SECTION A (30 MARKS)
Answer all Questions in this section
- Give four advantages of practicing crop rotation (2mks)
- Name any four records that should be kept by a poultry farmer (2mks)
- Give two areas of study that make agriculture to be regarded as a science (1mk)
- A farmer has the option of growing either wheat or maize in his one hectare of land. Wheat gives a return of sh 20000 while maize gives a return of sh.35000. What will be the opportunity cost? (1mk)
- State any two conditions under which opportunity cost is zero
- Give two practices that are commonly used in hardening seedlings in a nursery of kales (1mk)
- Outline four advantages of tissue culture (2mks)
- Name any four farming practices aimed at minimum tillage (2mks)
- Outline four factors that determine the depth of planting (2mks)
- State three factors that determine the quality of compost manure (1 ½mks)
- Distinguish between under sowing and over sowing as used in pasture establishment (1mk)
- State two disadvantages of shifting cultivation (1mk)
- Name any four methods of treating seeds before planting (2mks)
- Give four reasons why seeds may be preferred in crop propagation (2mks)
- Differentiate between soil structure and soil texture (1mk)
- State four reasons why burning of fields is discouraged in crop production (2mks)
- Name three diseases that attack cabbage (1 ½ mks)
- State four characteristics that make a crop suitable for green manure (2mks)
- State four different types of irrigation that can be used by farmers (2mks)
SECTION B (20 MARKS)
Answer all questions
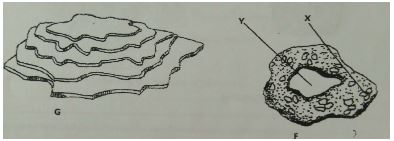
- The diagram below illustrates some soil structures. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the soil structures F and G (2mks)
- Name the parts labeled X and Y in diagram F (1mk)
- Sate two ways through which structure G influences crop production (2mks)
- The diagram below illustrates a type of fruit. Study nit and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the fruit (1mk)
- Name the parts A-D ((4mks)
- Name two crops propagated by the part labeled D (1MK)
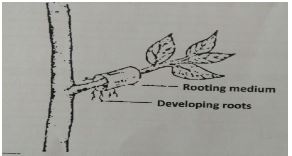
- The diagram below shows a method of layering. Study it and answer questions that follow
- Identify the method of layering illustrated above (1mk)
- State one circumstance in which this method of layering is recommended(1mk)
- A maize farmer was advised to apply 150 kg CAN per hectare while topdressing the maize crop. CAN contains 21%N. calculate the amount of Nitrogen applied per hectare. (3mks)
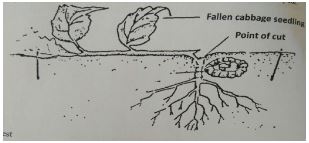
- The diagram below shows a seedling attacked by a certain pest.
- Identify the pest (1mk)
- Name any two types of vegetable crops likely to be attacked by the pests (2mks)
- State two methods of controlling the above pest (2mks)
SECTION C (40 marks)
Choose any two questions from this section
-
- Outline the effects of wind on agricultural products (11mks)
- Briefly mention the importance of soil organic matter (9mks)
-
- Describe the advantages of using seeds as planting materials (5mks)
- Give reasons for raising vegetable seedling through a nursery (5mks)
- Outline the process of chemical water treatment for use in the farm (10mks)
-
- Explain five factors that determine spacing to be used in crops (10mks)
- Describe six management practices carried out on a nursery bed (6mks)
- Explain four advantages of grafting (4mks)

MARKING SCHEME
- Give four advantages of practicing crop rotation (2mks)
- Maximum utilization of resources
- Control of soil borne pests and diseases
- Control of weeds
- Improvement of soil fertility
- Improves soil structure if grass layer is included
- Controls soil erosion
- Name any four records that should be kept by a poultry farmer (2mks)
- Health records
- Production records
- Feeding records
- Inventory records
- Marketing records
- Give two areas of study that make agriculture to be regarded as a science (1mk)
- Genetics
- Ecology
- Soil science
- Crop pathology
- Agricultural engineering
- Entomology
- A farmer has the option of growing either wheat or maize in his one hectare of land. Wheat gives a return of sh 20000 while maize gives a return of sh.35000. What will be the opportunity cost? (1mk)
- Sh.20000 for growing wheat
- State any two conditions under which opportunity cost is zero
- When there is no alternative
- When commodity is free
- When there is unlimited supply of resources
- Give two practices that are commonly used in hardening seedlings in a nursery of kales (1mk)
- Reduce rate of watering
- Reduce shade
- Outline four advantages of tissue culture (2mks)
- It is fast
- Produce pathogen free plants
- Mass propagation of propagates
- Requires less space
- Can be used to propagate seedless varieties
- Name any four farming practices aimed at minimizing tillage (2mks)
- Mulching
- Uprooting/slashing weeds
- Use of herbicides to control weeds
- Use of cover crops
- Cultivating only the planting hole
- Outline four factors that determine the depth of planting (2mks)
- Size of the seed
- Soil type
- Soil moisture content
- Type of germination
- State three factors that determine the quality of compost manure (1 ½mks)
- Type of materials used
- Method of preparation
- Method of storage
- Length of decay
- Distinguish between under sowing and over sowing as used in pasture establishment (1mk)
- Under sowing-establishment of a pasture crop under a cover crop
- Over sowing- establishment of a legume pasture in an existing grass pasture
- State two disadvantages of shifting cultivation (1mk)
- Low total yield per unit area
- Time consuming
- No incentive to develop land
- Not practical in densely populated areas
- Name any four methods of treating seeds before planting (2mks)
- Seed cleaning
- Seed inoculation
- Breaking seed dormancy
- Seed dressing
- Chitting
- Give four reasons why seeds may be preferred in crop propagation (2mks)
- Less bulky
- Can be stored for a long time
- Planting can be mechanized
- Easy to control pests and diseases
- Cheaper to buy than vegetative materials
- Differentiate between soil structure and soil texture (1mk)
- Soil structure is the relative arrangement of soil particles in aggregates while soil texture is the relative proportions of sand, silt and clay particles in a given soil sample
- State four reasons why burning of fields is discouraged in crop production (2mks)
- Burn important soil organisms
- Burns organic matter
- Destroys soil structure
- Fire can destroy other structures
- Evaporates the soil moisture
- Name three diseases that attack cabbage (1 ½ mks)
- Damping off
- Black rot
- Downy mildew
- State four characteristics that make a crop suitable for green manure (2mks)
- Rapid growth rate
- Production of abundant foliage
- Leguminous
- Ability to decay quickly
- Hardy
- State four different types of irrigation that can be used by farmers (2mks)
- Surface irrigation
- Overhead irrigation
- Sub surface
- Drip/trickle irrigation
SECTION B (20 MARKS)
- The diagram below illustrates some soil structures. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the soil structures F and G (2mks)
- F- granular
- G - platy
- Name the parts labeled X and Y in diagram F (1mk)
- X - humus with clay
- Y - air space
- Sate two ways through which structure G influences crop production (2mks)
- Impedes drainage/ water infiltration
- Prevent root penetration
- Influences soil aeration
- Identify the soil structures F and G (2mks)
- The diagram below illustrates a type of fruit. Study nit and answer the questions that follow
- Identify the fruit (1mk)
- Pineapple fruit
- Name the parts A-D ((4mks)
- A-crown
- B-fruit
- C-slip
- D-suckers
- Name two crops propagated by the part labeled D (1MK)
- Sisal
- Banana
- Identify the fruit (1mk)
- The diagram below shows a method of layering study it and answer questions that follow
- Identify the method of layering illustrated above (1mk)
- Marcotting/ aerial
- State one circumstance in which this method of layering is recommended (1mk)
- When the branch is hard and cannot bend to reach the ground
- Identify the method of layering illustrated above (1mk)
- A maize farmer was advised to apply 150 kg CAN per hectare while topdressing the maize crop. CAN contains 21%N. calculate the amount of Nitrogen applied per hectare. (3mks)
21 kg N= 100 kg CAN
21/100 ×150 = 31.5 kg N/ha - The diagram below shows a seedling attacked by a certain pest.
- Identify the pest (1mk)
- Cut worm
- Name any two types of vegetable crops likely to be attacked by the pests (2mks)
- Cabbage
- Kales
- Tomatoes
- State two methods of controlling the above pest (2mks)
- Use of appropriate pesticide
- Physically picking and killing
- Crop rotation
- Identify the pest (1mk)
SECTION C (40 marks)
Choose any two questions from this section
-
- Outline the effects of wind on agricultural products (11mks)
- Causes soil erosion
- Acts as a pollination agent
- Acts as a seed disposal agent
- Causes destruction of crops
- Spreads pathogens
- Spreads weed seeds
- Causes destruction of farm structures
- Influences relative humidity
- Causes stress by chilling of livestock and crops
- Briefly mention the importance of soil organic matter (9mks)
- Buffers soil ph
- Increases microbial activities
- Binds the soil particles together hence improving soil structure
- Increases soil fertility
- Improves workability of the soil
- Improves soil water retention capacity
- Improves water infiltration
- Reduces soil toxicity from pesticides
- Outline the effects of wind on agricultural products (11mks)
-
- Describe the advantages of using seeds as planting materials (5mks)
- Planting can be mechanized
- Less bulky
- Seeds can be mixed with fertilizers easily
- Easily available hence are cheaper planting materials
- Easy to treat against soil borne pests and diseases
- Possible to develop new crop varieties
- Seeds can be stored easily awaiting better conditions
- Easy to handle
- Give reasons for raising vegetable seedling through a nursery (5mks)
- Many seedlings produced
- Easy to carry out management practices
- Easy to plant small seeds
- Provide optimum growth condition
- Allow transplanting of strong and healthy seeds
- Reduce time taken in the field
- Extra seedlings sold to earn income
- Outline the process of chemical water treatment for use in the farm (10mks)
- filtration at intake
Water passed through a series of sieves - softening of water
Soda ash added to soften - Coagulation, sedimentation
Alum added to coagulate, Bilharzia worms killed - Filtration
Water passed through different layers of gravel - Chlorination
small amounts of Chlorine added to kill micro organisms - Storage
water stored in tanks and distilled
- filtration at intake
- Describe the advantages of using seeds as planting materials (5mks)
-
- Explain five factors that determine spacing to be used in crops (10mks)
- Type of machinery to be used
- Soil fertility
- Size of the plants
- Crop stand either pure or mixed
- Number of seeds per hole
- Moisture availability
- Use of the crop
- Pest and disease control
- Describe six management practices carried out on a nursery bed (6mks)
- Watering
- Mulching
- Weed control
- Pricking out
- Shading
- Pest and disease control
- Hardening off
- Explain four advantages of grafting (4mks)
- Helps to repair damaged trees
- Helps to shorten maturity age
- Helps to change the top of tree from undesirable to desirable
- Make it possible to produce more than one type of fruit
- Helps to utilize plants with desirable root characteristics such as disease resistance to produce more desirable produce.
- Explain five factors that determine spacing to be used in crops (10mks)
Download AGRICULTURE Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Form 3 End Term 1 Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students