PHYSICS
INSTRUCTIONS.
Answer all the questions in the spaces provided.

Questions
- Define the term fluid. (1mk)
- Distinguish between streamline flow and turbulent flow. (2mks)
- In deriving the equation of continuity, there are some assumption made. State the three assumption that the fluid must have. (3mks)
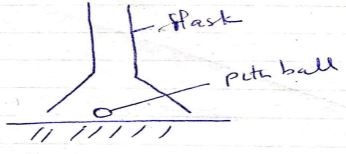
- The figure below shows a pithball placed in a flask. When a jet of air is blown over the month of the flask as shown, the pithball is observed to rise from the bottom. (2mks)
- Water with negligible viscosity flows steadily through a horizontal pipe of various cross-section area. At a point A of cross-section area 10cm2 the velocity is 0.2m/s. calculate:
- The velocity at a point B, of cross-section area 2.5cm2. (3mks)
- State two hazards of Bernoullis effect. (2mks)
- State and explain three factors affecting velocity of sound in air. (3mks)
- The diagram below shows sound waves passing through air. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
Label the following:- Compression (1mk)
- Rarefaction (1mk)
- Wavelength (1mk)
-
- Define moment of a force. (2mks)
- State two factors affecting moment of force. (2mks)
- A uniform metre rule pivoted at its centre is balanced by a force of 4.8N at 20cm mark and some other two forces, F and 2.0N on the 66cm and 90cm marks respectively. Calculate the force F. (2mks)
-
- Define magnetic field. (1mk)
- Draw the field pattern in following. (2mks)
- State three uses of magnets. (3mks)
- The air pressure at the base of a mountain is 75.0cm of mercury while at the top it is 60.0cm of mercury. Given that the average density of air is 1.25kg/m3 and the density of mercury is 13600kg/m3, calculate the height of the mountain. (3mks)
-
- Differentiate between a transverse wave and a longitudinal wave. (2mks)
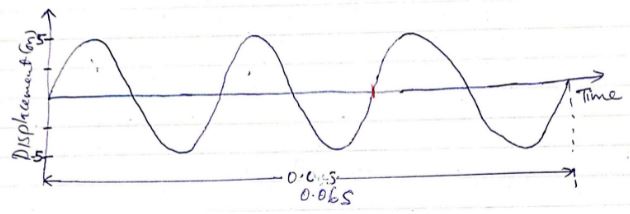
- The figure below shows the displacement time graph for a wave.
With reference to this wave motion, determine the:- Period (1mk)
- Frequency (2mks)
- If the wave travel at a speed of 340m/s, calculate the wavelength. (3mks)
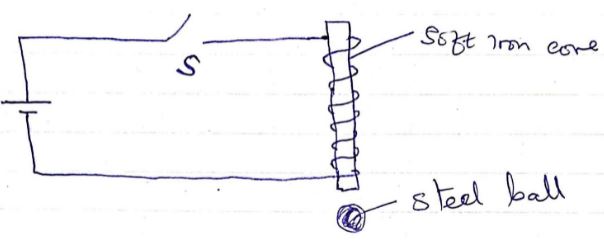
- A small electromagnet used for lifting and then releasing a small steel ball is made in the laboratory as shown below;
- Explain why soft iron is a better material than steel to use for the core. (1mk)
- In order to lift a slightly larger ball, it is necessary to make a stronger electromagnet. State two ways and explain the electromagnet could be made more powerful. (4mks)
-
- In an experiment to estimate the size of a molecule of olive oil, a drop oil of volume 0.12mm3 was placed on a clean water surface. The oil spread into a patch of areas 6.0x104mm2. Estimate the size of a molecule of olive oil. (3mks)
- Give two assumption made when calculating the thickness of the oil drop. (2mks)
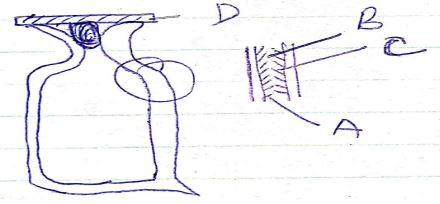
- The diagram below shows a vacuum flask with an enlarged view of the part in the circle.
- What materials are items A and C made of? (1mk)
- What types of heat energy are reduced by or prevented by the parts marked B,C and D. (3mks)
- Explain how A is effective in reducing heat transfer. (1mk)
- An object is placed 10cm in front of a:
- Convex mirror of a focal length 20cm. determine the position of the image.(2mks)
- Nature of the image. (1mk)
- Define the following terms as used in curved surface. (2mks)
Pole:
Radius of curvature:
- Sketch the field in each of the following. (4mks)
- Current in the same direction.
- Current in opposite direction.
- Current in the same direction.

Marking Scheme
- Define the term fluid. (1mk)
- Fluid refers to both gases and liquid.
- Fluid refers to both gases and liquid.
- Distinguish between streamline flow and turbulent flow. (2mks)
- Streamline flow- it is a flow in which at any given point each and energy particle of the fluid travels in the same direction and with the same velocity while turbulent flow is a flow in which the speed and direction of a the fluid particle passing at any point vary with time.
- Streamline flow- it is a flow in which at any given point each and energy particle of the fluid travels in the same direction and with the same velocity while turbulent flow is a flow in which the speed and direction of a the fluid particle passing at any point vary with time.
- In deriving the equation of continuity, there are some assumption made. State the three assumption that the fluid must have. (3mks)
- Flowing steadily
- Incompressible i.e. changes in pressure produce insignificant change in its density.
- Non-viscous
- The figure below shows a pithball placed in a flask. When a jet of air is blown over the month of the flask as shown, the pithball is observed to rise from the bottom. Explain the observation (2mks)
- Water with negligible viscosity flows steadily through a horizontal pipe of various cross-section area. At a point A of cross-section area 10cm2 the velocity is 0.2m/s. calculate:
- The velocity at a point B, of cross-section area 2.5cm2. (3mks)
- A1V1=A2V2
10 x 10-4 x 0.2 = VB X 2.5 x10-4
VB=0.8mls
- A1V1=A2V2
- State two hazards of Barnallis effect. (2mks)
- Blowing off of root-tops
- Road accident
- The velocity at a point B, of cross-section area 2.5cm2. (3mks)
- State and explain three factors affecting velocity of sound in air. (3mks)
- Temperature of the air: sound travels faster in hot air than in cold air.
- Humidity of the air: velocity of sound on air increase with humidity.
- Direction of the wind: wind blowing in the same direction as sound increases the velocity of the latter.
- The diagram below shows sound waves passing through air. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Label the following:
- Compression (1mk)
- Rarefaction (1mk)
- Wavelength (1mk)
-
- Define moment of a force. (2mks)
- Turning effect of the force or product of the force and perpendicular distance between the point of support (pivot) the line of the force.
- Turning effect of the force or product of the force and perpendicular distance between the point of support (pivot) the line of the force.
- State two factors affecting moment of force. (2mks)
- Amount of force
- Perpendicular distance between line of action of force and point of support.
- A uniform metre rule pivoted at its centre is balanced by a force of 4.8N at 20cm mark and some other two forces, F and 2.0N on the 66cm and 90cm marks respectively. Calculate the force F. (2mks)
- sum of clockwise moments=sum of a anticlockwise moment.
Fx0.16 +2.0x0.40=4.8 x0.30
0.16F+0.80=1.44
0.16F=0.64
F=0.64
0.16
F=4.0N
- sum of clockwise moments=sum of a anticlockwise moment.
- Define moment of a force. (2mks)
-
- Define magnetic field. (1mk)
- Space around a magnet where the magnetic influence is felt.
- Space around a magnet where the magnetic influence is felt.
- Draw the field pattern in following. (2mks)
- State three uses of magnets. (3mks)
- used in hospital for removing pieces of iron from the eyes of patients.
- Used in audio and video recorders.
- Used in loudspeakers
- In resolting six’s minimum and maximum thermometer.
- Used in industries as strainers, lifting iron scrap metals.
- Define magnetic field. (1mk)
- The air pressure at the base of a mountain is 75.0cm of mercury while at the top it is 60.0cm of mercury. Given that the average density of air is 1.25kg/m3 and the density of mercury is 13600kg/m3, calculate the height of the mountain. (3mks)
- Pressure difference due to column of air=pressure differences due to mercury column
Ha=(75-60) x 13600x10
100 1.25 x 10
= 15x13600x10
125x10
= 1632
The height of the mountain is 1632m
- Pressure difference due to column of air=pressure differences due to mercury column
-
- Differentiate between a transverse wave and a longitudinal wave. (2mks)
- The figure below shows the displacement time graph for a wave.
With reference to this wave motion, determine the:- Period (1mk)
- 0.025
- 0.025
- Frequency (2mks)
- T=1/f, I=1/t = 1/0.02 = 50H2
- T=1/f, I=1/t = 1/0.02 = 50H2
- If the wave travel at a speed of 340m/s, calculate the wavelength. (3mks)
- V=fx
340=50x
X=340/50
=6.8m
- V=fx
- Period (1mk)
- A small electromagnet used for lifting and then releasing a small steel ball is made in the laboratory as shown below;
- Explain why soft iron is a better material than steel to use for the core. (1mk)
- Easy to magnetize and demagnetize.
- Easy to magnetize and demagnetize.
- In order to lift a slightly larger ball, it is necessary to make a stronger electromagnet. State two ways and explain the electromagnet could be made more powerful. (4mks)
- Explain why soft iron is a better material than steel to use for the core. (1mk)
-
- In an experiment to estimate the size of a molecule of olive oil, a drop oil of volume 0.12mm3 was placed on a clean water surface. The oil spread into a patch of areas 6.0x104mm2. Estimate the size of a molecule of olive oil. (3mks)
- Volume of the drop = 0.12mm3
Area of the patch = 6.0 x 104mm2
Thickness, t, of patch =V/A
0.12
6.0 x104
=2.0 x 10-6mm
This thickness, t = 2.0x10-9m
- Volume of the drop = 0.12mm3
- Give two assumption made when calculating the thickness of the oil drop. (2mks)
- Oil drop is perfect Sphere
- Oil molecule is monolayer
- In an experiment to estimate the size of a molecule of olive oil, a drop oil of volume 0.12mm3 was placed on a clean water surface. The oil spread into a patch of areas 6.0x104mm2. Estimate the size of a molecule of olive oil. (3mks)
- The diagram below shows a vacuum flask with an enlarged view of the part in the circle.
- What materials are items A and C made of? (1mk)
- Silver
- Silver
- What types of heat energy are reduced by or prevented by the parts marked B,C and D. (3mks)
- B – conduction and convection
- C-Radiation
- D- Evaporation
- Explain how A is effective in reducing heat transfer. (1mk)
- Poor emitter and a poor absorber of heat.
- Poor emitter and a poor absorber of heat.
- What materials are items A and C made of? (1mk)
- An object is placed 10cm in front of a:
- Convex mirror of a focal length 20cm. determine the position of the image.(2mks)
- 1/f = 1/u + +1/v
=1/20=1/10+1/v
=1/v=-1/20-1/10
=3/20
V=-0.6667cm
- 1/f = 1/u + +1/v
- Nature of the image. (1mk)
- Image is virtual ( since v-is negative)
- Image is virtual ( since v-is negative)
- Define the following terms as used in curved surface. (2mks)
- Pole ,p
- Geometrical centre of the mirror.
- radius of curvature.
- Centre of the sphere of which the mirror forms a part.
- Pole ,p
- Convex mirror of a focal length 20cm. determine the position of the image.(2mks)
- Sketch the field in each of the following. (4mks)
- Current in the same direction.
- Current in opposite direction.
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Physics Questions and Answers - Form 3 Opener Term 1 Exams 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students