- This paper consists of three sections; A, B and C
- Answer ALL the questions in sections A, B and C.
- All answers to be written in English
SECTION A: 40 MARKS
ATTEMPT ALL QUESTIONS.
- Name two breeds of camel (2 mks)
- Give two factors which characterize small scale farming (2 mks)
- Give two examples for each of the following categories of water pipes
- Metal pipes (1 mk)
- Hose pipes (1 mk)
- State two factors that influence the quality of farmyard manure (2 mks)
- Name three farm records that should be kept by a poultry farmer (3 mks)
- Describe three properties of nitrogenous fertilizer (3 mks)
- Give three reasons for using certified seeds for planting (3 mks)
- Describe the procedure followed in preparing seed potatoes for planting. (3 mks)
- Differentiate between olericulture and pomoculture as used in crop production (1 mk)
- Give three factors to consider when choosing a nursery site. (3 mks)
- Give two advantages of crop rotation (2 mks)
- State three disadvantages of mono – cropping in crop production (3 mks)
- What is meant by the following words:
- Pruning (1 mk)
- Rouging (1 mk)
- State three reasons for maintaining livestock in good health. (3 mks)
- State three uses of water in the body of the animal. (3 mks)
- List two methods of testing soil pH in agriculture. (2 mks)
SECTION B: 30 MARKS.
ATTEMPT ALL QUESTIONS.
- An experiment was carried out with three different soils. The soils were put in different capillary tubes of equal sizes. The capillary tubes were placed in water trough containing water. The results after six hours are shown in the diagram below. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
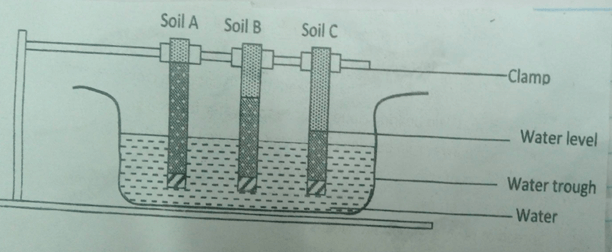
- What was the aim of this experiment? (1 mk)
- Name the soil A, B and C (3 mks)
- State two ways of improving soil C for growth of crops. (2 mks)
- The diagram below illustrates the stages of life cycle of a tick. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow.
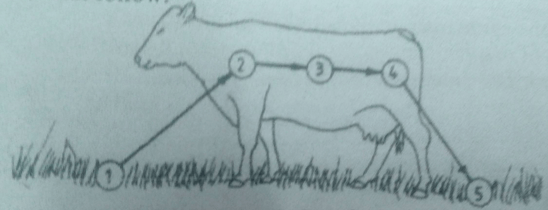
- Describe the development of ticks at stage 1, 2, 3, and 4. (4 mks)
- Classify the tick on the basis of the life cycle. (1 mks)
- Give three non – chemical methods of controlling ticks. (3mks)
- The diagram below illustrates a nursery practice. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
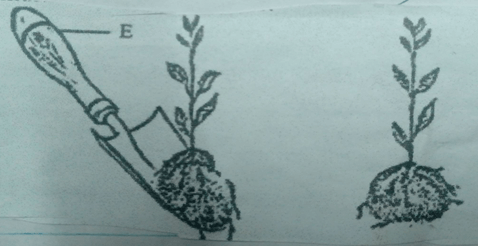
- Name the practice. (1 mk)
- Give a reason why the tool labeled E is important in the practice illustrated. (1 mk)
- What is the appropriate stage of growth for carrying out the illustrated practice in vegetables? (1 mk)
- Explain two activities that ensure the illustrated practice is called out successfully. (2 mks)
- The diagram shows the digestive system of cattle. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
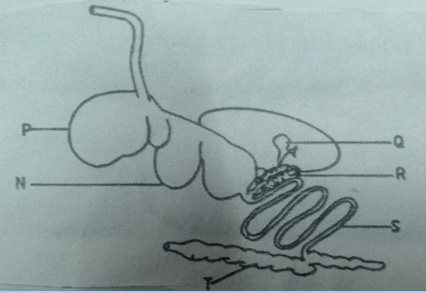
- Name the parts labeled N, P and Q. (3 mks)
- State one function of the parts labeled (2 mks)
- S
- T
- Give one enzyme produced by each of the parts labeled R and S. (2 mks)
- A member of Young Farmers Club in Sabasaba secondary school was advised to apply fertilizer 30:20:10 in a tomato plot measuring 10m by 5m at the rate of 300Kg per hectare. (1 ha = 10,000m2)
- State the percentage of:
- P2O5 in the complete fertilizer (1 mk)
- K2O in the complete fertilizer. (1 mk)
- Calculate the amount of fertilizer the member would require for the plot. Show your working. (2 mks)
- State the percentage of:
SECTION C: 40 MARKS
ATTEMPT ALL THE QUESTIONS.
- Describe the production of kales under the following sub headings
- Nursery preparation (3 mks)
- Management of seedlings in the nursery (4 mks)
- Give one condition under which blossom end rot disease may occur in tomatoes (1 mk)
-
- State five effects of strong winds in crop production. (5 mks)
- Explain eight environmental conditions that may lead to low crop yields (8 mks)
- State four advantages of irrigation (4 mks)
-
- Describe signs of ill health in livestock (10 mks)
- Describe five farming practices that help to achieve minimum tillage. (5 mks)

MARKING SCHEME
- Name two breeds of camel (2 mks)
- Dromedary
- Bacterian ( 2X1 = 2mk)
- Give two factors which characterize small scale farming (2 mks)
- Small size of land
- Limited capital
- Limited tools/implements
- Maximizes use of available labour
- Less labour required (2 X 1 = 2 mks)
- Give two examples for each of the following categories of water pipes
- Metal pipes (1 mk)
- Galvanized iron pipes
- Aluminum pipes
- Steel pipes
- Copper pipes (2X ½ = 1mk)
- Hose pipes (1 mk)
- Rubber hose pipes
- Plastic hose pipes (2X ½ = 1mk)
- Metal pipes (1 mk)
- State two factors that influence the quality of farmyard manure (2 mks)
- Feeding material given to the animal
- Species of the animal
- Type of the bedding material used
- Method of storage
- Age of the farmyard manure
- Age of the animal (2X 1=2mks)
- Name three farm records that should be kept by a poultry farmer (3 mks)
- Egg production record
- Feeding record
- Health record
- Labour record (3X1=3mks)
- Describe three properties of nitrogenous fertilizer (3 mks)
- Highly soluble in water
- Are corrosive
- Easily leached
- Has a scorching effect
- Easy to volatilize
- Are highly hygroscopic (3X1=3mks)
- Give three reasons for using certified seeds for planting (3 mks)
- High yielding
- Free from foreign materials e.g. weed seeds
- Give rise to vigorously growing plants
- Have high germinating percentage
- Free from pests and diseases
- True to the type (3X1=3mks)
- Describe the procedure followed in preparing seed potatoes for planting. (3 mks)
- Arrange the setts/tubers in a store with the rose end facing upwards
- Tubers are arranged 2 – 3 layers
- Allow diffuse light to pass through the store
- Dust the sets/tubers with appropriate insecticides to control pests
- Spray fungicides to control fungal infections
- Sprinkle some water in tubers if the condition is dry. (3X1=3mks)
- Differentiate between olericulture and pomoculture as used in crop production (1 mk)
- Olericulture is growing of vegetables while pomoculture is the growing of fruits (1X1=1mk)
- Give three factors to consider when choosing a nursery site. (3 mks)
- Near a reliable source of water
- Well drained area with deep fertile soils
- Accessible
- Gently sloping area
- Well secured area
- Sheltered area
- Should not have been used for the same crop species in the previous season (3X1 = 3mks)
- Give two advantages of crop rotation (2 mks)
- Improves soil structure
- Controls soil borne pests and diseases
- Ensure maximum utilization of farm labour
- Aids in weed control
- Controls soil erosion when cover crops are used
- Security in case of failure of one crop
- Improves soil fertility when legumes are included (2X1=2mks)
- State three disadvantages of mono – cropping in crop production (3 mks)
- High risk of total loss in case of crop failure
- Underutilization of some soil nutrients
- Build – up of crop pests and diseases
- Leads to destruction of soil structure
- Results in soil erosion in crops with poor ground cover
- Faster spread of pests and diseases
- Leads to loss of soil fertility ( 3X1=3mks)
- What is meant by the following words:
- Pruning (1 mk)
- It’s the removal of extra or unwanted parts of a plant (1X1=1mk)
- Rouging (1 mk)
- It’s the uprooting and destruction of plants infected by diseases to prevent further spread of the disease to healthy plants. (1X1=1mk)
- Pruning (1 mk)
- State three reasons for maintaining livestock in good health. (3 mks)
- Healthy animals produce good quality products hence get a high market value
- Healthy animals have a longer economic and productive life
- Healthy animals grow well and fast to reach maturity early
- Healthy animals do not spread diseases to other animals or human beings
- They are economical to keep and farmer spends less money leading to maximum profits (3X1=3mks)
- State three uses of water in the body of the animal. (3 mks)
- Helps to regulate body temperatures through sweating and evaporation
- Helps in the excretion of waste products from the body
- It is a component of body cells and many body fluids like blood
- It makes cells turgid, maintaining the shape of the body cells
- It is responsible for the transportation of nutrients from one part of the body to another
- Used in the bio chemical reactions in the body
- It forms part of animal products e.g. milk contains 83% water (3X1=3mks)
- List two methods of testing soil pH in agriculture. (2 mks)
- Use of colour indicator dyes
- Use of a PH meter (2X1=2mks)
SECTION B: 30 MARKS.
ATTEMPT ALL QUESTIONS.
- An experiment was carried out with three different soils. The soils were put in different capillary tubes of equal sizes. The capillary tubes were placed in water trough containing water. The results after six hours are shown in the diagram below. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- What was the aim of this experiment? (1 mk)
- To compare capillary action in different soils
- Name the soil A, B and C (3 mks)
- A – clay soil
- B – loamy soil
- C – sandy soil (3X1=3 mks)
- State two ways of improving soil C for growth of crops. (2 mks)
- Adding organic manure
- Applying inorganic fertilizers
- Cover cropping
- Use of organic mulching
- Liming the soil
- Leave the soil fallow (2X1=2mks)
- What was the aim of this experiment? (1 mk)
- The diagram below illustrates the stages of life cycle of a tick. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow.
- Describe the development of ticks at stage 1, 2, 3, and 4. (4 mks)
- Stage 1 – the eggs on the ground hatch into larvae which emerge and climb on to the host and feed on blood
- Stage 2 – the engorged larvae mount in to nymphs which emerge and feed on blood
- Stage 3 – the engorged nymphs mounts into adult which emerge and feed on the blood of host
- Stage 4 – the engorged adult mates and female drops to the ground to lay eggs (4X1=4mks)
- Classify the tick on the basis of the life cycle. (1 mks)
- One host tick (1X1=1mk)
- Give three non – chemical methods of controlling ticks. (3mks)
- Burning infested pastures
- Hand picking and killing of ticks
- Rotational grazing
- Double fencing of pastures
- Zero grazing
- Ploughing infested pastures (3X1=3mks)
- Describe the development of ticks at stage 1, 2, 3, and 4. (4 mks)
- The diagram below illustrates a nursery practice. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Name the practice. (1 mk)
- Transplanting (1X1=1mk)
- Give a reason why the tool labeled E is important in the practice illustrated. (1 mk)
- It ensures a seedling is lifted with a ball/lump of soil around the roots (1X1=1mk)
- What is the appropriate stage of growth for carrying out the illustrated practice in vegetables? (1 mk)
- 1 month / 4 weeks
- 4 – 6 true leaves
- Pencil thick
- 10 – 15 cm tall (1X1=1mk)
- Explain two activities that ensure the illustrated practice is called out successfully. (2 mks)
- Watering before lifting the seedling to prevent root damage
- Planting at the same depth it was in the nursery to prevent rotting
- Shading to prevent excess water loss
- Watering to maintain soil moisture
- Mulching to avoid evaporation of water
- Protection to prevent damage by animals
- Selecting healthy and vigorous growing seedlings (2X2=2mks)
- Name the practice. (1 mk)
- The diagram shows the digestive system of cattle. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Name the parts labeled N, P and Q. (3 mks)
- N – omasum
- P – rumen
- Q – gall bladder (3X1=3mks)
- State one function of the parts labeled (2 mks)
- S – digestion / absorption of food (1X1=1mk)
- T – absorption of water (1X1=1mk)
- Give one enzyme produced by each of the parts labeled R and S. (2 mks)
- R – lipase, trypsin, amylase (1X1=1mk)
- S – peptidase, maltase, sucrose (invertase), lactase (1X1=1mk)
*Reject pancreatic juice and intestinal juices
- Name the parts labeled N, P and Q. (3 mks)
- A member of Young Farmers Club in Sabasaba secondary school was advised to apply fertilizer 30:20:10 in a tomato plot measuring 10m by 5m at the rate of 300Kg per hectare. (1 ha = 10,000m2)
- State the percentage of:
- P2O5 in the complete fertilizer (1 mk)
- 20% (1X1=1mk)
- K2O in the complete fertilizer. (1 mk)
- 10 % (1X1=1mk)
- P2O5 in the complete fertilizer (1 mk)
- Calculate the amount of fertilizer the member would require for the plot. Show your working. (2 mks)
10,000m2 requires300kg fertilizer
Therefore, an area measuring (10X5)m2 = 50m2 would require
50m2 X300kg = 1.5kg
10000m2
= 1.5 kg of the fertilizer
- State the percentage of:
SECTION C: 40 MARKS
ATTEMPT ALL THE QUESTIONS.
- Describe the production of kales under the following sub headings
- Nursery preparation (3 mks)
- Clear the land if bushy
- Carry out primary cultivation/dig deep, remove perennial weeds
- Remove roots and stones from the site
- Measure the nursery bed 1m wide by any convenient length
- Prepare raised/sunken beds depending on moisture availability
- Level the nursery bed (3X1=3mk)
- Management of seedlings in the nursery (4 mks)
- Remove the mulching as soon as seedlings emerge and erect a shade
- Water the seedlings atleast twice daily, preferably in the morning and late in the evening
- Remove weeds by uprooting as they come up
- Thin out the overcrowded seedlings/ pluck out
- Control pests and diseases using appropriate methods
- Harden off the seedlings/ remove the shade and gradually reduce frequency of watering. (4X1=4mks)
- Give one condition under which blossom end rot disease may occur in tomatoes (1 mk)
- Irregular watering
- Calcium deficiency in the soil or young fruits
- Too much nitrogen in early stages of growth. (1X1=1mk)
- Nursery preparation (3 mks)
-
- State five effects of strong winds in crop production. (5 mks)
- Act as agent of seed dispersal
- Act as agents of soil erosion
- Brings a cooling effect in areas with high humidity
- Destroying farm structures
- Increasing the spread of pests and diseases
- Blowing away and bringing rain – bearing clouds
- Causing lodging in cereal crops and damage to crops
- Increasing the rate of evaporation of moisture from the soil (5X1=5mks)
- Explain eight environmental conditions that may lead to low crop yields (8 mks)
- Poor soil fertility due to lack of manure and fertilizer application
- Low rainfall/too much rainfall/ unreliable rainfall
- Poor soils e.g. poor drained soil leading to water logging
- Pests attack leading to reduced growth and death of plants
- Too high/low temperatures
- Extreme light intensity that may reduce rate of photosynthesis and exhausts plant nutrients
- Hail storms that damage crops
- Excess wind that causes lodging of crops, increase evapotranspiration
- Incorrect soil PH that reduces availability of nutrients (8X1=8mks)
- State four advantages of irrigation (4 mks)
- It does not encourage the growth of weeds between the rows
- Water under low pressure can be used as long as it can flow along the pipe
- It discourages fungal diseases like bright. CBD and others as it does not wet the leaves of the crop.
- Little amount of water is required compared to other types of irrigation. (4X1=4mks)
- State five effects of strong winds in crop production. (5 mks)
-
- Describe signs of ill health in livestock (10 mks)
- Aggressiveness/ over excitement/ production of abnormal sounds
- Restlessness/less responsive to touch
- Starry coat/ parts of skin peeling off
- Dull red/pale/dry mucous membrane
- Sudden decline in production/ performance
- Abnormal body temperature; too high or too low
- Pulse rate deviation from the normal
- Lack of appetite
- Abnormal urine color
- Abnormal feacal matter in terms of consistency (10X1=10mks)
- Describe five farming practices that help to achieve minimum tillage. (5 mks)
- Uprooting or slashing weeds in perennial crops
- Establishing a cover crop on the field
- Restricting cultivation to the area where seeds are to be planted
- Timing cultivation
- Use of mulching materials on the soil surface
- Application of herbicides in controlling the weeds. (5X1 = 5mks)
- Describe signs of ill health in livestock (10 mks)
Download Agriculture Questions and Answers - Form 3 Mid Term 1 Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

