QUESTIONS
SECTION A:ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS IN THIS SECTION (25MRKS)
-
- A part from planets, name two other members of the solar system (2mks)
- State three characteristics of planets (3mks)
-
- Name the three main layers of the atmosphere from the earths surface upwards (3mks)
- State two ways in which the atmosphere is heated up (2mks)
-
- Distinguish between minerals and rocks (2mks)
- The table below shows types of sedimentary rocks. Name the resultant rocks that forms after metamorphism (3mks)
Rock Metamorphism equivalent- Sand stone --------------------------------
- Limestone --------------------------------
- Clay -------------------------------
-
- Distinguish between vulcanicity and volcanicity (2mks)
- State three characteristics of basic lava domes (3mks)
-
- State two sources of underground water (2mks)
- Give three factors which influence the formation of features in limestone areas (3mks)
SECTION B
ANSWER QUESTIION 6 AND ANY OTHER TWO QUESTIONS FROM THIS SECTION
- Study the map of Busia (1:50.000) sheet 101/1 provided and answer the following questions
-
- Give the latitudinal and longitudinal position of South East corner of the map (2mks)
- Give two methods used to represents relief on the map (2mks)
-
- Calculate the area enclosed by the international boundary and Northing 40 up to the western margin of the map .Give your answers in Km² (2mks)
- What is the length of the loose surface road c 526 from the junction near Odiado school, grid reference 276318 to the end of the map on the East end ?(2mks)
- Give the bearing of the road junction at Matayo from the air photo principal point in the Grid square 3141. (2mks)
- Draw a square measuring 10cm x 10cm to represent the area from Easting 20 to 25 and Northing 28 to 33.
On it mark and label- Swamp
- A road C523
- River Wakhungu
- Thicket (6mks)
-
- Describe the drainage of the area covered by the map (5mks)
- Citing avidence from the map give two economic activities used in the area covered by the map (4mks)
-
-
-
- Differentiate between weather and climate (2mks)
- State three characteristics of the inter-tropical convergenze zone (I.T.C.Z ) (3MKS)
- The diagram below shows climatic regions of Kenya. Use it to answer questions which follow.
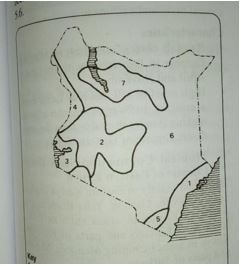
- Name the climatic regions marked 1,2 and 7 (3mks)
- State the climatic characteristics of the region marked 3 (4mks)
- Explain how the following factors influence climate
- Altitude (3mks)
- Ocean currents (3mks)
- Students of Wako secondary school carried out field study on a weather station near their school.
- Name three instruments that they are likely to identify in a weather station (3mks)
- State two reasons why they need a pre-visit before they set out for the study (2mks)
- Name two methods they would use to collect the data during the study (2mks)
-
-
-
- Define the term catchment area (2mks)
- State four features which results from river erosion (4mks)
-
- Differentiate between river capture and river rejuvenation (3mks)
- Name three features resulting from river rejuvenation (2mks)
- Explain four ways in which the river transports its load (8mks)
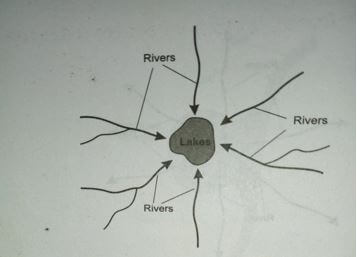
- Using diagrams describe the following drainage patterns
- centripetal (2mks)
- Radial (2mks)
- Dendritic (2mks)
-
-
-
- Define an ocean (2mks)
- List three types of tides (3mks)
-
- Name and describe two processes of wave erosion (4mks)
- The diagram below shows features resulting from wave action .Use it to answer questions which follows
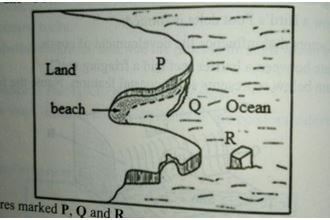
Name the features marked P,Q and R (3mks)
-
- Describe how a wave cut plat form is formed (5mks)
- State two types of submerged highland coast (2mks)
- Explain the significance of oceans to human activities (6mks)
-
-
-
- Distinguish between aridity and desertification (2mks)
- Identify two types of desert surfaces (2mks)
- Give two reasons why wind action is most active in hot deserts than in cold deserts (2mks)
- Explain the following processes of wind erosion
- Abrasion (2mks)
- Deflation (2mks)
- Attrition (2mks)
-
- State two factors that influence the transportation of material by wind in deserts (2mrks)
- Using a well labeled diagram explain the formation of a barchans (5mks)
- Explain three significance of desert features to human activities. (6mks)
-
MARKING SCHEME
-
- Apart from planets,name two other members of the solar system.
- The sun
- Asteroids
- Comets
- Meteoroids
- Meteors
- Meteorites
- Moon(satellite) 2x1=mrks
- State three characteristics of planets
- They are spherical in shape
- They don’t have their own light but reflect it from the sun
- They revolve around the sun in anticlockwise directions
- They have their own force of gravity 3X1=3MKS
- Apart from planets,name two other members of the solar system.
-
- Main layers of the atmosphere from the earths surface upwards
- Tropospere
- Stratosphere
- Mesosphere (3x1=3mks)
- Two ways in which the atmosphere is heated up
- Radiation
- conduction
- convection (2x1=2mks)
- Main layers of the atmosphere from the earths surface upwards
-
- Distinguish between minerals and rocks
- Minerals are naturally occurring inorganic substances with definite chemical composition and physical properties while rocks are substances made up of mineral particles forming the earths crust 1x2=2mks
- The table below shows types of sedimentary rocks name the resultant rocks that forms after metarmophism.
Rock Metarmophism equivalent- Sandstone Quartzite or slate (1mk)
- Limestone Marble (1mk)
- Clay Slate or schist (1mk)3x1=3mks
- Distinguish between minerals and rocks
-
- Distinguish between vulcanicity and volcanicity
- Vulcanicity is the process in which solids, liquids or gaseous materials are forced out of the interior into the earth’s crust or onto the surface of the earth while volcanicity is the formation of different features on the earth’s surface after vulcanicity. 1x2=2mrks
- Characteristics of basis lava domes
- Have low heights
- have a broad base
- have gentle slopes
- made up of several layers of basic lava 3x1=3mks
- Distinguish between vulcanicity and volcanicity
-
- Two sources of underground water
- rain water
- magmatic water
- snow melt
- lakes/oceans 2x1=2mks
- Factors influencing formation of features in limestone areas
- The surface rock must be thick limestone to allow solubility by rain water
- The rock should be hard and well jointed to allow water to percolate through the lines of weakness.
- The climate should be hot and humid.
- The water table should be far below the surface to allow for the formation of the features 3x1=3mks
- Two sources of underground water
-
-
- Latitudinal and longitudinal position of the South East corner of the map
- 0° 15’N 34° 15’E (2mks)
- Methods of representing relief
- contours
- trigonometrical station2x1=2mks
- Latitudinal and longitudinal position of the South East corner of the map
-
- The area enclosed by the international boundary and northing 40
- 18 complete squares
- 12 incomplete squares
18+12=6
2
=18+6=24sqkm 1x2=2mks
±0.5 sq km
NB: No mark if units are not mentioned
- The length of the loose surface road c 526 from junction near odiado school grid reference 276318 to the edge of the map on the East end
- 13.3 km ±0.5km 1x2=2mks
NB:A ward only if units are mentioned
- 13.3 km ±0.5km 1x2=2mks
- The bearing of the road junction at Matayo from the air photo principal:
- 3141 2380 ± 1 1x2=2mks
NB: Award only if degrees are stated
- 3141 2380 ± 1 1x2=2mks
- The area enclosed by the international boundary and northing 40
-
- A square representing a square representing the area from Easting 20 to 25 and Northing 28 to 33.
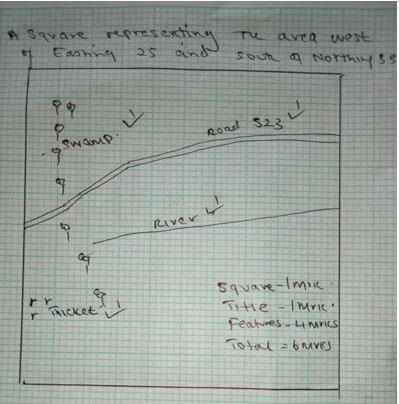
- A square representing a square representing the area from Easting 20 to 25 and Northing 28 to 33.
-
- The drainage of the area covered by the map.
- Main drainage feature are the rivers
- There are swamps
- The rivers are permanent
- The rivers form dendritic drainage pattern
- Main river is river Soi and it flows south westwards
- Some rivers have bends/meanders
- Some rivers are short and disappear underground eg River Wakhungu in the swamp. 5x1=5mks
- Economic activities in the area covered by the map
economic activity Evidence- Transport presence of all weather roads
- Trading presence of markets
- Crop growing/farming agriculture Presence of cotton shore2x2=4mks
NB: To award activity should be accompanied by evidence
- The drainage of the area covered by the map.
-
-
-
- Differentiate between weather and climate
- weather is the condition of the atmosphere for a short period of time usually a day while climate is the average weather conditions of a place over a long period of time usually 30-35 yrs 1x2=2mks
- Three characteristics of I.T.C.Z
- It’s a region of low pressure belt
- It experiences high temperature
- The zone migrates North or South of the equator depending with the apparent movement of the sun.
- A zone where N.E and S.E winds converge
- It receives high rainfall associated with lightning and thunderstorms
- The zone is within the tropics3x1=3mks
- Differentiate between weather and climate
-
- Name the climatic regions marked
- 1-Modified equatorial climate of the coast
- 2-Modified tropical climate of the highlands
- 7-Desert climate 3x1=3mks
- State three characteristics of the climatic region marked 3
- Has double maxima rainfall mostly in the afternoon
- Relative humidity is high
- experiences convectional type of rainfall
- experiences high temperatures
- receives high rainfall throughout the year
- There is no dry month 3x1=3mks
- Name the climatic regions marked
-
- Altitude
- Temperature decrease with increase in altitude
- Temperature decrease inland towards the highlands areas
- Areas along the coast with low altitude experience higher temperature.
- High mountains have lower pressure than lowlands
- The windward side of mountains receives higher rainfall than the leeward side.
- Ocean currents
- If the ocean currents are cold, the winds are cooled and as they approach the coast they bring cooling effects onto the land resulting in the lower temperate on the land
- If the ocean current is warm the winds which cross it will carry a warming influence onto the land
- In temperate lands winters tend to be warmer than expected and the coastal areas are free from snow.
- The cold ocean currents chill the rain-bearing winds which eventually drop the moisture over the sea on reaching the land the wind bring little rain to the coastal regions to have a semi-arid or arid-climate.
- If ocean currents are warm the on-shore bearing winds will be warmed up and they hold onto the moisture until they reach the land where they cause heavy rainfall. 3x1=3mrks
- Altitude
- Students of Wako secondary school carried outfield study on weather station near their school.
- Name instruments that they were likely to identify in the weather station
- Maximum and minimum thermometer
- raingauge
- hygrometer
- barometer
- anemometer
- sunshine recorder
- wind vane 3x1=3mks
- Reasons why they needed a pre-visit
- To seek permission from relevant authorities
- To enable them formulate objectives and hypothesis
- Helps in identifying appropriate equipments or instruments to be used in the study
- Identify problems they are likely to encounter
- To help them prepare for a working schedule
- Help to identify suitable data collecting methods.
- Help to access the suitability of the study area 2x1=2mks
- Method they would use to collect the data
- Observation
- oral interview
- photographing
- extracting/reading from secondary sources2x1=2mks
- Name instruments that they were likely to identify in the weather station
-
-
- Define the term catchment area
- This refers to the entire area drained by a river and its tributaries 2x1=2mks
- Features resulting from river erosion
- v-shaped valley
- interlocking spurs
- pot holes
- gorges
- waterfalls
- rapids
- bluffs 4x1=4mks
- Features resulting from river erosion
- This refers to the entire area drained by a river and its tributaries 2x1=2mks
-
- Differentiate between river capture and river rejuvenation
- River rejuvenation is the renewal of the rivers erosive activity while river capture is the diversion of the headwaters/beheading of one river into the system of adjacent more powerful river. 1x2=2mks
- Features of river rujevenation
- Knick point
- River terraces
- incised meanders
- rejuvenated gorges
- abandoned meanders 3x1=3mks
- Differentiate between river capture and river rejuvenation
- Ways in which the river transports its load
- suspension-fine particles such as silt are carried in suspension because they are light and can be maintained within the turbulence of the water
- Traction-The large and heavy particles slide or rolled along the river bed.
- Solution-soluble materials are dissolved in water and carried away.
- Hydraulic lift-The fairly heavy particles or pebbles are lifted and bounce over short distance by the turbulence of the water.4x2=8mks
- Using diagrams describe the following drainage patterns
- Centripetal
- Many rivers flow into a central basin from all directions
1mk diagram
1mk explanation (2mks)
- Many rivers flow into a central basin from all directions
- Radial
- It comprises rivers that flows out in all directions from a central high point such as volcanic cones
- The mountain forms a common source of water for rivers
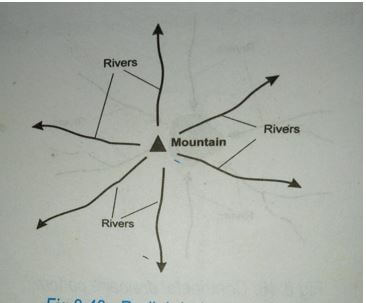
1mk diagram
1mk explanation total 2mks
- Dendritic
- The river has many tributaries that join the main river at acute angles
The river and its tributaries form a pattern of a tree and its branches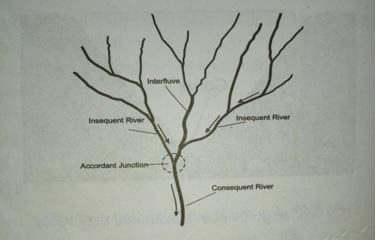
1mk diagram
1mk explanation
total( 2mks)
- The river has many tributaries that join the main river at acute angles
- Centripetal
- Define the term catchment area
-
-
- Define a coast
- An ocean is an extensive body of salty water on the earth’s surface that surrounds land or continents 1x2=2mks
- Types of tides
- Apogean tides
- perigean tides
- neap tides
- spring tides 3x1=3mks
- Define a coast
-
- Name and describe two processes of wave erosion
- abrasion or corrasion:rock fragments carried by waves are used as a tool to grid against cliff face as waves break rock fragments carried by backwash erodes the area.
- Solution or corrosion-The solvent and chemical action of the sea water dissolves and removes the soluble minerals that are found in the cliff or sea floor especially where there are limestone rocks.
- Hydraulic action-The swash or breaking waves hit against the cliffs shattering the rocks. The breaking waves compress air into the cracks or joints in the cliff face. This widens the cracks and parts of the rocks may break off
- Attrition –particles that are carried by waves are constantly colliding against each other and wears them into smaller sizes 2x2=4mks.
- Features resulting from wave action
- P Headland (1mk)
- Q Spit (1mk)
- R stack (1mk) Total (3mks)
- Name and describe two processes of wave erosion
-
- Describe formation of wave out platform
- wave erosion attacks steeply sloping coast at the high tide level forming a notch.
- Part of the steep land over the notch becomes an overhanging block
- The overhanging block collapses forming a cliff
- Wave erosion cuts a new notch into the cliff
- Eventually an overhanging block forms over a new notch
- When this block collapses a new cliff forms further inland
- The floor of the sea between the original position on the steep land and the new cliff forms a wave –cut platforms (5x1)=5mks
- Two types of submerged highland coasts
- Ria coast
- fiord coast
- Dalmatian coast/longitudinal coast 2x1=2mks
- Describe formation of wave out platform
- Significance of oceans to human activities
- oceans contribute the bulk of moisture to the atmosphere through evaporation
- This sustains the hydrological cycle and are the source of the bulk of rainfall which support agricultural activities
- oceans connect many countries of the world and are used by people as a mode of transporting people and goods
- Ocean waves are harnessed which generate tidal/electric power for industries
- Oceans provides sites for recreation activities such as swimming, surfing, water and yatching. These activities promote tourism.
- Oceans are major fishing ground because they contain a large variety of fish. many countries do commercial fishing within their territorial waters and beyond.
- Oceans promote education and research
- Oceans provide base for military activities such as the navy.3x2=6mks
NB: Students should not confuse the significance of oceans to coastal features
-
-
-
- Distinguish between aridity and desertification
- Aridity is the state of insufficient moisture on the earth’s surface leading to scarcity of vegetation while desertification is the slow but steady encroachment of desert like conditions into formely productive land 1x2=2mks
- Identify two types of desert surface
- erg/sandy desert
- reg/stony deserts
- rocky/Hamada deserts
- badlands 2x1=2mks
- Give two reasons why wind action is most active in hot deserts than cold deserts.
- presence of loose unconsolidated materials of rock easily carried away by wind.
- Strong tropical storm in deserts leading to high velocity winds
- Absence of vegetation hence no obstruction to the wind load 2x1=2mks
- Distinguish between aridity and desertification
- Process of wind erosion
- Abrasion-is the mechanical erosion caused by the windborne materials as they grid,scrab and polish desert surface features 2x1=2mks
- Deflation-it is the blowing away of loose unconsolidated materials like dust and fine sand particles by rolling and lifting them up the ground 2x1=2mks
- Attrition-wearing away of windborne materials as they rub against each other during transportation 2x1=2mks
total=6mks
-
- Two factors that influence the transportation of materials by wind in desert.
- strength and speed of wind
- presence of obstacles
- nature of the load
- weather changes changes.2x1=2mks
- Formation of a barchans using a well labeled diagram
- A Barchans develop in arid areas when sand accumulates around an obstacles that lies in the path of the wind.
- The gradual accumulation of sand -forms a hill.
- Eddy currents on the leeward side of the dune causes the formation of a shallow depression or concave or steep slope.
- With time the -prevailing wind forces the sand at the edge of the dune to move forward forming the horns.
- The continuous extension of the horns lead to a crescent shaped feature called barchans.
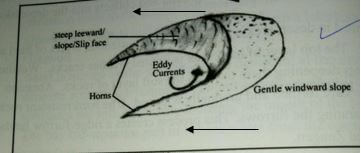
- Two factors that influence the transportation of materials by wind in desert.
- Explain the significance of desert features to human activities
- desert features form good sites for tourist attraction, thereby earning foreign exchange
- wind deflation hollows or oasis are source of water for domestic and agricultural use.
- wind deposited sands or loess form fertile plains for farming
- Salty flats are economically used for salt production
- shifting sand dunes hinder transports activities
- desert sceneries are ideal for film making
- The vast sand seas are ideal for military training and nuclear testing.
3x2=6mks
-
Download Geography P1 Questions and Answers - Form 3 Term 3 Opener Exams 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

