QUESTIONS
- You are provided with photographs of specimens labeled M,N and P which were obtained from an animal. Study them.
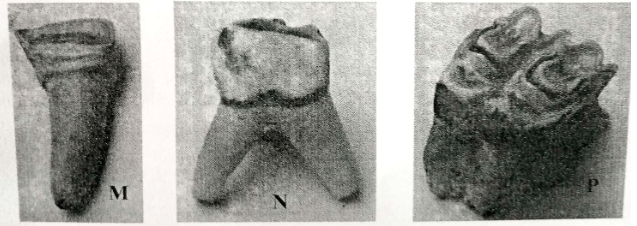
- Identify specimens: (3mks)
- M
- N
- P
- For each specimen, name, observe features and state how each feature adapts the specimen to it functions. (6mks)
Specimen Feature Adaptation and function M N P
- Identify specimens: (3mks)
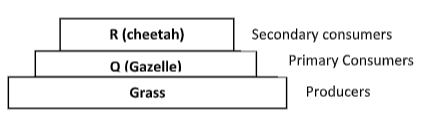
- Below is a photograph depicting interaction of organisms in a certain ecosystem?

- Write down a possible food chain involving three organisms found in the photograph above. (1mk)
- Draw a well labeled pyramid of biomass using the food chain in (a) above. (3mks)
What feeding relationships are exhibited by the animals shown in the photographs? (2mks) - Give the adaptations of animal R regarding its feeding relationship mentioned in b (ii) above. (3mks)
- A number of leaves are represented by leaves A, B, C, D and E. Use the dichotomous key made using leaves A, B, C, D and E below.
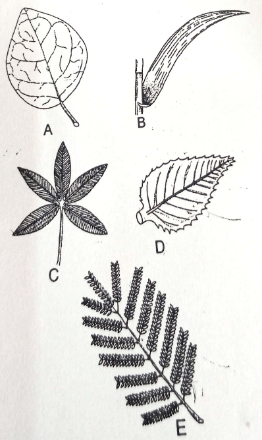
-
- Leaf veins network……………………………………go to 2
- Leaf veins parallel……………………………………… B (maize)
-
- Leaf simple………………………………………………… go to 3
- Leaf compound ………………………………………………go to 4
-
- Leaf margin smooth………………………………………. A (Bougainvillae)
- Leaf margin serrated…………………………………….. D (Hibiscus)
-
- Leaf with five leaflets……………………………………. C (Bombax)
- Leaf with many leaflets………………………………….E (Acacia)
-
- Using the above dichotomous key show the steps and identify at the leaves shown above. (10mks)
- You are provided with three unknown solutions labeled F, G1 and G2. G1 is the same as G2 except that G2 has been boiled. You are also provided with iodine solution, Benedict’s solution, means of heating 250ml beaker labeled for a warm water bath, thermometer, tripod stand, means of timing, test-tubes, test tube holder and test tube rack.
- Place 2ml of solution F in a test tube and add an equal volume of Benedict’s solution.
- Shake to mix and then heat to boil and write down your observation. (1mk)
- What conclusion do you make from your observation in a (i) above? (1mk)
-
- Place 2ml of solution F in a test tube. Add 3 drops of iodine solution and shake to mix and write down your observation.(1mk)
- What conclusion do you make from your observation in b(i) above? (1mk)
- Place 4ml of solution F in a test tube and add 10 drops of solution G1 and mix. Allow the mixtures to stand in a warm water bath between 35°C – 38°C for 10 minutes. Divide the resulting mixture into two portions.
- To one portion in a test tube add 3 drops of iodine solution and shake to mix and write your observation. (1mk)
- What conclusion can you make from your observation in c (i) above? (1mk)
- To the second portion in a test tube add 2ml of Benedict’s solution, shake to mix and heat to boil and write your observation. (1mk)
- What conclusion can you make from your observation in c (iii) above? (1mk)
- To about 4ml of solution F in a test tube add 10 drops of G2 and mix, allow the mixture to stand in a warm water bath between 35°C – 38°C for 10minutes. Divide the resulting mixture into two, carry out iodine test and Benedict’s test as described in ( c ) above and complete the table below. (4mks)
Test Observations Conclusion Iodine test Benedict's test
- Place 2ml of solution F in a test tube and add an equal volume of Benedict’s solution.
CONFIDENTIAL
- F – starch solution
- Solution G1- unboiled diastase enzyme
- G2 – Boiled diastase enzyme
- Thermometer
- 250ml beaker labeled warm water bath
- Benedict’s solution
- Iodine solution
- Means of timing
- 6 test tubes
- Test tube rack
- Means of heating
- Tripod stand
MARKING SCHEME
- You are provided with photographs of specimens labeled M,N and P which were obtained from an animal. Study them.
- Identify specimens: (3mks)
- M - Incisors
- N - Premolar
- P - Molar
- For each specimen, name, observe features and state how each feature adapts the specimen to it functions. (6mks)
Specimen Feature Adaptation and function M Crown sharp and chisel - shaped For biting and cutting food N Partially ridged with few cusps. Crushing food P Broad surface ridged with cusps crown Crushing and grinding food
- Identify specimens: (3mks)
- Below is a photograph depicting interaction of organisms in a certain ecosystem?
- Write down a possible food chain involving three organisms found in the photograph above. (1mk)
GrassQ (gazelle)
R (cheetah)
- Draw a well labeled pyramid of biomass using the food chain in (a) above. (3mks)
What feeding relationships are exhibited by the animals shown in the photographs? (2mks)- Q – Prey
- R - Predator
- Give the adaptations of animal R regarding its feeding relationship mentioned in b (ii) above. (3mks)
- High speed, leaps on prey, powerful sharp canines for seizing prey, special carnassials teeth on the upper jaw for crushing bones, has binocular vision giving it ability to accurately judge distance of prey for a fruitful leaping.
- A number of leaves are represented by leaves A, B, C, D and E. Use the dichotomous key made using leaves A, B, C, D and E below.
-
- Leaf veins network……………………………………go to 2
- Leaf veins parallel……………………………………… B (maize)
-
- Leaf simple………………………………………………… go to 3
- Leaf compound ………………………………………………go to 4
-
- Leaf margin smooth………………………………………. A (Bougainvillae)
- Leaf margin serrated…………………………………….. D (Hibiscus)
-
- Leaf with five leaflets……………………………………. C (Bombax)
- Leaf with many leaflets………………………………….E (Acacia)
-
- Using the above dichotomous key show the steps and identify at the leaves shown above. (10mks)
Leaf Steps Identity A 1a, 2a, 3a Bougainvillae B 1b Maize C 1a, 2b, 4a Bombax D 1a, 2a, 3b Hibiscus E 1a, 2b, 4b Acacia
- Write down a possible food chain involving three organisms found in the photograph above. (1mk)
- You are provided with three unknown solutions labeled F, G1 and G2. G1 is the same as G2 except that G2 has been boiled. You are also provided with iodine solution, Benedict’s solution, means of heating 250ml beaker labeled for a warm water bath, thermometer, tripod stand, means of timing, test-tubes, test tube holder and test tube rack.
- Place 2ml of solution F in a test tube and add an equal volume of Benedict’s solution.
- Shake to mix and then heat to boil and write down your observation. (1mk)
- A blue colour of Benedict’s solution persists
- What conclusion do you make from your observation in a (i) above? (1mk)
- Reducing sugar absent
- Shake to mix and then heat to boil and write down your observation. (1mk)
-
- Place 2ml of solution F in a test tube. Add 3 drops of iodine solution and shake to mix and write down your observation. (1mk)
- The solution changed from yellow / brown to blue- black.
- What conclusion do you make from your observation in b(i) above? (1mk)
- Starch present
- Place 2ml of solution F in a test tube. Add 3 drops of iodine solution and shake to mix and write down your observation. (1mk)
- Place 4ml of solution F in a test tube and add 10 drops of solution G1 and mix. Allow the mixtures to stand in a warm water bath between 35°C – 38°C for 10 minutes. Divide the resulting mixture into two portions.
- To one portion in a test tube add 3 drops of iodine solution and shake to mix and write your observation. (1mk)
- The yellow/brown colour of iodine solution persist.
- What conclusion can you make from your observation in c (i) above? (1mk)
- Starch is absent
- To the second portion in a test tube add 2ml of Benedict’s solution, shake to mix and heat to boil and write your observation. (1mk)
- The colour changes from blue, yellow, orange to brown.
- What conclusion can you make from your observation in c (iii) above? (1mk)
- A reducing sugar is present.
- To one portion in a test tube add 3 drops of iodine solution and shake to mix and write your observation. (1mk)
- To about 4ml of solution F in a test tube add 10 drops of G2 and mix, allow the mixture to stand in a warm water bath between 35°C – 38°C for 10minutes. Divide the resulting mixture into two, carry out iodine test and Benedict’s test as described in ( c ) above and complete the table below. (4mks)
Test Observations Conclusion Iodine test Colour changes from yellow/ brown to blue - black Starch present Benedict's test Blue colour of benedict’s solution persists Reducing sugar absent
- Place 2ml of solution F in a test tube and add an equal volume of Benedict’s solution.
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Biology Paper 3 Questions and Answers - Form 3 Term 2 Opener Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students