INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES:
Answer ALL the questions
Answers should be written in the spaces provided
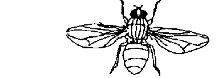
- Study the diagram of the organism shown below then answer the questions that follow.
- State the phylum to which the organism belongs. (1mark)
- With reasons state the class to which the organism belongs. (1 mark)
- Name two diseases of the respiratory system. (2 marks)
-
- Name the gaseous exchange structure in the following organisms.
- Amoeba .(1 mark)
- Grasshopper.(1mark)
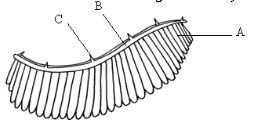
- The diagram below illustrates the structure of a gill from a bony fish.
- Name the parts labelled A, B, C (3 marks)
A
B
C - State the function of the part labelled C (1 mark)
- How is part A adapted to carry its functions (2 marks)
- Name the parts labelled A, B, C (3 marks)
- Name the gaseous exchange structure in the following organisms.
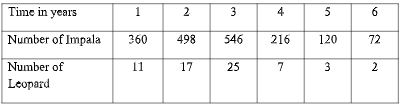
- The table below shows the number of Leopards and Impala in a grassland park over a period of six years.
Time in years 1 2 3 4 5 6 Number of Impala 360 498 546 216 120 72 Number of
Leopard11 17 25 7 3 -
- What is the average number of Impala in the park during the six years. (2marks)
- Account for the decrease in the number of leopards between the 4 th and 6 th year? (2marks)
- Identify the trophic level occupied by
- Leopards (1 mark)
- Tick feeding on the leopard. (1 mark)
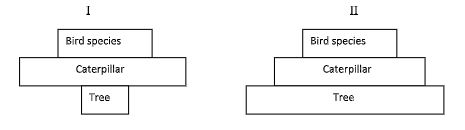
- The two pyramids shown were obtained in the park.
- Identify each type of pyramid. (2 marks)
I
II
- Identify each type of pyramid. (2 marks)
-
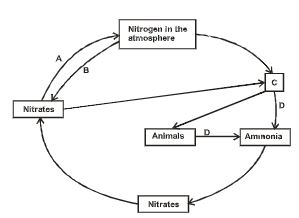
- The diagram below represents a simplified nitrogen cycle.
- Name the group of bacteria represented by: (2 marks)
A.
B. - Name the group of organisms represented by C(1 mark)
- Give the reasons for your answer in b (i) above. (2 marks)
- Define the term nitrification. (1 mark)
- Explain how excessive use of pesticides will affect nitrification. (2 marks)
- Name the group of bacteria represented by: (2 marks)
-
- State three structural differences between an artery and a vein of a mammal. (3 marks)
- How are the capillary suited to their function? (3 marks)
-
- What is blood transfusion? (1 mark)
- A person whose blood group is A died shortly after receiving blood from a person of blood group B. Explain the cause of death. (2marks)
Answer question 6 (Compulsory) and EITHER question 7 or 8 in the spaces provided
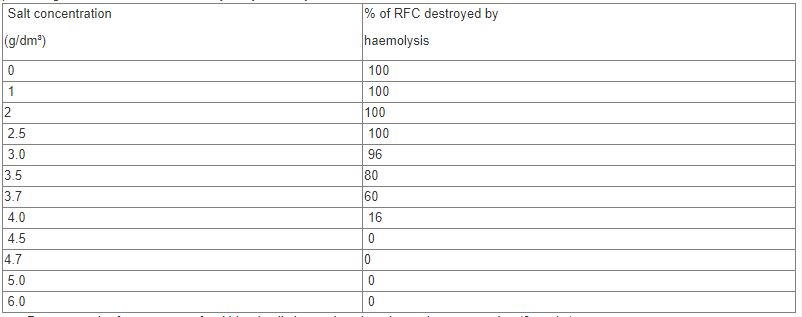
- An experiment was carried out in which red blood cells were put in salt solutions of different concentrations. The table below shows the percentage of cells which were destroyed by haemolysis in different salt concentration.
Salt concentration
(g/dm³)
% of RFC destroyed by
haemolysis
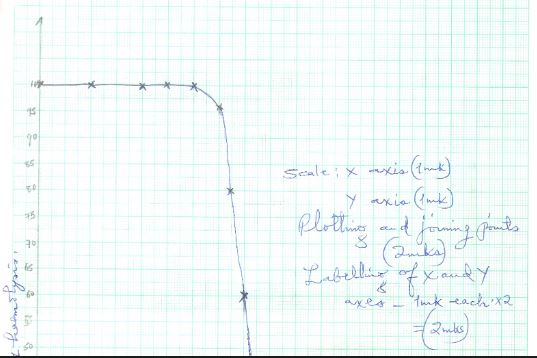
0 100 1 100 2 100 2.5 100 3.0 96 3.5 80 3.7 60 4.0 16 4.5 0 4.7 0 5.0 0 6.0 0 - Draw a graph of percentage of red blood cells haemolysed against salt concentration (6 marks)
- Explain haemolysis of red blood cells. (3marks)
- From the graph, state:
- The salt concentration at which 50% red blood cells were haemolysed. (1 mark)
-
- The highest salt concentration when the largest number of red blood cells were haemolysed. (1 mark)
-
- Suggest the normal salt concentration in the blood of the mammal from which the red blood cells were obtained. (2 marks)
- Give a reason for your answer in (d) (i) above. (1 mark)
- What term is used to describe the solution with equal solute concentration as that of the cells? (1 mark)
- Name the process in the human body that ensures that haemolysis of red blood cells is prevented. (1mrk)
- State the role of osmosis in organisms. (4 marks)
- Describe the adaptation of the skin to its functions (20mks)
-
- Describe how the digestion of a protein is achieved in the following portions of the alimentary canal.
- Stomach (4 marks)
- Duodenum (4marks)
-
- Describe the process of absorption at the root hair to the xylem of the root. (8mks)
- Describe how temperature and light intensity affect the rate of transpiration. (4 mks)
- Describe how the digestion of a protein is achieved in the following portions of the alimentary canal.
MARKING SCHEME
- Study the diagram of the organism shown below then answer the questions that follow.
- State the phylum to which the organism belongs. (1mark)
Arthropoda - With reasons state the class to which the organism belongs
Class Insecta (1 mark)
Reasons: Three body parts/Head, thorax and abdomen(3 marks)- hree pairs of legs/six legs
- A pair of antennae
- Name two diseases of the respiratory system. (2 marks)
- Lung cancer
- Asthma
- Bronchitis
- State the phylum to which the organism belongs. (1mark)
-
- Name the gaseous exchange structure in the following organisms.
- Amoeba (1 mark)
Contractile vacuole - Grasshopper (1mark)
spiracles
- Amoeba (1 mark)
- The diagram below illustrates the structure of a gill from a bony fish.
- Name the parts labelled A, B, C (3 marks)
A gill filament
B gill bar
C gill raker - State the function of the part labelled C (1 mark)
- Prevents the entry of solid particles into the delicate gill filaments.
- How is part A adapted to carry its functions (2 marks)
thinmembrane
Large surface area
Moist
Highly vascularised
- Name the parts labelled A, B, C (3 marks)
- Name the gaseous exchange structure in the following organisms.
- The table below shows the number of Leopards and Impala in a grassland park over a period of six years.
- What is the average number of Impala in the park during the six years. (2marks)
360 + 498 + 546 + 216 + 120 + 72 = 1812/6; = 302; - Account for the decrease in the number of leopards between the 4 th and 6 th year?(2marks)
Decrease in number of impala / prey hence starved to death; immigration / poaching / Immigration leading to increased competition; disease epidemic; pollution / human activities;
- What is the average number of Impala in the park during the six years. (2marks)
- Identify the trophic level occupied by
- Leopards (1 mark)
Secondary consumer; - Tick feeding on the leopard. (1 mark)
Tertiary consumer
- Leopards (1 mark)
- The two pyramids shown were obtained in the park.
- Identify each type of pyramid. (2 marks)
- Pyramid of numbers;
- Pyramid of biomass
- Identify each type of pyramid. (2 marks)
- The diagram below represents a simplified nitrogen cycle.
- Name the group of bacteria represented by: (2 marks)
A. denitrifying bacteria
B. nitrifying bacteria - Name the group of organisms represented by C. (1 mark)
Plants - Give the reasons for your answer in b (i) above. (2 marks)
Die and decompose to form ammonia
Are fed upon by the animals - Define the term nitrification. (1 mark)
Process by which nitrobacter converts nitrites to nitrates - Explain how excessive use of pesticides will affect nitrification. (2 marks)
use of excess pesticides would kill the nitrobacter hence hindering the conversion of nitrites to nitrates.
- Name the group of bacteria represented by: (2 marks)
-
- State three structural differences between an artery and a vein of a mammal. (3 marks)
Artery Vein Wider lumen Narrower lumen Thick muscular walls Thin muscular walls; Absence of vales Presence of valves; - How are the capillary suited to their function? (3 marks)
Walls made up of endothelium cells or only one-cell thick to facilitate exchange of materials across the capillary wall; Numerous to be close to each other; Pores between capillary walls to enable cells (leucocytes) to squeeze through into the tissue fluid; [mark 1 st 2] -
- What is blood transfusion? (1 mark)
Transfer of blood from donor/ blood bank to a recipient’s bloodstream; - A person whose blood group is A died shortly after receiving blood from a person of blood group B. Explain the cause of death. (2marks)
After transfusion, the anti b antibodies in the patient plasma reacted with B antigen of the donor; causing haemagglutination/ clumping of donor’s red blood cells;
- What is blood transfusion? (1 mark)
- State three structural differences between an artery and a vein of a mammal. (3 marks)
Answer question 6 (Compulsory) and EITHER question 7 or 8 in the spaces provided
- An experiment was carried out in which red blood cells were put in salt solutions of different concentrations. The table below shows the percentage of cells which were destroyed by haemolysis in different salt concentration.
- Draw a graph of percentage of red blood cells haemolysed against salt concentration (6 marks)On the graph.
- Explain haemolysis of red blood cells. (3marks)
Haemolysis of red blood cells occurs when they are placed in a hypotonic solution; they gain a lot of water; swell an then burst; - From the graph, state:
- The salt concentration at which 50% red blood cells were haemolysed. (1 mark)
4.1 g/dm3; + 0.1;
The highest salt concentration when the largest number of red blood cells were haemolysed. (1 mark)
3.0 g/dm3; + 1;
- The salt concentration at which 50% red blood cells were haemolysed. (1 mark)
-
- Suggest the normal salt concentration in the blood of the mammal from which the red blood cells were obtained. (2 marks)
4.7 g / dm3+ 0.1; - Give a reason for your answer in (d)(i) above. (1 mark)
At 4.7 g / dm3 salt concentration; as there is no haemolysis / haemolysis was zero; - Whatterm is used to describe the solution with equal solute concentration as that of the cells? (1 mark)
Isotonic solution;
- Suggest the normal salt concentration in the blood of the mammal from which the red blood cells were obtained. (2 marks)
- Name the process in the human body that ensures that haemolysis of red blood cells is prevented.
- Osmoregulation; Rej. Homeostasi(1 mark)
- State the role of osmosis in organisms. (4 marks)
- Osmosis enables movement of water from one cell to another;
- Osmosis helps in closing and opening of the stomata;
- Osmosis helps in support when cells become turgid in plants;
- Osmosis helps in absorption of water by the root hairs; (max 4)
- Draw a graph of percentage of red blood cells haemolysed against salt concentration (6 marks)On the graph.
- Describe the adaptation of the skin to its functions ( 20 mks)
Cornified layer made up of dead cells;/ filled with keratin; that protect against entry of bacteria; Granular layer made of living cells;give rise to new cornified layer; Malphigian layer made of actively dividing cells; give rise to new epidermis; amphibian layer has melanin; protect the body against ultra-violet radiations; Sebaceous glands produce sebum; that is anti-septic/keeps skin supple; Have blood arterioles which (vaso) dilate when hot; and increase heat loss (by radiations); vaso constrict when cold; and heat is retained; Sweat glands produce sweat; sweat evaporation the skin surface; cooling the body; Has sensory nerve endings; which are sensitive to touch/pressure/temperature/pain; Has blood capillaries to supply nutrients; remove waste products of metabolism; Has erector pilli muscle which contracts when cold; hair stand upright trapping a layer of air is non-conductor of heat retained; it relaxes when hot; hair falls on skin surface no air is trapped; increasing heat loss; Has subcutaneous fat layer/adipose tissue; acts as heat insulating layer; (max 20 Marks) -
- Describe how the digestion of a protein is achieved in the following portions of the alimentary canal.
- Stomach (4 marks)
Pepsin; acts on proteins to polypeptides; Rennin; Acts on milk protein caseinogens to casein; this occurs in acidic medium. - Duodenum (4 marks)
Trypsin; in pancreatic juice; hydrolyses polypeptides to peptides molecules; in alkaline conditions provided by bile juice.
- Stomach (4 marks)
-
- Describe the process of absorption at the root hair to the xylem of the root. (8 marks)
he root hair cell sap is hypertonic to the soil water; water from the soil moves into the root hair cell sap by osmosis; this makes the cell sap hypotonic/dilute; compared to hypertonic adjacent cortex cells; water moves into the cortex cells by osmosis; till it reaches the casparian layer; which pumps water into the xylem of the root; this is called the root pressure; - Describe how temperature and light intensity affect the rate of transpiration. (4 marks)
Increase in temperature causes evaporation of water into the intercellular airspace of the leaf; this makes water vapour from adjacent cells to move into the stoma; creating diffusion gradient deficit between the atmosphere and intercellular space increased transpiration; Increase in light intensity; increases rate of photosynthesis; leading to opening of stomata which leads to increased transpiration.
- Describe the process of absorption at the root hair to the xylem of the root. (8 marks)
- Describe how the digestion of a protein is achieved in the following portions of the alimentary canal.
Download Biology Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Form 3 End Term 1 Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students