QUESTIONS
SECTION A (40 MARKS)
Answer all questions in this section in the spaces provided.
-
- Define the term denature (1 Mark)
- In an experiment to investigate the action of pepsin on egg albumen, equal amounts of pepsin were added to equal amounts of egg albumen in different test-tubes. The test tubes were placed in water baths at different temperatures. The graph below shows time taken for the enzyme to digest protein in each.
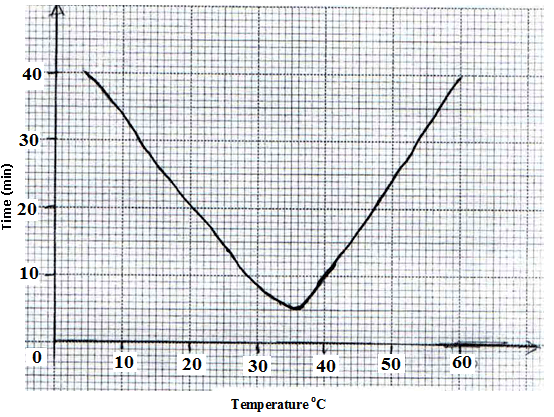
- What is the optimum temperature for the enzyme? (1 Mark)
- Account for the time taken to digest egg albumen at 45ºC. (1 Mark)
-
- In which form is the enzyme pepsin secreted. (1 Mark)
- Give a reason for your answer in c (i) above. (1 Mark)
- Name four plant tissues which lack chloroplast. (2 Marks)
- State the function of the pad of gum in herbivorous feeding. (1 Mark)
- During ecological study, students collected and marked 120 ants and released them. After 48 hours, the students captured another 90 ants, 20 of which had been marked previously.
- How many ants were there in the compound? Show your working. (3 Marks)
- What are the limitations of this method in sampling animal populations? (3 Marks)
- State two other methods which could be used to determine the population? (2 Marks)
- The experiment below was set-up to investigate some physiological processes. The glucose solution was first boiled then cooled. The set-up was left for 24 hrs.
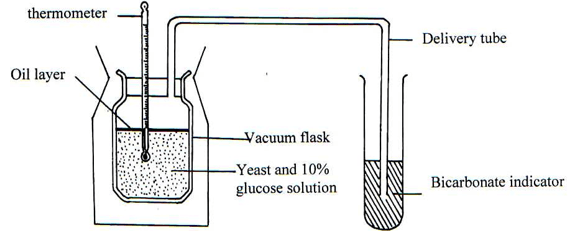
- Suggest two aims of the experiment. (2 Marks)
-
- State the expected observations after 24 hours. (2 Marks)
- Explain your observations in b (i) above. (1 Mark)
- Why was glucose solution boiled then cooled? (1 Mark)
- Suggest a control for the above experiment. (1 Mark)
- The diagram below shows an experimental set up to investigate an aspect of germination.
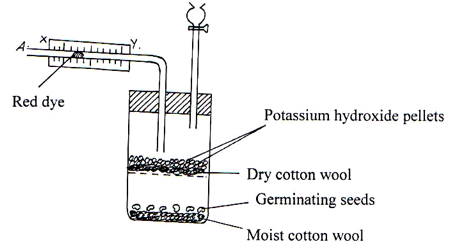
- Why are the following used in this experiment?
- Potassium hydroxide pellets? (1mark)
- Moist cotton wool? (1 mark)
-
- With reference to points x and y state the direction the dye would move towards during the experiment. (1 mark)
- Give reasons for your answer in (b) (i) (2 Marks)
- Why are the following used in this experiment?
- In an experiment to investigate a factor affecting photosynthesis, a leaf of a potted plant which had been kept in the dark overnight was covered with alluminium foil as shown in the diagram below.
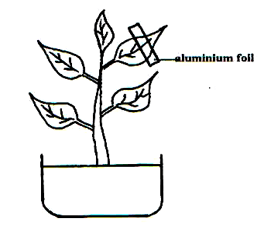
The set up was kept in sunlight for three hours after which a food test was carried out on the leaf.- Which food test was carried out? (1 Mark)
-
- State the results of the food test. (2 Marks)
- Account for the result of the food test. (2 Marks)
-
- Why was the set up kept in sunlight for three hours. (1 Mark)
- Why was it necessary to keep the plant in the darkness before the experiment? (1 mark)
- Other than light state one other factor that affects the rate of photosynthesis. (1 Mark)
SECTION B – 40 MARKS
Answer question 6 (compulsory) and either 7 or 8
- In an experiment to investigate a certain process in a given plant species, the rate of carbon (IV) oxide consumption and the rate of Carbon (IV) oxide release were measured over a period of time for the day. The results of the investigation are as shown in the table below.
Time of days (hrs)
6.00
8.00
10.00
12.00
14.00
16.00
18.00
20.00
22.00
24.00
CO2 consumption mm3/min
0
43
69
91
91
50
13
0
0
0
CO2 release mm3/min
38
22
10
3
3
6
31
48
48
48
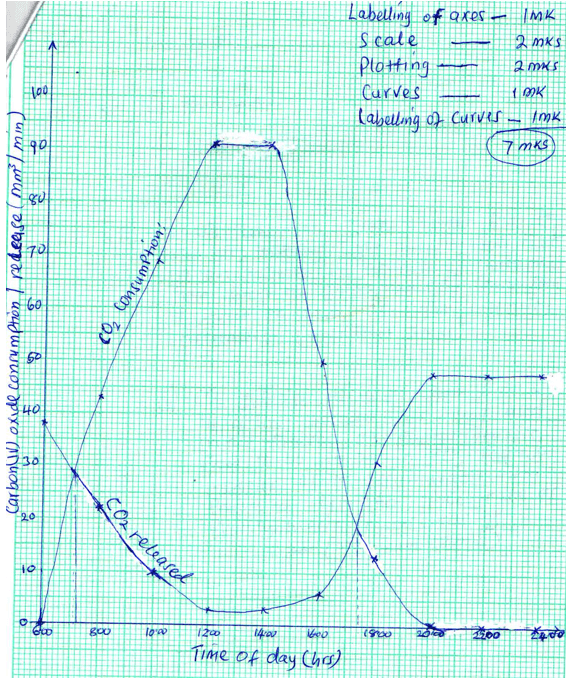
- On the same axes, draw the graphs of volume of Carbon (IV) oxide consumed and Carbon (IV) oxide released against time. (7 Marks)
- Name biochemical processes represented by;
- Carbon (IV) oxide consumption (1 Mark)
- Carbon (IV) oxide release (1 Mark)
- Account for the shape of the curve for
- Carbon (IV) oxide consumption. (3 Marks)
- Carbon (IV) oxide release (3 Marks)
-
- From the graph, state the time of the day when the plant attains compensation point. (1 Mark)
- What is meant by compensation point. (1 Mark)
- Explain how temperature affects the rate of Carbon (IV) Oxide consumption in a plant. (3 Marks)
- On the same axes, draw the graphs of volume of Carbon (IV) oxide consumed and Carbon (IV) oxide released against time. (7 Marks)
-
- Name five methods of excretion in plants. (5 Marks)
- Give three reasons why plants lack complex excretory system. (3 Marks)
- State six excretory products in plants and give their economic uses. (12 Marks)
-
- What is pollination? (2 Marks)
- Discuss the sequence of events that take place from the time a pollen grain falls on the stigma until a seed is formed. (18 marks)
MARKING SCHEME
-
- Denature –change in protein structure so that some of its original properties /configuration stop
functioning; -
- Optimum temperature 36 ± 1;
- At 45º C time taken is more than at 35ºC because enzyme /pepsin is being denatured;
-
- Pepsinogen;
- Digest stomach /digest lumen in its active form (pepsin) in absence of protein food;
- Epidermal tissue
Parenchyma;
Schlerenchyma;
Xylem tissue;
Collenchyma; - Provides surface on which food /grass is pressed and cut:
- Denature –change in protein structure so that some of its original properties /configuration stop
-
- Approximate population=
No.of organisms in first catch X No. of organisms in second catch
No. of marked organisms recaptured
i.e P = FM X SC
MR 1mk
= 120 x 90 = 540 1mk
20 -
- Does not consider migration of organisms into and out of study area;
- Does not consider the effects of paint used on the animals behavior;
- Released animals may not mix freely with the remaining population;
- Marked organisms may not have adequate time to mix with the rest;
- Does not consider the effects of weather on the organisms behavior; any 4 @ 1mk each
-
- Quadrant method
- Belt transect method
- Line transect method any 2@½mk each
- Approximate population=
-
-
- To find out whether energy /heat is released in anaerobic respiration /fermentation;
- To investigate the gas produced during fermentation/anaerobic respiration. 2mks
-
- (significant)rise in temperature ;color of bicarbonate indicator turns yellow. 2mks
- Yeast will respire aerobically releasing energy /and carbon dioxide gas that turn indicator yellow. 1mk
- Expel /drive out oxygen; 1mk
- Use glucose solution without yeast cells/killed yeast cells. 1mk
-
-
-
- Absorb carbon (IV)oxide produced by germinating seedlings. 1mk
- Provide moisture /water for seeds to germinate. 1mk
-
- Towards Y; / X → Y;
- Seeds use up oxygen in flask for respiration during germination; creating a vacuum in the flask; air is drawn in the tube at point A (causing the red dye to move towards Y) 3mks
-
-
- Starch ; 1mk
-
- The covered part remained brown ;uncovered part turned blue-black 2mks
- Starch formed in uncovered part of the leaf (because of light) 1mk
Starch not formed in Covered part of the leaf (because of lack of light); 2mks
-
- To allow photosynthesis /manufacture of food;
- To de-starch the leaf /remove starch from the leaf; 1mk
- Carbon dioxide concentration /soil water; 1mk
-
-
-
- photosynthesis
- Respiration
-
- CO2 consumption increases between 6.00 to 14.00 hrs ;increasing light intensity ;leads to an increase in the rate of photosynthesis, from 16.00 to 24.00, as light intensity decreases;(maximum 3mks)
- CO2 release decreases from 6.00 to 14.00 hrs, because its being used in the process of photosynthesis.
From 16.00 to 24.00 CO2 release increases as it accumulates from process of respiration, since rate of photosynthesis is decreasing. (maximum 3mks)
-
- 7.12 hrs ± 5 (7.07 - 7.17 ) and
17.24 hrs ± 5 (17.19 – 17.29) - The point where the rate of carbon (IV) oxide consumption (during photosynthesis) is equal to rate of carbon (iv)oxide release (during respiration);
- 7.12 hrs ± 5 (7.07 - 7.17 ) and
- Low temperatures inactivate enzymes leading to low rate of photosynthesis /low rate of CO2 consumption/photosynthesis is highest at optimum temperature; temperature above optimum denatures enzymes hence low rate of photosynthesis/ CO2 3mks
-
-
-
- Diffusion .
- Transpiration/guttation;
- Exudation;
- Accumulation in old leaves /flowers/leaf fall
- Storage in bark /wood;
- Re-used e.g. in photosynthesis 6mks
-
Excretory products
use
Caffein;
Papain
Tannin
Nicotine
Latex
Quinine
Atropine
Morphine
Central nervous system stimulant;
Meat tenderizer/treat indigestion;
Leather tanning;
Heart stimulant/ insecticide /reduce stress
Manufacture of tire rubber products;
Anti-malarial drug;
Increase heart beat /drug up secretion/dilate eye pupil;
Cancer treatment;
-
-
- Pollination is the transfer of pollen grains from the other to the stigma in a flower;
- Upon falling on the stigma, the pollen grain uses the nutrients from the stigma to germinate; and from a pollen tube; The pollen tube grows down the style ;The tube nucleus takes a leading position ;followed by the generative nucleus ;The generative nucleus divides by mitosis ;to form two male gamete nuclei; The nuclei passes through the micropyle into the ovary .On arrival at the embryo sac ,the tube nucleus degenerates one male gamete nucleus fuses with the polar nuclei to form a triploid primary endosperm .The other male gamete nucleus fuses with the functional egg to form a diploid zygote. This is known as double fertilization. The integument becomes the testa while the zygote is differentiated into plumule and radical. The primary endosperm becomes the endosperm tissue.
Download Biology Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Form 3 End Term 3 2022 Exams.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

