aids in active transport of materials across the epithelium.
- Have intestinal glands that secretes intestinal juices that complete digestion process since they contain various enzymes e.g.maltase,sucrase,peptidase,lipase to complete digestion of maltose,sucrose,proteins and lipids respectively.(each point 2mrks).
-
- Adaptations of xerophytes
- Some have leaves reduced in size / to spine of reduces the surface area for water loss.
- Some xerophytes have photosynthetic stems that take the place of leaves; to reduce the surface area for transpiration;
- Some shed-off leaves during dry season; reduce surface exposed to transpiration;
- Some have thick wax cuticle; which reduces cuticular transpiration;
- Some xerophytes have fleshy / succulent /juicy stems / roots for storage of water;
- Some have sunken stomata; that accumulate moisture / creating low diffusion gradient; thus reducing transpiration rate;
- Most have reduced number of stomata; mostly on the lower leaf surface to reduce the rate of transpiration; The stomata are also small in size to reduce loss of water by transpiration;
- Some show reversed stomatal rhythm (open stomata at night and close during the day) to prevent excessive loss of water by transpiration;
- Some have succulent stem; that stores water; used in dry season;
- Some have long tap roots that extend deep into the soil to absorb water far below.
- Some xerophytes have shallow roots that spread widely / extensively in order to trap water from any little shower of rain;
- Some xerophytes roll their leaves to reduce surface area exposed thus reducing rate of water loss by transpiration;
- Some xerophytes have thorns on their stems / branches / midribs / leaves to protect the plant from predator / browsers / herbivorous animals;
- Some xerophytes have a very short life cycle thus grow fast to use the little rain within a very short time; and produce seeds that can survive the drought.
- Adaptations of insect pollinated flowers
- Large; brightly coloured petals/ bracts; to attract insects; scented; to attract insects.
- Have nectar guides that direct insects into nectaries which secrete nectar;
- Pollen grains rough/ sticky surface; to stick on insects body;
- Special shaped corolla tube; to enable insects to land
- Anthers situated inside the flowers; to ensure that they get into contact with the insect;
- Sticky stigma; for pollen to stick and adhere; Total 12 marks = max 10 marks
- Adaptations of xerophytes
Download Biology P2 Questions and Answers - Form 3 Term 3 Opener Exams 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

