INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Answer all the questions in the spaces provided after each.
- All working must be clearly shown where necessary.
- All answers should be written in English.
- Element A has atomic mass 23 and element B has atomic mass 7 and also have 12neutorns and 4 neutrons respectively.
- Write the electronic arrangement of A and B (2mks)
- Which element has higher ionization energy? Explain (2mks)
- The number of protons, neutrons and electrons in atoms A to F are given in the table below the letters do not represent the actual symbol of the elements:-
Choose from the table the letters that represent:Atoms Protons Neutrons Electrons A
B
C
D
E
F3
9
12
17
17
184
10
12
18
20
222
10
12
17
17
18- An atom of a metal (1mk)
- A neutral atom of a non-metal (1mk)
- An atom of a noble gas (1mk)
- A pair of isotopes (1mk)
- A cation (1mk)
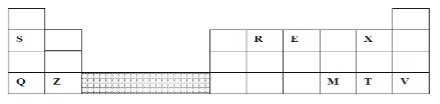
- The grid below represents part of the periodic table. Study it and answer the questions that follow:
- Identify the element that gains electrons most readily (1mk)
- Which of the metal is most reactive? Explain (2mks)
- What name is given to the family of elements to which elements X and T belong? (1mk)
- Explain why:-
- Ionic radius of Q is larger than that of M (1mk)
- Atomic radius of Q is greater than that of S (1mk)
- Which of the element in the table does not have the ability to form an ionic or covalent bond? Explain (2mks)
- Give the formula of the compound formed between R and Z (2mks)
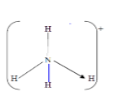
- The structure of ammonium ion is shown below;
- Name the type of bond represented in the diagram by N → H (1mk)
- Study the table below and answer the questions that follow:-
Identify with reasons the substances that:Substance A B C D E F Melting Point (°C) 801 113
119−39 5 − 101 1356 Boiling Point (°C) 1410 445 457 54 −36 2860 Electrical Conductivity Solid Poor Poor Good Poor Poor Poor Liquid Good Poor Good Poor Poor Poor - Have a metallic structure (1½mk)
- Have a molecular structure and exist in the liquid state at room temperature and pressure (1½mk)
- Suggest a reason why substance B has two melting points (1mks)
- Substances A and C conduct electric current in the liquid state. State how the two substances differ as conductors of electric current (2mks)
- In an experiment, ammonium chloride was heated in test-tube. A moist red litmus paper placed at the mouth of test first changed blue then red. Explain these observations:- (2mks)
- Give the name of each of the processes described below which takes place when salts are exposed to air for sometime:- (3mks)
- Anhydrous copper sulphate becomes wet
- Magnesium chloride forms an aqueous solution
- Fresh crystals of sodium carbonate, Na2CO3.10H2O become covered with white powder of formula Na2CO3.H2O
- Write an equation to show the effect of heat on the nitrate of:- (2mks)
- Potassium
- Silver
- You are provided with the following:- solid lead (II) nitrate, magnesium oxide powder, dilute sulphuric (VI)acid and distilled water. Describe how you can prepare a dry sample of lead (II) sulphate. (3mks)
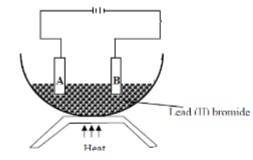
- Study the diagram below and use it to answer the questions that follow:-
- Identify electrodes A and B (2mks)
- Name the product formed at the anode (1mk)
- Write the electrode half equation of reaction at electrode A (1mk)
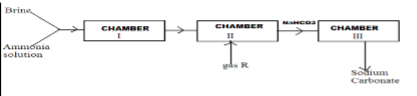
- Below is a simplified scheme of Solvay process. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify gas R. (1mk)
- Write an ionic equation for the process in chamber III. (1mk)
- Give two uses of sodium carbonate. (2mks)
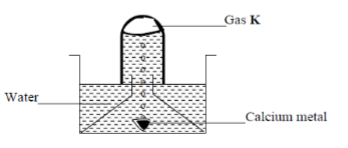
- The set up below was used to collect gas K, produced by the reaction between water and calcium metal.
- Name gas K (1mk)
- At the end of the experiment, the solution in the beaker was found to be a weak base. Explain why the solution is a weak base
- Name the process which takes place when (2mks)
- Solid Carbon (Iv) Oxide (dry ice) changes directly into gas
- A red litmus paper turns white when dropped into chlorine water
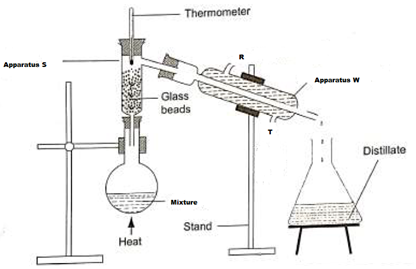
- A student left some crushed fruit mixture with water for some days. He found the mixture had fermented. He concluded that the mixture was contaminated with water and ethanol with boiling point of 100°C and 78°C respectively. The set-up of apparatus below are used to separate the mixture.
- Name the piece of apparatus labelled W (1mk)
- What is the purpose of the thermometer in the set-up? (1mk)
- At which end of the apparatus W should tap water be connected? (1mk)
- Which liquid was collected as the first distillate? Explain (1mk)
- What is the name given to the above method of separating mixture? (1mk)
- State two applications of the above method of separating mixtures (1mk)
- What properties of the mixture makes it possible for the component to be separated by the above methods? (1mk)
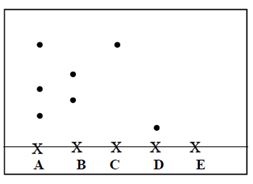
- The following diagram shows a paper chromatogram of substances A, B, C, and D which are coloured
- Indicate the solvent front on the chromatogram (1mk)
- Which substance is pure? (1mk)
- Substance E is a mixture of C and D. Indicate its chromatogram in the diagram (1mk)
- The diagram below shows students set-up for the preparation and collection of oxygen gas
- Name substance X used (1mk)
- Write an equation to show the reaction of sodium peroxide with the substance named in (1mk)
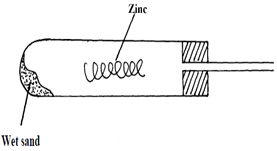
- A student set-up the experiment as shown below to collect a gas. The wet sand was heated before heating zinc granules
- Complete the diagram for the laboratory preparation of the gas (3mks)
- Why was it necessary to heat wet sand before heating Zinc granules? (1mks)
- Below are PH values of some solutions.
Solution A B C D PH 6.7 13.0 2.1 7.0 - Which solution is likely to be
- rain water (½ mark)
- Sodium hydroxide (½ mark)
- Which substances will be formed when magnesium reacted with solution C?(1 mark)
- Which solution is likely to be
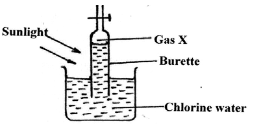
- .An experiment was set up using chlorine water as shown below.
- Identify gas X. (1mk)
- Write an equation for the production of gas X. (1mk)
- State any TWO uses of chlorine gas. (2mks)
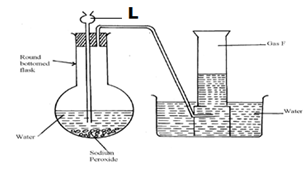
- The set-up below was used to collect gas F produced by the reaction between sodium peroxide and water.
- Name gas F (1mk)
- At the end of the experiment, the solution in the round bottomed flask was found to be a strong base. Explain why this was so. (1mk)
- Which property of gas F makes it be collected by the method used in the set-up? (1mk)
- Give one industrial use of gas F (1mk)
- Complete the following table to show the colour of the following indicators in acidic and basic solution (2mks)
Indicator Colour In Acidic Solution Basic Solution Phenopthalein Methyl Orange Yellow Litmus Red - Define the following terms (2mks)
- Cation
- Isotopes
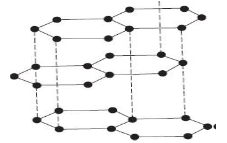
- The diagram below represents an allotrope of carbon.
- name the allotrope. (1mk)
- Explain why:- (2mks)
- Its slipperly
- Conducts an electric current

MARKING SCHEME
- Element A has atomic mass 23 and element B has atomic mass 7 and also have 12neutorns and 4 neutrons respectively.
- Write the electronic arrangement of A and B (2mks)
- A = 2.8.1
- B = 2.1
- Which element has higher ionization energy? Explain (2mks)
- B
- Strong attraction of the outermost energy level electron to the nucleus make it difficult to remove an electron. This is due to smaller atomic radius compared to A
- Or - Outermost electrons are closer to the nucleus hence higher force of attraction
- Write the electronic arrangement of A and B (2mks)
- The number of protons, neutrons and electrons in atoms A to F are given in the table below the letters do not represent the actual symbol of the elements:-
Choose from the table the letters that represent:- An atom of a metal (1mk)
- C
- A neutral atom of a non-metal (1mk)
- F
- An atom of a noble gas (1mk)
- F
- A pair of isotopes (1mk)
- D and E
- A cation (1mk)
- A
- An atom of a metal (1mk)
- The grid below represents part of the periodic table. Study it and answer the questions that follow:
- Identify the element that gains electrons most readily (1mk)
- X
- Which of the metal is most reactive? Explain (2mks)
- Q. It looses the outermost energy level most readily.
- What name is given to the family of elements to which elements X and T belong? (1mk)
- Halogens
- Explain why:-
- Ionic radius of Q is larger than that of M (1mk)
- Moving across a period there is increased nuclear charge.
- Atomic radius of Q is greater than that of S (1mk)
- Going down a group the occupied energy levels increase in number.
- Ionic radius of Q is larger than that of M (1mk)
- Which of the element in the table does not have the ability to form an ionic or covalent bond? Explain (2mks)
- V- Explanation It has a complete outermost energy level/ Has a stable octet.
- Give the formula of the compound formed between R and Z (2mks)
- Z2R Reject Interchange of letters, RZ2.
- Identify the element that gains electrons most readily (1mk)
- .The structure of ammonium ion is shown below;
- Name the type of bond represented in the diagram by N → H (1mk)
- Coordinate/Dative bond
- Study the table below and answer the questions that follow:-
Identify with reasons the substances that:- Have a metallic structure (1½mk)
- C Reason:- Good conductor of electricity in both molten and solid state. electrons.(Both must be correct for the 1 mk).
- Have a molecular structure and exist in the liquid state at room temperature and pressure (1½mk)
- D-Its melting point is below room temperature and boiling point above room temperature.
- Suggest a reason why substance B has two melting points (1mks)
- It exist in allotropic form.
- Substances A and C conduct electric current in the liquid state. State how the two substances differ as conductors of electric current (2mks)
- A conducts electricity by use of mobile ions while C conducts by use of delocalized electrons
- Have a metallic structure (1½mk)
- Name the type of bond represented in the diagram by N → H (1mk)
- In an experiment, ammonium chloride was heated in test-tube. A moist red litmus paper placed at the mouth of test first changed blue then red. Explain these observations:- (2mks)
- NH4Cl decomposes on heating to produce NH3 and HCl (g). NH3(g) is lighter than HCl(g) hence diffuses faster and turns red-litmus to blue HCl is denser hence diffuses at a slower rate: changes blue litmus to red
- Give the name of each of the processes described below which takes place when salts are exposed to air for sometime:- (3mks)
- Anhydrous copper sulphate becomes wet
- Hydroscopy// hygroscopic
- Magnesium chloride forms an aqueous solution
- Deliquescence// Deliquescent
- Fresh crystals of sodium carbonate, Na2CO3.10H2O become covered with white powder of formula Na2CO3.H2O
- Efflorescence// Efflorescent
- Anhydrous copper sulphate becomes wet
- Write an equation to show the effect of heat on the nitrate of:- (2mks)
- Potassium
2KNO3(s) → 2KNO2(s) + O2(g) - ½mk for wrong states - Silver
2AgNO3(s) → 2Ag(s) + 2NO2 (g) + O2 (g)
- Potassium
- You are provided with the following:- solid lead (II) nitrate, magnesium oxide powder, dilute sulphuric (VI)acid and distilled water. Describe how you can prepare a dry sample of lead (II) sulphate (3mks)
- Dissolve lead (ii) nitrate crystal in a given amount of distilled water in a beaker
- To dilute sulphuric (vi) acid √½ in a beaker add magnesium√ oxide ½ powder
- React the two solutions obtained
- Filter the mixture and wash the residue
- Dry the residue between filter papers to obtain a dry sample of lead (ii) sulphate
- Study the diagram below and use it to answer the questions that follow:-
- Identify electrodes A and B (2mks)
- A is Anode √ 1
- B is cathode. √ 1
- Name the product formed at the anode (1mk)
- Bromine gas. √ 1
- Write the electrode half equation of reaction at electrode A (1mk)
2Br-1(l) - 2e- → Br2(g) √ 1
- Identify electrodes A and B (2mks)
- Below is a simplified scheme of Solvay process. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify gas R. (1mk)
- Carbon (iv) oxide//CO2
- Write an ionic equation for the process in chamber III. (1mk)
2NaHCO3(L) → Na2CO3 (s) + CO2(g) + H2O (l) - Give two uses of sodium carbonate. (2mks)
- Softening hard water
- manufacture of glass
- making sodium silicate use to manufacture soap
- Identify gas R. (1mk)
- The set up below was used to collect gas K, produced by the reaction between water and calcium metal.
- Name gas K (1mk)
- Hydrogen
- At the end of the experiment, the solution in the beaker was found to be a weak base. Explain why the solution is a weak base
- Ca(OH)2 is sparingly soluble in water forming a weak base.
- Name gas K (1mk)
- Name the process which takes place when (2mks)
- Solid Carbon (Iv) Oxide (dry ice) changes directly into gas
- Sublimation
- A red litmus paper turns white when dropped into chlorine water
- Bleaching
- Solid Carbon (Iv) Oxide (dry ice) changes directly into gas
- A student left some crushed fruit mixture with water for some days. He found the mixture had fermented. He concluded that the mixture was contaminated with water and ethanol with boiling point of 100°C and 78°C respectively. The set-up of apparatus below are used to separate the mixture.
- Name the piece of apparatus labelled W (1mk)
- Condenser
- What is the purpose of the thermometer in the set-up? (1mk)
- To indicate when a liquid is boiling, a thermometer reads a constant temperature
- At which end of the apparatus W should tap water be connected? (1mk)
- T
- Which liquid was collected as the first distillate? Explain (1mk)
- Ethanol
- Reason:- It has a lower boiling of 78°C compared to water with a boiling point of 100°C
or - The liquid with the lower boiling point boils first and its vapours are condensed and the condenser to be collected as the first distillate
- What is the name given to the above method of separating mixture? (1mk)
- Fractional distillation
- State two applications of the above method of separating mixtures (1mk)
- To separate components of crude oil
- To isolate O2 and N2 from air
- To manufacture spirits
- What properties of the mixture makes it possible for the component to be separated by the above methods? (1mk)
- They are miscible liquids
- They have different but close boiling points
- Name the piece of apparatus labelled W (1mk)
- The following diagram shows a paper chromatogram of substances A, B, C, and D which are coloured
- Indicate the solvent front on the chromatogram (1mk)
- Which substance is pure? (1mk)
- C
- It contains only one pigment
- Substance E is a mixture of C and D. Indicate its chromatogram in the diagram (1mk)
- The diagram below shows students set-up for the preparation and collection of oxygen gas
- Name substance X used (1mk)
- Hydrogen peroxide
- Write an equation to show the reaction of sodium peroxide with the substance named in (1mk)
2H2O2(l) → 2H2O(aq) + O2(g)
- Name substance X used (1mk)
- A student set-up the experiment as shown below to collect a gas. The wet sand was heated before heating zinc granules
- Complete the diagram for the laboratory preparation of the gas (3mks)
- Why was it necessary to heat wet sand before heating Zinc granules? (1mks)
- to generate/produce steam and expel air initially in the apparatus
- Complete the diagram for the laboratory preparation of the gas (3mks)
- Below are PH values of some solutions.
- Which solution is likely to be
- rain water (½ mark)
- A
- Sodium hydroxide (½ mark)
- B
- rain water (½ mark)
- Which substances will be formed when magnesium reacted with solution C?(1 mark)
- salt and hydrogen gas
- Which solution is likely to be
- An experiment was set up using chlorine water as shown below.
- Identify gas X. (1mk)
- Oxygen
- Write an equation for the production of gas X. (1mk)
2HOCl(aq) → 2HCl(aq) + O2(g) - State any TWO uses of chlorine gas. (2mks)
- manufacture of bleaching agent
- killing micro-organsms in water treatment works
- manufacture of hydrochloric acid
- manufacture of PVC
- Identify gas X. (1mk)
- The set-up below was used to collect gas F produced by the reaction between sodium peroxide and water.
- Name gas F (1mk)
- oxygen
- At the end of the experiment, the solution in the round bottomed flask was found to be a strong base. Explain why this was so. (1mk)
- sodium peroxide reacted with water to form basic sodium hydroxide
- Which property of gas F makes it be collected by the method used in the set-up? (1mk)
- it’s slightly soluble in water
- Give one industrial use of gas F (1mk)
- in oxy-acetylene flame used for welding and cutting of metals
- removes impurities from iron during steel making
- a reactant in fuel cells
- Name gas F (1mk)
- Complete the following table to show the colour of the following indicators in acidic and basic solution (2mks)
Indicator Colour In Acidic Solution Basic Solution Phenopthalein Colourless Pink Methyl Orange Red/pink Yellow Litmus solution Red Blue - Define the following tems (2mks)
- Cation
- a positively charged ion
- Isotopes
- Atoms of the same element with different mass numbers.
- Cation
- The diagram below represents an allotrope of carbon.
- name the allotrope. (1mk)
- graphite
- Explain why:- (2mks)
- its slipperly
- made layers joined together by weak van-der-waal’s forces hence slide over each other.
- Conducts an electric current
- has delocalized electrons in its structure
- its slipperly
- name the allotrope. (1mk)
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Chemistry Questions and Answers - Form 3 Mid Term 1 Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students