Questions
- A substance contains 25.6% copper, 12.8% sulphur, 25.6% oxygen and 36.0% water of crystalisation. Calculate its simplest formula. (Cu=64, S=32, O=16 and H1) (4mks)
- An organic compound has an empirical formula CH3O and relative molecular mass 62. What is its molecular formula? (2mks)
-
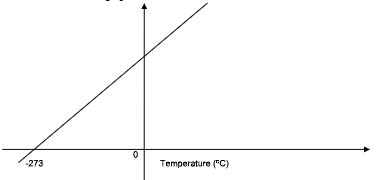
- State Charles’s law. (1mk)
- Draw a sketch graph to illustrate Charles’s law. (2mks)
- At a temperature of 57OC, nitrogen gas occupies a volume of 750cm3. At what temperature will the gas occupy 100cm3? Express the answer in degrees Celsius. (3mks)
- A given mass of a gas occupies 20cm3 at 25OC and 670mmHg pressure. Find out the volume it will occupy at;
- 10OC and 335mmHg. (3mks)
- OOC and 760mmHg. (3mks)
- Write ionic equation for the reactions between:
- Barium chloride solution and copper (II) Sulphate solution. (2mks)
- Zinc and copper (II) sulphate. (2mks)
- Zinc metal and hydrochloric acid reacts according to the following equation.
Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) → ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g)
1.96g of Zinc metal were reacted with 100cm3 of 0.2m hydrochloric acid.- Determine the reagent that was in excess. (Zn=65.4) (2mks)
- Calculate the total volume of hydrogen gas that was liberated at S.T.P (S.T.P = 22.4l) (2mks)
- Complete the table below which show properties of indicators used in titrations. (3mks)
Indicator Colour in Acid Colour un Alkali Colour in neutral Phenolphthalein Pink Colourless Methyl orange Pink Orange Screened methyl orange Red Green - Solution A was made up by dissolving 2.65g, of a metal carbonate, X2CO3 in water and diluting the solution to 250cm3. B is a 0.25m solution of hydrochloric acid. 20cm3 portions of A were titrated with solution B using methyl orange indicator with the following results.
-
- Complete the following table. (1 ½ mks)
Burette readings 1st 2nd 3rd Final reading (cm3) 48.1 Initial reading (cm3) 0.0 16.1 32.1 Volume of solution B used (cm3) 16.1 16.0 - The volume of the pipette used. (1mk)
- Calculate the average volume of solution B used. (1mk)
- Complete the following table. (1 ½ mks)
- The equation of the reaction is;
2HCl(aq) + X2CO3(aq) → 2XCl(aq) + H2O(l) +CO2(g)
Calculate the concentration of the solution A in;- Moles/litre (3mks)
- g/litres (2mks)
- Calculate the Relative Atomic Mass of X. (C=12, O=16, X=?) (3mks)
-
- State the Gay Lussac’s law. (1mk)
- If it takes 30 seconds for 100cm3 of Carbon (IV) Oxide to diffuse across a porous plate. How long will it take 150cm3 of nitrogen (IV) oxide to diffuse across the same plate under similar condition? (C=12, N=14, O=16) (3mks)
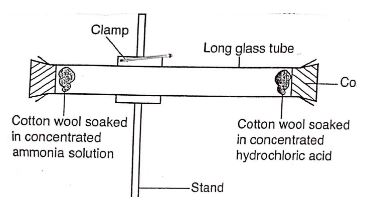
- A form three student set up an experiment to explain the rate of diffusion of ammonia and hydrogen chloride in air. Study it and answer the question that follows.
- What observation is made in the glass tube? Explain? (2mks)
- Determine the molecular masses of ammonia (NH3) and hydrogen chloride (HCl) (N=14, H=1, Cl=35.5) (1mk)
- Which gas covered a longer distance? ( ½ mk)
- Name two laboratory apparatus that are used to measure fairly accurate volumes of liquids. (2mks)
Marking Scheme
- A substance contains 25.6% copper, 12.8% sulphur, 25.6% oxygen and 36.0% water of crystalisation. Calculate its simplest formula. (Cu=64, S=32, O=16 and H1) (4mks)
Empirical formula CuSO4.5H2OElements Cu S O H2O % by mass 25.6 12.8 25.6 36.0 R.A.M/RFM 64 32 16 18 Ratio of moles 25.6=0.4
64128=0.4
3225.6=1.6
1636=2
18Simplest ratio of moles 0.4 =1
0.40.4 =1
0.41.6 =4
42 =5
0.4 - An organic compound has an empirical formula CH3O and relative molecular mass 62. What is its molecular formula? (3mks)
- Relative E.F mass = 12 + 3 16 =31
(CH3O)n = 62
n= 62 = 2
31
Molecular formula is C2H6O2
- Relative E.F mass = 12 + 3 16 =31
-
- State Charles’s law. (1mk)
- The volume of a given mass of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature, its pressure being kept constant
- The volume of a given mass of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature, its pressure being kept constant
- Draw a sketch graph to illustrate Charles’s law. (2mks)
- At a temperature of 57OC, nitrogen gas occupies a volume of 750cm3. At what temperature will the gas occupy 100cm3? Express the answer in degrees Celsius. (3mks)
- V1 = V2 V1= 750cm3 V2=100cm3
T1 T2 T1= 57 + 273 = 330K T2=?
750 = 100 T2 = 44K = - 229OC
330 T2 t = T - 273
T2= 100 x 330 = 44-273
750
- V1 = V2 V1= 750cm3 V2=100cm3
- State Charles’s law. (1mk)
- A given mass of a gas occupies 20cm3 at 25OC and 670mmHg pressure. Find out the volume it will occupy at;
- 10OC and 335mmHg. (3mks)
- P1V1 = P2V2
T1 T2
P1= 670
V1= 20cm3
T1= 25 +273 = 298K
P2= 335mmHg
V2=?
T2=10+273=283K
670x20 = 335 x V2
298 283
V2= 670 x 20 x 283
298 335
V2 = 38cm3
- P1V1 = P2V2
- OOC and 760mmHg. (3mks)
- P1V1 = P2V2
T1 T2
P1= 670mmHg
V1= 20cm3
T1= 25 + 273=298K
P2= 760mmHg
V2 = ?
T2= 0+273 =273K
670 x 20 = 760 x V2
298 273
V2= 670 x 20 x 273
298 760
V2= 16cm3
- P1V1 = P2V2
- 10OC and 335mmHg. (3mks)
- Write ionic equation for the reactions between:
- Barium chloride solution and copper (II) Sulphate solution. (2mks)
- BaCl2(aq) + CuSO4(aq) → BaSO4(s)+ CuCl2(aq)
Ba2+(aq) + SO42-(aq) → BaSO4(s)
- BaCl2(aq) + CuSO4(aq) → BaSO4(s)+ CuCl2(aq)
- Zinc and copper (II) sulphate. (2mks)
- Zn(s) + CuSO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq)+ Cu(s)
Zn(s) + Cu2+(aq) → Zn2+(aq ) + Cu(s)
- Zn(s) + CuSO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq)+ Cu(s)
- Barium chloride solution and copper (II) Sulphate solution. (2mks)
- Zinc metal and hydrochloric acid reacts according to the following equation.
Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) → ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g)
1.96g of Zinc metal were reacted with 100cm3 of 0.2m hydrochloric acid.- Determine the reagent that was in excess. (Zn=65.4) (2mks)
- Moles of Zn = 1.96 = 0.03
65.4
Moles of HCl = 0.02 → 1000cm3
? → 100cm3
0.02 x 100 = 0.002 of HCl
1000
Zinc was in excess since 0.002 moles of HCl needs to react with 0.001 moles of Zinc.
- Moles of Zn = 1.96 = 0.03
- Calculate the total volume of hydrogen gas that was liberated at S.T.P (S.T.P = 22.4l) (2mks)
- Moles of H2= 0.001
Volume = 1 mole → 22.4
0.001 mole → ?
= 0.001 x 22.4
1
= 0.0224 litre
- Moles of H2= 0.001
- Determine the reagent that was in excess. (Zn=65.4) (2mks)
- Complete the table below which show properties of indicators used in titrations. (3mks)
Indicator Colour in Acid Colour un Alkali Colour in neutral Phenolphthalein Colourless Pink Colourless Methyl orange Pink Yellow Orange Screened methyl orange Red Green Grey - Solution A was made up by dissolving 2.65g, of a metal carbonate, X2CO3 in water and diluting the solution to 250cm3. B is a 0.25m solution of hydrochloric acid. 20cm3 portions of A were titrated with solution B using methyl orange indicator with the following results.
-
- Complete the following table.
Burette readings 1st 2nd 3rd Final reading (cm3) 16.1 32.1 48.1 Initial reading (cm3) 0.0 16.1 32.1 Volume of solution B used (cm3) 16.1 16.0 16. - The volume of the pipette used. (1mk)
- 20cm3
- 20cm3
- Calculate the average volume of solution B used. (1mk)
- = 16+16+16.1
3
= 16.0cm3
- = 16+16+16.1
- Complete the following table.
- The equation of the reaction is;
2HCl(aq) + X2CO3(aq) → 2XCl(aq) + H2O(l) +CO2(g)
Calculate the concentration of the solution A in;- Moles/litre (3mks)
- 2HCl + X2CO3
Ratio 2:1
Moles of HCl used = 16 x 0.25 = 0.004
1000
Moles of X2CO3 used = ½ x 0.004 = 0.002
20cm3 → 0.002 moles
1000cm3 → ?
0.002 x 1000 = 0.1M
20
- 2HCl + X2CO3
- g/litres (2mks)
- 250cm3 → 2.65g
100cm3 → ?
2.65 x 1000 = 10.6g/L
250
- 250cm3 → 2.65g
- Moles/litre (3mks)
- Calculate the Relative Atomic Mass of X. (C=12, O=16, X=?) (3mks)
- molar mass of A = g/litre
morality
= 10.6
0.1
= 106
Molar mass of X2CO3
= (2xx) + 12 + (3x16) =106
2x=106-60
2x=46
X=23
- molar mass of A = g/litre
-
- State the Gay Lussac’s law. (1mk)
- When gases react; they do so in volumes that bear a simple ratio to one another and to the volumes of the produce if gaseous, temperature and pressure remaining constant.
- When gases react; they do so in volumes that bear a simple ratio to one another and to the volumes of the produce if gaseous, temperature and pressure remaining constant.
- If it takes 30 seconds for 100cm3 of Carbon (IV) Oxide to diffuse across a porous plate. How long will it take 150cm3 of nitrogen (IV) oxide to diffuse across the same plate under similar condition? (C=12, N=14, O=16) (3mks)
- 100cm3 → 30 seconds of CO2
150cm3 → ?
30 x 150
100
= 45 seconds
TCO2
TNO2
√(MrCO2/MrrO2)
45 = √44/28
TNO2
45 = 0.978
TrO2
TrO2= 45
0.978
TrO2 = 46 seconds
- 100cm3 → 30 seconds of CO2
- A form three student set up an experiment to explain the rate of diffuse of ammonia and hydrogen chloride in air. Study it and answer the question that follows.
- What observation is made in the glass tube? Explain? (2mks)
- White solid is formed, because concentrated ammonia solution generates ammonia and concentrated hydrochloric acid generated hydrogen chloride gas which reacted to form solid ammonia chloride.
- White solid is formed, because concentrated ammonia solution generates ammonia and concentrated hydrochloric acid generated hydrogen chloride gas which reacted to form solid ammonia chloride.
- Determine the molecular masses of ammonia (NH3) and hydrogen chloride (HCl) (N=14, H=1, Cl=35.5) (1mk)
- NH3= 12 + (1 x 3) = 15
HCl = 1 + 35.5 = 36.5
- NH3= 12 + (1 x 3) = 15
- Which gas covered a longer distance? ( ½ mk)
- NH3 gas
- NH3 gas
- What observation is made in the glass tube? Explain? (2mks)
- Name two laboratory apparatus that are used to measure fairly accurate volumes of liquids. (2mks)
- Volumetric flasks
- Syringes
- Pipettes
- Burettes
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Chemistry Questions and Answers - Form 3 Mid Term 1 Exams 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students