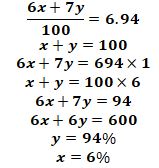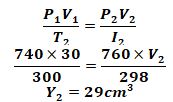Answer All questions in the spaces provided.
-
- Give the main allotrope of sulphur. (2mks)
- Define transition temperature. (1mk)
- Define crystallization. (1mk)
- A student added some pure potassium nitrate crystals to cold water and stirred the mixture. A few of the crystals did not dissolve at room temperature.
- Give a reason why some crystals did not dissolve. (1mk)
- What would happen if the contents of the mixture in a beaker were warmed? Explain. (2mks)
- Name two substance that can be reacted to give copper (II) sulphate. (1mk)
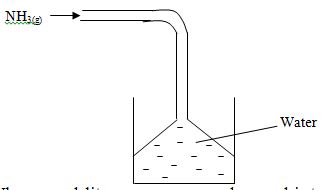
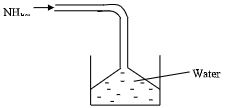
- Ammonia gas was passed into water as shown below.
- When a red litmus paper was dropped into the resulting solution, it turned blue. Give a reason for this observation. (1mk)
- What is the function of the funnel? (1mk)
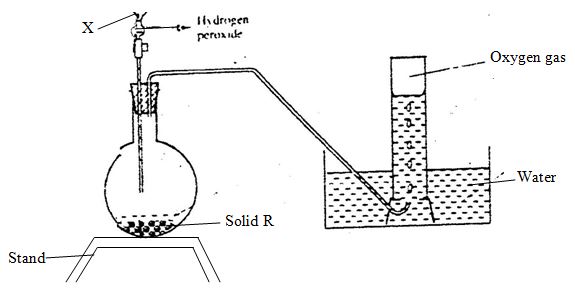
- The diagram below is set-up for the laboratory preparation of oxygen gas.
- Name solid R. (1mk)
- Name the apparatus X. (1mk)
- Write an equation for the reaction that takes place in the flask. (2mks)
- An element Y has electronic arrangement of 2.8.5.
- State the period and the group which the element belong. (2mks)
- Write the formula of the most stable ion formed when the element Y ionizes. (1mk)
- Lithium has two isotopes with mass number 6 and 7. If the R.A.M (relative atomic mass) of Lithium is 6.94, determine the percentage abundance of such isotope. (3mks)
- Give the name of each of the following processes described below when salts are exposed to air for some time.
- Anhydrous copper (II) sulphate becomes blue.
- Magnesium chloride forms an aqueous solution.
- Fresh crystals of sodium carbonate Na2CO3.10H2O covered with a white powder of formula Na2CO3H2O.
- A hydrated salt has the following composition by mass; Iron 20.2%, oxygen 23.0%, sulphur 11.5%, water 45.3%. Its relative formula is 278.(Fe=56, S=32, O=16)
- Determine the formula of hydrated salt. (3mks)
- When magnesium is burnt in air it reacts with oxygen and nitrogen gas giving a white ash. Write two equations for the two reactions that take place. (3mks)
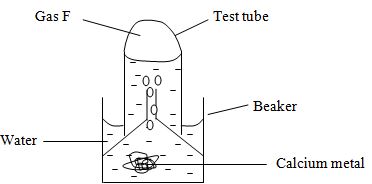
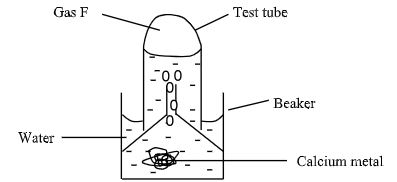
- The set-up was used to collect gas F, produced by the reaction between water and calcium metal.
- Name gas F. (1mk)
- At the end of the experiment, the solution in the beaker is a weak base. Explain. (2mks)
- Give the laboratory use of solution of solution formed in the beaker. (1mk)
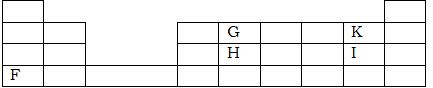
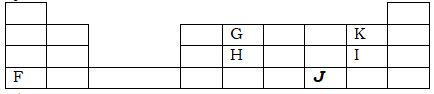
- The grid below sow part of the periodic table. The letters are not the actual symbol of the element.
- Select;
- Element which has the largest atomic radius. (1mk)
- Most reactive non-metal. (1mk)
- Show on the grid the position of element ‘J’ which forms J -2 ions with electronic configuration of 2.8.8.8. (1mk)
- Write the equation between element F and I. (2mks)
- Select;
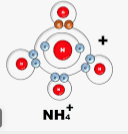
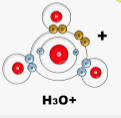
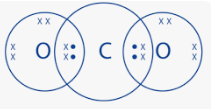
- Use dots (.) and crosses (x) to represents electrons. Draw diagram to show bonding in
- NH4+ (1mk)
- H3O+ (1mk)
- CO2 (1mk)
- In terms of structure and bonding, explain why graphite is used as a lubricant. (2mks)
- The following diagram, show the structure of two allotropes of carbon. Study them and answer the questions that follow
.
- Name the allotropes. (2mks)
M -
N - - Give one use N. (1mk)
- Name the allotropes. (2mks)
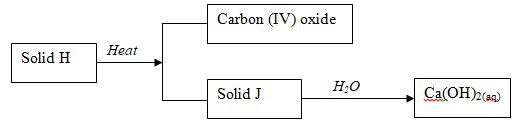
- Use the scheme below to answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the solids J and H. (2mks)
- State one commercial use of solid H. (1mk)
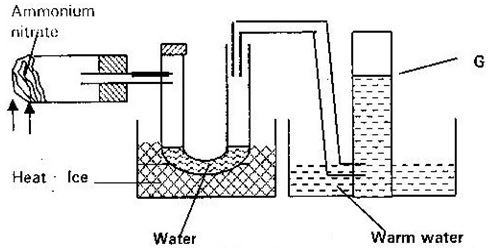
- Ammonium nitrate was gently heated and the products collected as shown in the diagram below.
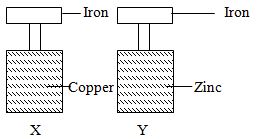
Describe one chemical test and physical properties that can be used to identify gas G. (3mks) - Form two student in an attempt to prevent rusting, put copper and zinc in contact with iron as shown below.
State what would happen in the set up X and Y. (2mks) - Explain how you would separate a mixture of ammonium chloride and sodium chloride into its pure components. (2mks)
- Calculate the mass of lead (II) nitrate that must be heated to give 22.3 g of lead (II) oxide. (pb = 207, N=14, O=16) (3mks)
- 0.84g of aluminium reacted completely with chlorine gas. Calculate the volume of gas used. (Molar gas volume is 24dm3 , Al=27) (3mks)
- State Gay Lussac’s Law. (1mk)
- In an experiment 20cm3 of sulphur (IV) oxide are found to react completely with 10cm3 of oxygen to produce 20cm3 of sulphur (VI) oxide. Determine the equation for the reaction. (3mks)
- Define absolute temperature. (1mk)
- At 27°C and 740mmHg pressure, a sample of nitrogen gas occupies 30cm3 , what will be its volume at standard temperature and pressure (s.t.p)(3mks)
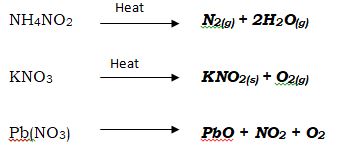
- Complete the following equation and balance. (3mks)
NH4NO2→
KNO3→
Pb(NO3 )→ - The molecular formula of gas R is 28 and its empirical formula is CH2 . (C=12, H=1) Determine the molecular formula of gas R. (2mks)
-
- Define the terms:
- Electrolyte - (1mk)
- Electrolysis - (1mk)
- Explain the difference in conductivity between magnesium and molten magnesium chloride. (1mk)
- Define the terms:
- 30cm3 of hydrogen gas were reacted with 40cm3 of oxygen according to the equation.2H2(g) + O2(g) 2H2 O(g) Identify the gas that was in excess and by how much volume?
MARKING SCHEME
-
- Give the main allotrope of sulphur. (2mks)
- Rhombic
- Monoclinic
- Define transition temperature. (1mk)
- Temperature at which one allotrope of an element changes to another.
- Give the main allotrope of sulphur. (2mks)
- Define crystallization. (1mk)
- This is the process by which crystals are formed when solution are heated to saturation.
- A student added some pure potassium nitrate crystals to cold water and stirred the mixture. A few of the crystals did not dissolve at room temperature.
- Give a reason why some crystals did not dissolve. (1mk)
- The solution reached the saturation point.
- What would happen if the contents of the mixture in a beaker were warmed? Explain. (2mks)
- All the solution will dissolve. Temperature increase solubility.
- Name two substance that can be reacted to give copper (II) sulphate. (1mk)
- Copper metal + dilute sulphuric acid → Copper (II) sulphate
- Give a reason why some crystals did not dissolve. (1mk)
- Ammonia gas was passed into water as shown below.
- When a red litmus paper was dropped into the resulting solution, it turned blue. Give a reason for this observation. (1mk)
- Ammonia gas hydrolysed to form hydroxide OH - which is basic
- What is the function of the funnel? (1mk)
- Funnel prevent the water from ‘sucking back’ into flask. Hence provide large surface area for absorption of ammonia.
- When a red litmus paper was dropped into the resulting solution, it turned blue. Give a reason for this observation. (1mk)
- The diagram below is set-up for the laboratory preparation of oxygen gas.
- Name solid R. (1mk)
- Manganese (IV) oxide
- Name the apparatus X. (1mk)
- Dropping funnel
- Write an equation for the reaction that takes place in the flask. (2mks)
3H2O2(g) MnO2(g) + 3H2O (l)
- Name solid R. (1mk)
- An element Y has electronic arrangement of 2.8.5.
- State the period and the group which the element belong. (2mks)
- Period (III), group (V)
- Write the formula of the most stable ion formed when the element Y ionizes. (1mk)
- Y3-
- Lithium has two isotopes with mass number 6 and 7. If the R.A.M (relative atomic mass) of Lithium is 6.94, determine the percentage abundance of such isotope. (3mks)
- Let x and y be related abundance
- Let x and y be related abundance
- State the period and the group which the element belong. (2mks)
- Give the name of each of the following processes described below when salts are exposed to air for some time.
- Anhydrous copper (II) sulphate becomes blue.
- Hygroscopic
- Magnesium chloride forms an aqueous solution.
- Deliquescence
- Fresh crystals of sodium carbonate Na2CO3 .10H2O covered with a white powder of formula Na2CO3H2O.
- Efflorescence
- Anhydrous copper (II) sulphate becomes blue.
- A hydrated salt has the following composition by mass; (3mks) Iron 20.2%, oxygen 23.0%, sulphur 11.5%, water 45.3%. Its relative formula is 278.(Fe=56, S=32, O=16)
- Determine the formula of hydrated salt. (3mks)
- When magnesium is burnt in air it reacts with oxygen and nitrogen gas giving a white ash. Write two equations for the two reactions that take place. (3mks)
2Mg(s) + O2(g) → 2MgO(s)
3Mg(s) + N2(g) →Mg3N2(s)
- Determine the formula of hydrated salt. (3mks)
- The set-up was used to collect gas F, produced by the reaction between water and calcium metal.
- Name gas F. (1mk)
- Hydrogen gas
- At the end of the experiment, the solution in the beaker is a weak base. Explain. (2mks)
- Form hydroxide which is an alkaline solution.
- Give the laboratory use of solution of solution formed in the beaker. (1mk)
- Used to test presence of carbon (IV) oxide.
- Name gas F. (1mk)
- The grid below sow part of the periodic table. The letters are not the actual symbol of the
- Select;
- Element which has the largest atomic radius. (1mk)
- F
- Most reactive non-metal. (1mk)
- K
- Element which has the largest atomic radius. (1mk)
- Show on the grid the position of element ‘J’ which forms J -2 ions with electronic configuration of 2.8.8.8. (1mk)
- Write the equation between element F and I. (2mks)
F (s) + 2I (g) → FI 2(s)
- Select;
- Use dots (.) and crosses (x) to represents electrons. Draw diagram to show bonding in
- NH4+ (1mk)
- H3O+ (1mk)
- CO2 (1mk)
- NH4+ (1mk)
- In terms of structure and bonding, explain why graphite is used as a lubricant.(2mks)
- Graphite has weak van der waals forces which make them to slide over each other.
- The following diagram, show the structure of two allotropes of carbon. Study them and answer the questions that follow.
- Name the allotropes. (2mks)
- M - …Graphite
- N - …Diamond
- M - …Graphite
- Give one use N. (1mk)
- Use to make ornament
- Name the allotropes. (2mks)
- Use the scheme below to answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the solids J and H. (2mks)
- CaCO3
- State one commercial use of solid H. (1mk)
- Used in making glass
- Identify the solids J and H. (2mks)
- Ammonium nitrate was gently heated and the products collected as shown in the diagram below.
Describe one chemical test and physical properties that can be used to identify gas G. (3mks)- Physical properties it has a faint sweet smell.
- Chemical properties – when a glowing wooden splint is brought in the jar containing the gas, it relight the glowing splint.
- Form two student in an attempt to prevent rusting, put copper and zinc in contact with iron as shown below.
- State what would happen in the set up X and Y. (2mks)
- Rust will occur in X but no rust in Y. reason, copper is higher in reactivity series than iron hence form rust.
- State what would happen in the set up X and Y. (2mks)
- Explain how you would separate a mixture of ammonium chloride and sodium chloride into its pure components. (2mks)
- Put both Ammonium chloride and sodium chloride in a beaker. Cover using a watch glass. Heat the mixture, Ammonium chloride shall sublime leaving behind sodium chloride in the beaker.
- Calculate the mass of lead (II) nitrate that must be heated to give 22. 3 g of lead (II) oxide. (pb = 207, N=14, O=16) (3mks)
2Pb(NO3)2 → 2PbO + 4NO2 + O2
Moles PbO =22.3/22.3=0.1mole
Mass = RFM No. of moles
331×0.1
= 33.1g - 0.84g of aluminium reacted completely with chlorine gas. Calculate the volume of gas used. (Molar gas volume is 24dm3 , Al=27) (3mks)
2Al + 3Cl 2 → 2AlCl3
Moles of Al =0.84/27=0.03mole
Mole = 24dm3
0.045
0.045×24=1.08dm³ - State Gay Lussac’s Law. (1mk)
- When gases reacts, they do so in volumes that bear a simple ratio to one another and to the volumes of the product if gaseous, temperature and pressure remaining constant.
- In an experiment 20cm 3 of sulphur (IV) oxide are found to react completely with 10cm 3 of oxygen to produce 20cm 3 of sulphur (VI) oxide. Determine the equation for the reaction. (3mks)
SO 2(g) + O2 (g) → SO3
20cm3 10cm3 20cm3
2 vol 2vol 2vol
Mole rate 2:12
The balanced equation
2SO2(g)+O2(g) → 2SO3(g) - Define absolute temperature. (1mk)
- This is the temperature at which the volume of the gas is assumed to be zero.
- At 27°C and 740mmHg pressure, a sample of nitrogen gas occupies 30cm3 , what will be its volume at standard temperature and pressure (s.t.p)(3mks)
- Complete the following equation and balance. (3mks)
- The molecular formula of gas R is 28 and its empirical formula is CH 2 . (C=12, H=1) Determine the molecular formula of gas R. (2mks)
(CH2)n = 28
14n = 28
n = 2
(CH 2) 2 = C2H4 -
- Define the terms:
- Electrolyte - (1mk)
- A substance which conducts electricity in molten or aqueous state.
- Electrolysis - (1mk)
- Decomposition of an electrolyte by passing an electric current through it.
- Electrolyte - (1mk)
- Explain the difference in conductivity between magnesium and molten magnesium chloride. (1mk)
- Magnesium uses delocalized electrons while MgCl2 (molten) uses mobile/ free ions.
- Define the terms:
- 30cm3 of hydrogen gas were reacted with 40cm3 of oxygen according to the equation.2H2(g) +O2(g)2H2O(g)
Identify the gas that was in excess and by how much volume? (2mks)
2H2 + O2 → 2H2O
30cm3 15cm3
Oxygen was in excess by 40 – 15 = 25cm3
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download CHEMISTRY Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Form 3 End Term 1 Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students