QUESTIONS
SECTION A (25MKS).Answer all questions.
- The fig. 1 below shows a vernier calliper. State the reading indicated on the instrument. (2marks)
Figure 1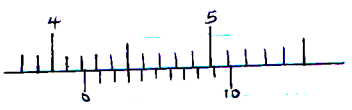
- When a body of mass 0.25kg is acted on by a force, its velocity changes from 5m/s to 7.5m/s. determine the work done by the force. (3marks)
- An object weighs 7N on earth where acceleration due to gravity is 10N/kg. Find the acceleration due to gravity on another planet where the same object weighs 5N. (2 marks)
- The fig.2 below shows a funnel dipped into a liquid soap solution.
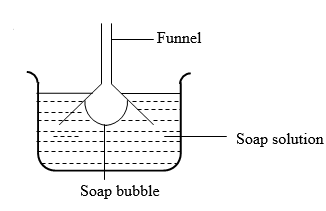
Figure 2
Explain what happens to the soap bubble when the funnel is removed from the soap solution. (1mark) - Highlight two facts which shows that heat from the sun does not reach the earth surface by convection. (2marks)
- The fig 3 below shows a uniform beam of length 1.2m pivoted near one end. The beam is kept in equilibrium by a spring balance as shown.
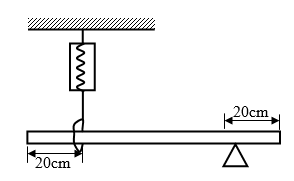
Figure 3
Given that the reading on the spring balance is 0.75N, determine the weight of the beam. (2marks) - The fig.4 below shows a U- tube manometer open at one end and the other end connected to the gas supply.
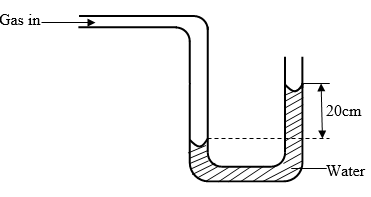
Figure 4
Given that the atmospheric pressure is 1 x 105pa and density of water= 100kg/m3, determine the pressure of the gas. (3marks) - Smoke particles are observed through the eye piece of a microscope. They are seen to move randomly. Explain what causes this motion. (1 Mark)
- State how the length of a conductor affects its rate of thermal conductivity. (1mark)
- A tape attached to a moving trolley is run through a thicker timer. A section is shown in Fig 5 below. If the frequency of the ticker timer is 50HZ, calculate the acceleration of the trolley. 3marks)
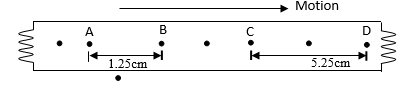
Figure 5 - A load (L) was raised using the system shown in fig.6 (a).The system was modified as shown in fig 5 below and used to raise the same load. Explain the change in efficiency. (1mark)
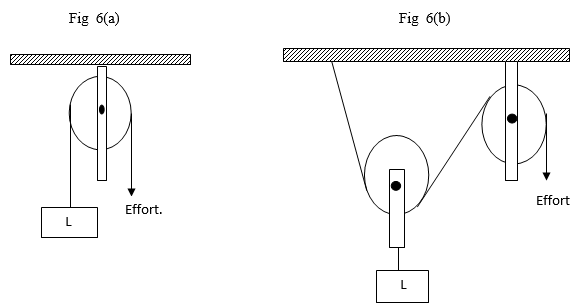
- A tout placed a boy on the carrier of a matatu and forgot to tie it up. State and explain what happened to the boy when the matatu suddenly came to a stop. (2marks)
- The fig. 7 below shows water entering a pipe at a velocity of 40m/s. The pipe widens on the outlet. Use the information to calculate the velocity of water at end B.
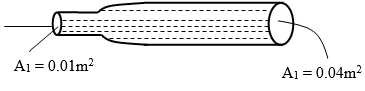
Fig 7
SECTION B. 55MKS
Answer all questions in the spaces provided below each question.
-
- Define the term specific heat capacity of a substance. (1mark)
- Fig 8 below shows a heating curve of a substance W.
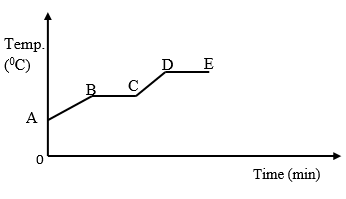
Fig 8- Explain the shape of the graph between points.
- B and C (1 Mark)
- Dand E (1 Mark)
- State a reason why the graph did not start from the origin O. (1mark)
- Explain the shape of the graph between points.
- A block of metal of mass 150g at 120ºC is dropped into lagged calorimeter of heat capacity 40JK-1 containing 100g of water at 40ºC.The temperature of the resulting mixture is 46ºC.Taking 4200JKg-1K-1, determine:
- The heat gained by the calorimeter (2marks)
- The heat gained by water (2marks)
- The heat lost by the metal block (2marks)
- The specific heat capacity of the metal block. (2marks)
-
- State Boyle’s law. (2marks)
- With the aid of labeled diagram describe an experiment to verify Boyle’s law. (5marks)
- Why does an air bubble increase in volume as it rises to the surface of water in a boiler. (2marks)
- A bubble of air rising from the bottom of pond doubles its volume first as it reaches the surface of the pond. Calculate the depth of the pond assuming that the temperature remains constant. (3marks)
-
- Define impulse interms of momentum. (1mark)
- A particle of mass m, is initially moving vertically downwards with a velocity u, m/s, obtain an expression for changes in kinetic energy after:
- It has moved freely under gravity for time t. seconds. (2marks)
- It has moved freely under gravity for a vertical distance ,s, meters. (2marks)
- A lead ball is placed on the surface of a viscous fluid and released.
- State three forces acting on the ball as it falls through the fluid. (3marks)
- State the force which vary as the ball falls and why the variation. (2marks)
- What is meant by the term terminal velocity of the ball. (1mark)
- Sketch a graph showing the variation of the displacement of the ball with time from when it was released. (1mark)
-
- Define the following terms:
- Velocity ratio (1mark)
- Mechanical advantage (1mark)
- Name a device that is used to convert sound energy to electrical energy. (1mark)
- A bullet of mass 20g travelling at 4000m/s is stopped by a concrete wall. Calculate the amount of energy transferred to the wall. (2marks)
- A spring with a spring constant of 68N/m stretches by 0.22m when a force is applied on it . Determine the energy stored in the stretch spring. (3marks)
- A pulley system having a velocity ratio of 4 is used to raise a load of 80N through a height of 0.6m at a constant speed using an effort of 20N in a time of 15 seconds . Calculate the power developed by the effort. (3marks)
- Define the following terms:
-
- A matatu starts from rest and accelerates to cover a distance of 49m in 7 seconds. Determine
- Its acceleration (2marks)
- Its velocity after 7 seconds (2marks)
- A trolley moving in a horizontal bench of height 1.2m strikes a barrier at the edge of the bench. The brass mass on top of the trolley flies off on impact and lands on the ground 2.5m from the edge of the bench. Determine
- The time taken by the brass to reach the ground . (2 Marks)
- The speed at which the trolley struck the barrier. (2 marks)
- A matatu starts from rest and accelerates to cover a distance of 49m in 7 seconds. Determine
MARKING SCHEME
- Main scale = 4.20
Vernier scale = 0.03 +
Actual reading = 4.23cm - Work done = Δ K.E
=1/2mv2 -1/2mu2
=1/2x 0.25 x (7.5)-1/2x 0.25 x52
=3.906J - W1=mf1
7N=m x 10N/kg
m=7N/10N/kg=0.7kg
W2 =mg2 g2 =5N/0.7kg
g2= 7.143N/kg - Bubbles flattens to a film, and moves up the funnel in order to make its surface area as small as possible.
- Convection current takes place upwards.
Convection requires material medium but the space between the sun and atmosphere has no material medium. -
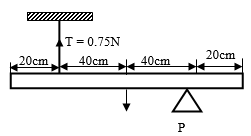
wt x 40 =0.75 x 80
wt= 1.5N - P= Pa +h∂g
= 1x 105 +(0.2 x1000 x10)
=1x 105 +2000
=102000 Pa - The motion is due to the constant collision between the smoke and air particles, which are in random motion.
- The longer the conductor the slower the rate of thermal conductivity.
- T= 1/50= 0.02 sec
VAB = 1.25
2 x 0.02
=31.25cm/s
VCD = 5.25
0.04
=131.25cm/s
Acceleration = (VCD-VAB)
(7 x 0.02)
=131.25 -31.25
0.14
=100/0.14 =714.29cm/s
=7.143m/s - Velocity ratio (V.R)increases
efficiency decreases. - The boy falls in front of the matatu . This is because of inertia.
- A1V1 =A2V2
= 0.01X 40=0.04x V2
v2= 0.01 x40
0.04
=10m/s -
- Quantity of heat required to change the temperature of a unit mass of a substance by 1 Kelvin.
-
-
- Temperature remains constant as the solid changes to a liquid, (melting point).
- Temperature constant .Heat absorbed used to change liquid to gaseous state (boiling point).
- The substance had some heat energy before it was heated.
-
-
- Qc = C Δ θ
=40JK-1 X6
=240 J - QW = Mw Cw Δ θ
=100/1000x 4200x 6
=2520J - Heat lost = Heat gained
= 2520+240
=2760J - Mm Cm Δ θ=2760
Cm = 2760
0.15x74
=248.65J
- Qc = C Δ θ
-
- Volume of a fixed mass of a gas is inversely proportional to the pressure provided temperature is kept constant.
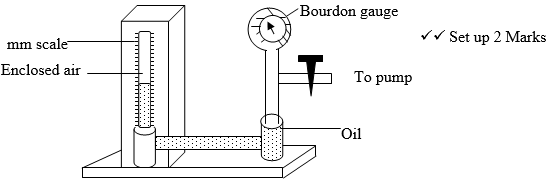
The pump is used to compress air. The pressure is recorded on the bourdon gauge and corresponding volume read on the mm scale. - A graph of V against P is plotted from a set of readings obtained.
- As it rises the pressure exerted on it decreases hence volume increases according to Boyle’s law.
- P1V1 = P2V2
but V1 =2V2
P2 = P1V1
V2
=P1 X 2V1
V1
=2P1
P2=2 X 1.013 X105
=2.026 X105 Pa
Pressure due to the liquid =P2-P1
=(2.026 -1.013) X 105
=1.013 X105 Pa
height h = 1.013x 105
1000 x10
=10.13m
- Volume of a fixed mass of a gas is inversely proportional to the pressure provided temperature is kept constant.
-
- Impulse =change in momentum .
-
- after t seconds
v=u +gt
Δ K.E = ½ mv 2
½ m(u+gt)2
½ mu2+2x ½ mu gt + ½ mg2t2
=1/2mu2+ mugt + ½ mg2t - After s meters
V2=U2+2 GS
Δ K.E =1/2m (u2+2gs)
=1/2 mu2 +mgs
=1/2mu2+mgs.
- after t seconds
-
-
- up thrust
- weight
- Viscous drag
- Viscosity varies
Reason: Acceleration causes a change in Viscosity. - Constant velocity when upward forces equals the downward forces
-
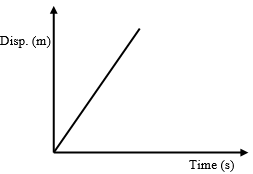
-
-
-
- Velocity ratio is the ratio of effort distance to load distance.
- M.A is the ratio of load to effort.
- Microphone
- Lose in k.e =Gain in heat energy
½ mv2
½ x 20/100 x (400)2
=1600J. - k= ½ ke2
½ x 68 x (0.22)2
=1.6J - Power = work done by effort
time
= effort x effort distance
time
but V.R = effort distance
load distance
=4= x/0.6
x=2.4m
power p =(20x 2.4) =3.2w
15
-
-
-
- s= u t +1/2 at2
=θ+1/2 a x 72=49
A = 2m/s2 - V= u + at
v = 0+(2x 7)
= 14m/s
- s= u t +1/2 at2
-
- s = u t + ½ gt2
=0+ ½ x10x t2 =1.2
t= 0.49 seconds - s=u t
u =s/t
=2.5/0.49
= 5.102m/s
- s = u t + ½ gt2
-
Download Physics Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Form 3 End Term 3 2022 Exams.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

