- This paper has TWO Sections A and B
- Answer All the questions in section A
- Answer questions 6 and any other Two questions from Section B.
- Answer must be written in the spaces provided.
- Students should check the questions paper and ascertain that all the pages are printed as indicated and that no questions is missing,
- Students should answer the questions in English.
SECTION A
-
- What is practical Geography? (2mks)
- State THREE practical aspects we study in Geography. (3mks)
- Identify FIVE activities that may be undertaken in your school to conserve trees. (5mks)
- Outline the advantages of using photographs in learning geography. (5mks)
-
- Name THREE major categories of minerals (3mks)
- Give TWO examples of fossil fuels. (2mks)
-
- What is Agro-forestry? (2mks)
- State THREE reasons for encouraging agro-forestry in Kenya. (3mks)
SECTION B: ANSWER Question 6 and any other two questions in the section.
-
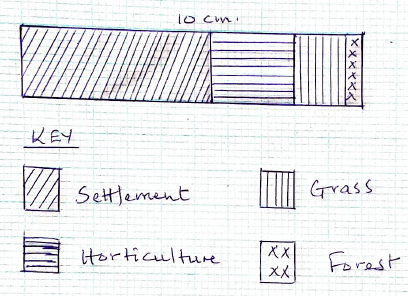
- The table below shows land use in Nairobi area in 2003. Use it to answer questions that follow.
Land use Area in ‘000’ km2 Length of portions in cm Settlement
Grass
Horticulture
forest110
30
50
10TOTAL 200 - Calculate the length of each portion in the divided bar graph. (4mks)
-
- Name the TWO types of statistical data (2mks)
- Give FOUR characteristics of statistical data. (4mks)
- The table below shows land use in Nairobi area in 2003. Use it to answer questions that follow.
-
-
- What is mining? (2mks)
- Why is mining termed as a ‘robber’ industry? (2mks)
- Identify THREE factors that influence the exploitation of minerals. (3mks)
-
- Explain how the following factors influence the exploitation of minerals. (3mks)
- level of technology or skills, (5mks)
-
- Explain THREE problems associated with the shaft method of mining. (6mks)
- Apart from shaft method of mining, name other methods of underground mining. (3mks)
-
-
- Distinguish between:
- Forestry and a forest. (2mks)
- Afforestation and re-afforestation. (2mks)
- Apart from coniferous forests, name FIVE other types of natural forests. (5mks)
- List FIVE factors that influence the distribution of forests in Kenya. (5mks)
-
- Explain THREE factors that favour the growth of natural forests on the slopes of Mt. Kenya. (6mks)
- Outline the steps taken in forest exploitation (5mks)
- Distinguish between:
- Use the map of East Africa below showing the distribution of major minerals to answer the question that follows.
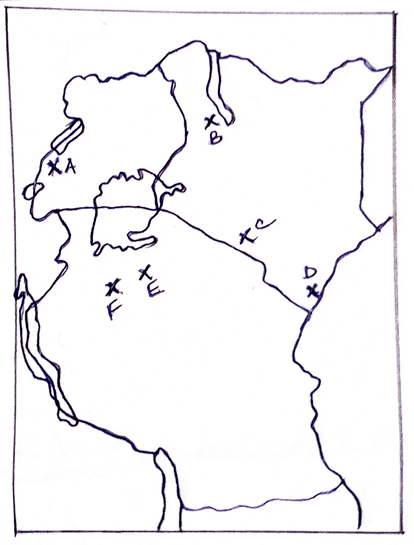
- Name the major minerals mined in the areas marked A- F. (6mks)
- Give reasons why coal in Tanzania is underexploited. (5mks)
- Explain THREE negative effects of mining to the environment. (6mks)
-
- Give THREE uses of Soda ash. (3mks)
- Name FIVE major Oil producing countries in Africa. (5mks)
-
- The map of Kenya below shows some forested areas. Name the forest reserves marked a-h. (8mks)
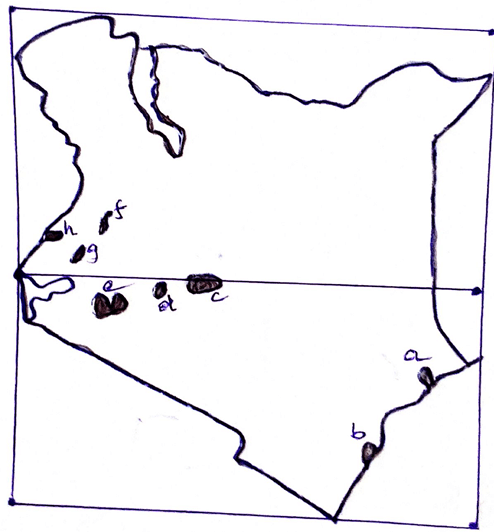
- State FIVE ways in which clearing of forests has affected the natural environment in Kenya. (5mks)
-
- Name THREE softwood tree species grown in forests of Canada. (3mks)
- Give FIVE characteristics of softwood forests of Canada. (5mks)
- Give the differences between softwood forests in Kenya and Canada under the following sub- headings:
- Period of harvesting. (2mks)
- Period of growth (2mks)
- The map of Kenya below shows some forested areas. Name the forest reserves marked a-h. (8mks)

MARKING SCHEME
-
- This is the study of practical skills which enhance the understanding and interpretation of geographical phenomena
-
- Maps and map reading/ maps and map work
- Photograph work
- Field work
- Statistical methods
-
- Start tree planting days in the school calendar
- Establish tree nurseries to raise seedlings
- Start environmental or tree planting clubs to create awareness on tree conservation
- Use alternative sources of energy
- Use energy saving jokis
- Taking care of young trees through mulching and watering
- Control tree pests and diseases
-
- Photographs show actual objects as they appear
- Photographs record things/objects in real time
- Photographs can be used to show historical facts and changes that have occurred
- Unfamiliar features can be seen on photographs and be used in learning
- Photographs may carry a lot of information
- Photographs are an attractive and an interesting way of learning geography
-
-
- Metallic minerals
- Non-metallic minerals
- Energy minerals
-
- Petroleum/ crude oil
- Natural gas
- Coal
-
-
- A land use system that involves planting of trees, crops and keeping livestock on the same unit of land
-
- To maximize land use
- To conserve the land and protect it from erosion or increase water retention on land
- To provide raw materials for industries
- To conserve forests
- Leaf litter decomposes and adds humus to the soil
- Some trees have medicinal value
- Some trees provide fodder for animals
- Trees act as wind breakers and shade for young plants
SECTION B
-
-
-
- Settlement = 110/200 x 10 = 5.5cm
- Grass = 30/200 x 10 = 1.5cm
- Horticulture = 50/200 x 10 = 2.5cm
- Forest = 10/200 x 10 = 0.5cm
- DIVIDED BAR GRAPH SHOWING LAND USE IN NAIROBI AREA IN 2003
-
- Settlement covered more than half of Nairobi area in 2003
- The second largest area was covered by horticultural farming
- Forest covered the least area
- The rest of the area was covered by grass
-
- Comparisons of variables can be made with ease
- A wide range of data can be respresented
- Gives a clear visual impression of individual components
- Easy to read becasue of the descending order of the arrangement
- Easy to draw
- Covers less space
-
-
- Primary data
- Secondary data
-
- Discrete data i.e statistics given as whole numbers
- Individual data i.e exact value is given for each item in a sample range
- Continuous data i.e statistics given in any value
- Grouped data - i.e no exact figures are quoted, but values are arranged in groups
-
-
-
-
- This is the process of extracting valuable minerals that occur on or below the earth's crust
- Through mining, the minerals get depleted, they cannot be regenerated and mining operations cause many negative environmental effects resulting in dereliction of land
-
- Vulcanicity
- Rock metamorphism
- Denudation or weathering and erosion
- Folding/Faulting
- Evaporation
- Deposition/Sedimentation
-
-
- Determine method of mining and the cost of extraction
- Minerals at shallow depths are easier and cheaper to extract, while deep seated minerals are expensive to mine.
- Minerals close to the surface in layers, beds and seams are extracted using open cast/ placer mining methods, while minerals found deep underground in veins and lodes are extracted using shaft method
-
- Advanced technology improves mining operations, leading to high quality/ quantity production of mineral products
- Low level technology limits level of mineral exploitation and low quantities
- High level technology allows effective exploration leading to accurate location of minerals
- Advanced technology promotes effective mineral production reducing wastage
- High level technology reduces the destruction of the environment
-
-
-
- Sometimes the mines get flooded with underground water which stops mining
- Emissions of poisonous gases may occur in the mines, which is a health hazard to animals, plants and miners/people
- The dust produced through blasting in the mines may casue respiratory diseases
- Underground tunnels may collapse resulting in death of miners
-
- Solution method
- Adit/ Drift method
- Drilling
-
-
-
-
- Forestry is the science of planting, caring or managing and the exploitation of forests and forest resources whereas a forest is a continuous growth of trees and undergrowths covering a large tract of land
- Afforestation is the planting of trees in an area which has had no forests/ establishments of new forests whereas re-afforestation in the planting of trees in an area where they have been cut down
-
- Equatorial forests/tropical hardwoods
- Tropical monsoon forests
- Temperate hardwoods/ temperate evergreen forests
- Mongrove forests
- Mediterraean forests
- Temperate decidious forests
- Mixed forests
-
- Attitude
- Temperate variations
- Soil type, texture and structure
- Human activities
- Government policy
- Amount of precipitation
-
-
- High rainfall throughout the year for continuous growth of trees
- Deep, well-drained volcanic soils that allow roots to penetrate deep into the ground for proper support of trees
- Moderate to high temperature/ cool to warm conditions that allow growth of a variety of trees
- Steep, rugged slopes that discourage settlement and cultivation thus allowing forest growth
- Gazetted forest reserve where settlements and cultivation are prohibited allowing forests to grow
-
- Minerals are obtained from the forestry department
- Forest camps are established and minerals taken to the forest
- Tress to be cut are marked selectively
- Trees are cut using simple power saws
- Logs are hauled by tractors to the central area
- Logs are loaded on tracks and taken by factories/saw mills
-
-
-
-
- Coppper
- Oil
- Trona
- Titanium
- Diamond
- Gold
-
- Inadequate capital to invest in its exploitation
- Low market demand for coal
- Deposits found far in remote areas with poor transport networks
- There are cleaner alternative sources of energy which have been developed
- Poor quality coal/small coal reserves
-
- Dumping of rock wastes leads to loss of biodiversity
- Dereliction of land due to dumping of waste and scars which are an eyesore that destroys the natural beauty of land
- Open scars expose land to soil erosion and soil degeneration
- Pollution by noisy blasts smoke, dust and water pools that are a health hazard
- Underground mining disrupts/ lowers the water table which may lead to water shortage
-
-
- Used in glass making
- Used in making detergents and soaps
- For petroleum refining
- As a water softener/water treatment
- Used in desulphurising steel
- For paper smoothening in paper making
- In manufacture of textiles
- In production of salts
-
- Libya
- Tunisia
- DRC
- Nigeria
- Angola
- Sudan(North and South)
- Egypt
- Algeria
- Morocco
- Gabon
-
-
-
-
- Boni/Dodori forest
- Arabuko Sekoke forest
- Mt. Kenya forest
- Aberdare forest
- Cherangani forest
- Kakamega forest
- Mt. Elgon forest
-
- Reduced water volume in rivers/drying up of some rivers
- Has led to changes in rainfall patterns and desertification
- Has interfered with environmental beauty
- Has disrupted the ecosystem
- Has accelerated soil erosion
- Destruction of natural habitats for wildlife that has endangered some wildlife species
-
-
- Spruce
- Douglas fiv
- White pine
-
- Trees are conical
- Trees are light in weight
- Trees occur in pure stands
- Trees are soft woods
- Trees are tall and straight
- Trees have needle like leaves
- Trees bear cones
- Forests are evergreen
- Have little or no undergrowth
- Trees have thick waxy barks
- Trees have shallow root systems that spread widely
- Trees take long to mature due to long cold winters
-
-
- In Canada logging is done in winter or early spring while in Kenya logging is done throughout the year
- In Canada trees take longer to mature due to the cold climate while in Kenya trees mature faster due to the warm/tropical conditions
-
Download Geography Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Form 3 End Term 1 Exams 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

