INSTRUCTION.
Answer all questions in the spaces provided.
-
- Outline three ways a student benefit from learning geography. (3mks)
-
- Define the term weather. (2mks)
- The table below shows the temperature and rainfall readings for station K in one week. Use it to answer the questions below.
Calculate:Day Mon Tue Wed Thur Fri Sat Sun Temp °C 23 23 24 21 25 25 23 Rainfall (mm) 50 49 55 45 60 60 49 - The range of temperature for the week. (1mk)
- The weekly rainfall total (2mks)
- Give four characteristics of stratosphere. (4mks)
-
-
- What is a rock? (2mks)
- Describe three ways through which sedimentary rocks are formed. (6mks)
- Give examples of each of the following igneous rocks.
- Plutonic rocks (1mk)
- Hypabyssal rocks (1mk)
- Volcanic rocks (1mk)
- Students of Charakali High School were to carry out field study of rocks within the vicinity of their school.
- Name three secondary source of information they would use to prepare for field study. (3mks)
- State four activities they would carry out during the field study. (4mks)
- State three problems they likely to face during the study. (3mks)
-
- Study the diagram below and answer the question that follows.
-
- What force is depicted on the diagram above? (1mk)
- Identify the type of fault shown on the diagram. (1mk)
- List three features formed due to faulting. (3mks)
-
-
- List two factors that influence the climate of a place. (2mks)
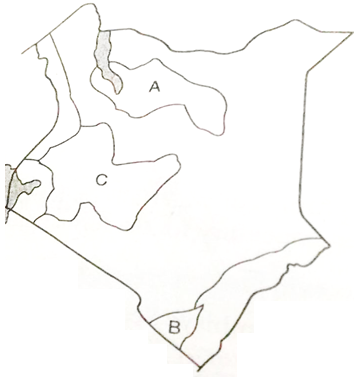
- The map below shows the climate regions of Kenya.
Name the climatic regions marked A, B, C. (3mks)- A
- B
- C
-
- Identify three natural vegetation types found in Africa. (3mks)
- State five characteristics of Tropical Monsoon Forests. (5mks)
-
- Give two differences between hardwood and softwood forests. (4mks)
- State four problems facing forestry in Canada. (4mks)
- Explain four measures of management and conservation of forests. (8mks)
- State three disadvantages of presenting statistical data using compound bar graphs (3mks)

MARKING SCHEME
-
- Outline three ways a student benefit from learning geography. (3mks)
- Learners are able to explain the origin of the earth and solar system.
- Learners develop skills of observation reading analysing.
- Help the learner to study the way of life as they interact.
-
- Define the term weather. (2mks)
- Is the condition of the atmosphere of a given place at specific time over a short period of time
Calculate:
- Is the condition of the atmosphere of a given place at specific time over a short period of time
- The table below shows the temperature and rainfall readings for station K in one week. Use it to answer the questions below'
Calculate- The range of temperature for the week. (1mk)
- 25 – 21 = 4°C
- The weekly rainfall (2mks)
= 50 + 49 + 55 +45 + 60 + 60 + 49
= 368mm
- The range of temperature for the week. (1mk)
- Define the term weather. (2mks)
- Give four characteristics of stratosphere. (4mks)
- Is a layer above, troposphere
- Contain very little dust and water vapour
- No cloud is found in this layer
- Temperature increase with increase in altitude
- Wind are light in the lower parts
- Upper limit of stratosphere is marked by stratopause.
- Outline three ways a student benefit from learning geography. (3mks)
-
-
- 'What is a rock? (2mks)
- A rock is a substance made up of minerals or combination of mineral particles cemented together to form a solid part of the earth crust.
- Describe three ways through which sedimentary rocks are formed. (6mks)
- Mechanically formed sedimentary rocks- formed when eroded rock material are transported by agents and deposited in layers.
- Organically formed sedimentary rocks are formed when remains of previous existing plants and animals are accumulated over a period of time forming layers.
- Chemically formed sedimentary rocks are formed when rocks are precipitated or when a solution of salt is evaporated and particles accumulated in layers.
- 'What is a rock? (2mks)
- Give examples of each of the following igneous rocks.
- Plutonic rocks (1mk)
- Granite, Syenite, gabbro, diorite, Peridotite
- Hypabyssal rocks (1mk)
- Dolerite, porphyrite, porphyry, Lamprophyre
- Volcanic rocks (1mk)
- Andesite, Pumice, Trachyte, Rhyolite, Basalt scoria, Phonolite, obsidian
- Plutonic rocks (1mk)
- Students of Charakali High School were to carry out field study of rocks within the vicinity of their school.
- Name three secondary source of information they would use to prepare for field study. (3mks)
- Textbook/magazine, newspaper
- Maps/ geological maps
- Photographs/pictures/films
- Tape recorded information
- State four activities they would carry out during the field study. (4mks)
- Drawing of sketches
- Observations
- Collecting rock samples
- Making notes
- Asking questions
- Studying geological maps
- State three problems they likely to face during the study. (3mks)
- Harsh weather condition – Hot sun
- Inaccessibility
- Hostility from unfriendly people
- Fatigue
- Name three secondary source of information they would use to prepare for field study. (3mks)
-
- Study the diagram below and answer the question that follows.
-
- What force is depicted on the diagram above? (1mk)
- Compressional force
- What force is depicted on the diagram above? (1mk)
- Name the type of fault shown on the diagram. (1mk)
- Reversal fault
- Name three features that are likely to result from the kind of force shown on the diagram. (3mks)
- Horst/block mountain
- Rift valley
- Fault scarp
-
-
- Name two factors that influence the climate of a place. (2mks)
- Latitude
- Distance from the sea
- Altitude
- Nature of prevailing wind
- Inland water bodies
- ITCZ
- The map below shows the climate regions of Kenya.
Name the regions marked A, B, C. (3mks)- A – Tropical desert climate
- B – Tropical climate
C – Modified tropical climate
- Name two factors that influence the climate of a place. (2mks)
-
- Identify three natural vegetation types found in Africa. (3mks)
- Tropical rain forest
- Tropical savanna grassland
- Health and Moorland
- State FIVE characteristic of Tropical Monsoon Forests. (5 MKS)
- Trees are tall but like equatorial ones
- Trees grow quite far apart
- There is heavy undergrowth
- Trees have more branches
- Trees shade their leaves in some region.
- Trees are limited species and appear more or less pure stands.
- Identify three natural vegetation types found in Africa. (3mks)
-
- List two differences between hardwood and softwood forests. (4mks)
- Hardwood forest is hard to exploit while softwood forest are easy to exploit.
- Hardwood forest takes longtime to mature while softwood forest matures faster.
- Hardwood trees are durable while softwood is less durable.
- Identify four problems Canada faces in exploiting her forest resources. (4mks)
- Slow growth
- Northern parts are inaccessible
- Forest fire and disease.
- Exhaustion of valuable species
- Explain four measures of management and conservation of forests. (8mks)
- Research on characteristics of trees to establish the suitable trees that can be grown in specific area.
- Public campaign on the value of forest through mass media like newspapers, posters, radio and T.V.s
- Establishing training institutions deciding with forestry to train the forest personnel on effective ways of managing forests.
- Use of alternative sources of energy to reduce the over dependence of would fuel.
- Reduction of wastage industry by recycling the waste of produce other useful product.
- Enacting of laws to govern the management of forests.
- List two differences between hardwood and softwood forests. (4mks)
- What are the demerits of compound bar graphs? (3mks)
- It involves a lot of calculation
- Quantities from many regions are emerged giving false impression.
- Not easy to read and interpret.
- Not easy to make quick comparison.
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Geography Questions and Answers - Form 3 Term 1 Opener Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students