INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Answer ALL questions in the spaces provided.
- All workings must be clearly shown where necessary.
-
- In binomial nomenclature, which name is supposed to begin with. (2mks)
- Small letter
- Capital letter
- State any other guideline that should be followed when scientific names are typed or printed. (1mk)
- In binomial nomenclature, which name is supposed to begin with. (2mks)
- Define the following terms as used in the study of living organisms
- Ornithology (1mark)
- Ecology (1mark)
- Cytology (1mark
- State three adaptations of the alveolus to its functions. (3mks)
-
- Explain the term cell specialization. (1mk)
- State how the following cells are specialized to perform their function.
- Red blood cell (1mks)
- Root hair cell (1mk)
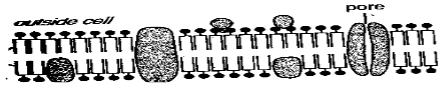
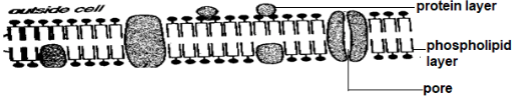
- Below is a diagram of a structure found in Eukaryotic cells? Study it and answer the questions that follow
- Identify the structure (1 mark)
- State two properties of the structure (2 marks)
- On the diagram, label protein layer and phospholipid layer (2 marks)
- List down any two importance of translocated food substances in plants. (2mks)
- State two differences between open and closed circulatory system. 2mks)
- State TWO reasons why it is important for plants to lose water vapour to the atmosphere. (2mks)
-
- What is blood transfusion? (2mks)
- From among the following blood vessels, place each in its correct description.
Artery, capillary, vein, (3mks)
Carry blood at highest pressure Carry blood at lowest pressure Has thick muscular wall
- Write down two adaptations of the root hairs to perform their function. (2mks)
-
- Explain why the leaf of a sisal plant has a thick and shiny cuticle (2mks)
- Which blood vessel supplies oxygenated blood to the liver.? (1mk)
- Name the gaseous exchange site in :
- Man (1 mk)
- Fish (1 mk)
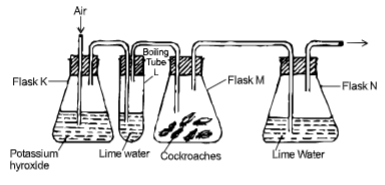
- The diagram below represents a set-up that students used in an investigation.
- Name the physiological process that was being investigated. (1 mark)
-
- What observation would be made in boiling tube L and N. (2 mark)
- Give reason for the observation made in flask N. (2mark)
- How do the following factors affect active transport?
- Glucose concentration. (2mks)
- Change in pH. (2mks)
- State three differences between glycolysis and krebs cycle. (3mks)
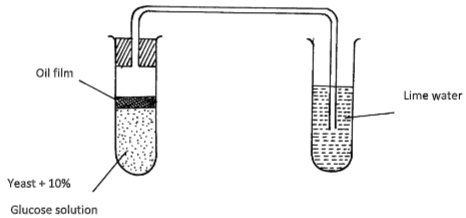
- The apparatus below was used to investigate anaerobic respiration:-
- How would you remove dissolved oxygen from the glucose before the experiment Commencing? (1mk)
- State what happens to the lime water as the experiment proceeds to the end (1mk)
- Describe the reactions in the experiment (3mks)
- State 2 ways through which plants eliminate their waste products. (2mks)
- State the functions of the following parts of the human skin. (2mks)
- Nerve endings,
- Cornified layer.
- Name two components of blood that are not present in the glomerular filtrate. (2mks)
-
- Distinguish between digestion and absorption as used in animal nutrition. (2mks)
- Amylase is an enzyme involved in the digestion of starch. Name two parts of digestive system where it digests food. (2mks)
- How is the palisade layer of the leaf adapted for photosynthesis? (2mks)
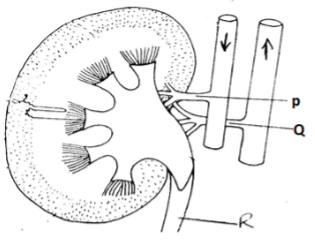
- The diagram below illustrates an internal section of a mammalian kidney.
- State three differences in composition of fluids passing through vessels P and Q. 3marks)
- State two similarities between vessel P and vessel Q in terms of composition of fluids passing through them. (2marks)
- State the substances that would be in high concentration in fluids that pass through vessel R in individuals:- (2marks)
- Suffering from diabetes mellitus.
- Suffering from diuresis.
- Name the organ where R empties its content to. ( 1mark)
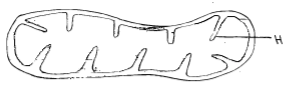
- The diagram below shows an organelle that is found in most cells. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
-
- Name the organelle. (1 mark)
- State the function of the organelle in a (i) above. (1 mark)
-
- Give the full name of the major chemical compound that is formed in the organelle. (1 mk)
- Identify the gas that is required in order to form the compound you have stated in b (i)above. (1 mark)
- Give the name of the structure labeled H and state its function. (2 marks)
- Identity
- Function
-
- In which cells between spermatozoa or ova would you expect to find a high number of the organelles named in a (i) above? (1 mark)
- Give a reason for your answer in d (i) above. (1 mark)
-
- Describe the:
- Process of inhalation in mammals. (8marks)
- Mechanism of opening and closing of the stomata using the photosynthetic theory. (12marks)

MARKING SCHEME
-
- In binomial nomenclature, which name is supposed to begin with. (2mks)
- Small letter
- Specific name/species name;
- Capital letter
- Generic/genus name;
- Small letter
- State any other guideline that should be followed when scientific names are typed or printed. (1mk)
- They should be written in italics;
- In binomial nomenclature, which name is supposed to begin with. (2mks)
- Define the following terms as used in the study of living organisms
- Ornithology (1mark)
- Study of birds
- Ecology (1mark)
- Study of organisms in relation to their surrounding
- Cytology (1mark
- Study of cell
- Ornithology (1mark)
- State three adaptations of the alveolus to its functions. (3mks)
- Thin epithelium for reduction of diffusion distance of respiratory gases;
- Highly vascularized to transport gases/maintain a steep concentration gradient;
- Moist surface to dissolve respiratory gases so that they diffuse in solution form;
-
- Explain the term cell specialization. (1mk)
- Structural modification of a cell to perform a specific function;
- State how the following cells are specialized to perform their function.
- Red blood cell (1mks)
- Biconcave to increase surface area for diffusion of gases;
- Lack nucleus and other organells to create room for packing of haemoglobin;
- Presence of carbonic anhydrase involved in transport of carbon (IV) oxide;
- Presence of haemoglobin which has a high affinity for oxygen ;
- Root hair cell (1mk)
- Elongated /has an extension to increase surface area for absorption of water and mineral salts.
- Thin walled to shorten distance over which water and mineral salts diffuse.
- Lack cuticle to allow faster absorption of substances;
- Red blood cell (1mks)
- Explain the term cell specialization. (1mk)
- Below is a diagram of a structure found in Eukaryotic cells? Study it and answer the questions that follow
- Identify the structure (1 mark)
- Cell membrane/plasma membrane
- State two properties of the structure (2 marks)
- Semi permeability
- Sensitivity to change in temperature and pH
- Possession of electric charges
- on the diagram, label protein layer and phospholipid layer (2 marks)
- Identify the structure (1 mark)
- List down any two importance of translocated food substances in plants. (2mks)
- Glucose is required for respiration;
- Proteins are used for growth;
- Protein are used for repair and replacement of worn out tissues;
- Oils are converted to lipids to be structural components of cell membranes.
- Waste products are stored in tissues that are dropped or shed for excretion;
- Oil is deposited on some leaf surfaces as wax, to make it water proof.
- State two differences between open and closed circulatory system. 2mks)
Open Closed (a) Transport fluid conveyed in general body Cavity, no blood vessels. Transport fluid conveyed in blood vessel, has Blood vessels’ (b) Fluid flow under low pressure Blood flows under high pressure. (c) Fluid is in direct contact with tissues blood not in contact with tissues - State two reasons why it is important for plants to lose water vapour to the atmosphere. (2mks)
- It serves to cool the plant in hot environment;
- Removes excess water in hydrophytes;
- It serves to replace water lost through the leaves;
- Through the process, mineral salts and water are transported;
- Its responsible for turgor hence support in plants;
-
- What is blood transfusion? (2mks)
- It’s the medical transfer of screened compatible blood; to the circulatory system of recipient;
- From among the following blood vessels, place each in its correct description.
Artery, capillary, vein, (3mks)Carry blood at highest pressure Carry blood at lowest pressure Has thick muscular wall Capillary Vein Artery
- What is blood transfusion? (2mks)
- Root hairs grow from piliferous layer of young roots. Write down the adaptations of the root hairs to perform their function. (3mks)
- Elongated/numerous, hence increase surface area for water and mineral salt absorption;
- Have many mitochondria to supply energy for active transport;
- Have thin cell wall ensures rapid movement of minerals;
-
- Explain why the leaf of a sisal plant has a thick and shiny cuticle (2mks)
- Cuticle is waxy and water proof; a thick cuticle reduces transpiration to conserve water;
- A shiny cuticle reflects light landing on a leaf, reducing internal heating of the leaf;
- Reducing rate of transpiration;
- Which blood vessel supplies oxygenated blood to the liver.? (1mk)
- Hepatic artery;
- Explain why the leaf of a sisal plant has a thick and shiny cuticle (2mks)
- Name the gaseous exchange site in :
- Man (1 mk)
- Alveolus
- Fish (1 mk)
- Gill filament
- Man (1 mk)
- The diagram below represents a set-up that students used in an investigation.
- Name the physiological process that was being investigated. (1 mark)
- Respiration
-
- What observation would be made in boiling tube L and N. (2 mark)
- L- Remained clear/colourless
- N-white precipitates formed in limewater
- Give reason for the observation made in flask N. (2mark)
- Carbon (IV) produced by cockroaches ; react with lime water forming white precipitates;/insoluble calcium carbonate
- What observation would be made in boiling tube L and N. (2 mark)
- Name the physiological process that was being investigated. (1 mark)
- How do the following factors affect active transport?
- Glucose concentration. (2mks)
- Glucose is oxidized to provide energy during respiration hence a higher concentration of glucose increases the rate of active transport;
- Change in pH. (2mks)
- Carrier proteins work best at optimum pH; extreme pH /change in pH from optimum denature carrier proteins/respiratory enzymes, lowering the rate of active transport;
- Glucose concentration. (2mks)
- State three differences between glycolysis and krebs cycle. (3mks)
Glycolysis Kreb's cycle occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell; Occur in the matrix of the mitochondria; one molecule of glucose yields two molecules of ATP; In kreb’s cycle one molecule of glucose yields 36 molecules of ATP: does not require oxygen; require oxygen; - The apparatus below was used to investigate anaerobic respiration:-
- How would you remove dissolved oxygen from the glucose before the experiment Commencing? (1mk)
- Boiling the glucose solution;
- State what happens to the lime water as the experiment proceeds to the end (1mk)
- Forms a white precipitate;
- Describe the reactions in the experiment (3mks)
- Yeast produces enzyme amylase which catalyze breakdown of glucose anaerobically into energy (heat), CO2 and Ethanol
- CO2 reacts with the lime water to form a white precipitate;
- How would you remove dissolved oxygen from the glucose before the experiment Commencing? (1mk)
- State 2 ways through which plants eliminate their waste products. (2mks)
- Reutilization of some of the wastes; e.g. oxygen a waste of photosynthesis used in respiration and carbon (IV) oxide a waste of respiration used in photosynthesis;
- The gaseous waste removed through diffusion;
- Exudation of resins;
- Transpiration of water vapour;
- Guttation of water droplets;
- State the functions of the following parts of the human skin. (2mks)
- Nerve endings,
- Detect changes from the external environment e.g. temperature, pressure and touch;
- Cornified layer.
- Provide protection against mechanical damage and invasion by bacteria;
- Reduces loss of water by evaporation;
- Nerve endings,
- Name two components of blood that are not present in the glomerular filtrate. (2mks)
- Plasma proteins;
- Blood cells;
-
- Distinguish between digestion and absorption (2mks)
- Digestion is the breakdown of food into simpler forms (that can be absorbed); while absorption is the uptake of digested food in the blood stream;
- Amylase is an enzyme involved in the digestion of starch. Name two parts of digestive system where it digests food. (2mks)
- Mouth
- Duodenum; acc ileum
- How is the palisade layer of the leaf adapted for photosynthesis? (4mks)
- Cells are closely packed; trap any/all light that reaches them,
- Cells have many chloroplasts; to trap light; energy
- Distinguish between digestion and absorption (2mks)
- The diagram below illustrates an internal section of a mammalian kidney.
- State three differences in composition of fluids passing through vessels P and Q. 3marks)
P Q More urea Less urea; More water Less water; More salts Less salts; - State two similarities between vessel P and vessel Q in terms of composition of fluids passing through them. (2marks)
- Same concentration of blood cells;
- Same concentration of plasma proteins;
- State the substances that would be in high concentration in fluids that pass through vessel R in individuals:- (2marks)
- Suffering from diabetes mellitus.
- Glucose;
- Suffering from diuresis.
- Water;
- Suffering from diabetes mellitus.
- Name the organ where R empties its content to. ( 1mark)
- Urinary bladder;
- State three differences in composition of fluids passing through vessels P and Q. 3marks)
- The diagram below shows an organelle that is found in most cells. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
-
- Name the organelle. (1 mark)
- Mitochondrion
- State the function of the organelle in a (i) above. (1 mark)
- Site for respiration.
- Name the organelle. (1 mark)
-
- Give the full name of the major chemical compound that is formed in the organelle. (1 mk)
- Adenosine Triphosphate.
- Identify the gas that is required in order to form the compound you have stated in b (i)above. (1 mark)
- Oxygen
- Give the full name of the major chemical compound that is formed in the organelle. (1 mk)
- Give the name of the structure labeled H and state its function. (2 marks)
- identity; Cristae
- Function; To increase the surface area for attachment of respiratory enzymes.
-
- In which cells between spermatozoa or ova would you expect to find a high number of the organelles named in a (i) above? (1 mark)
- Spermatozoa
- Give a reason for your answer in d (i) above. (1 mark)
- Spermatozoa rely on their own means of propulsion (swimming) to move up the female reproductive tract hence uses/ requires a lot of energy while ova are propelled by cilia present on the inner lining of the oviduct. 2 marks
- In which cells between spermatozoa or ova would you expect to find a high number of the organelles named in a (i) above? (1 mark)
-
- Describe the:
- Process of inhalation in mammals. (8marks)
- Muscles of diaphragm contract; causing the diaphragm to flatten (from dome position); The external intercostals muscles contract; internal intercostals muscles relax; pulling the ribcage upward/forward and outward in man;
- These movements increase the volume of the thoracic cavity reducing the pressure; of the thoracic cavity compared to atmospheric pressure; this causes the atmospheric air to rush into the lungs; (Through the nostrils, trachea bronchioles and alveoli).
max 8
- Mechanism of opening and closing of the stomata using the photosynthetic theory. (12marks)
- Opening
- In the guard cells there are chloroplast which carry out photosynthesis in the presence of light; ( in the day)
- During photosynthesis glucose is produced in the guard cells; this increases osmotic pressure compared to the neighbouring epidermal cells; water then moves into the guard cells by osmosis and increase their turgidity;
- The inner walls of guard cells are thicker than the outer walls; which stretch more than the inner walls causing guard cells to bulge outwards causing the stomata to open; (Max 6)
- Closing
- During the night when there is no light no photosynthesis takes place in the guard cells; Glucose in the guard cells is converted into starch; this lowers osmotic pressure of the guard cells than the neighbouring cells;
- Water is then drawn away from the guard cells into the neighbouring cells by osmosis, making them to be flaccid;
- Thinner outer wall shrink and the curvature of the thicker inner wall reduces; then the stomata closes; (Max 6)
- Opening
- Process of inhalation in mammals. (8marks)
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Biology Questions and Answers - Form 3 Mid Term 1 Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students