INSTRUCTIONS TO STUDENTS.
- Answer all questions in this question paper.
- The set up below was used to determine the percentage of oxygen in air. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
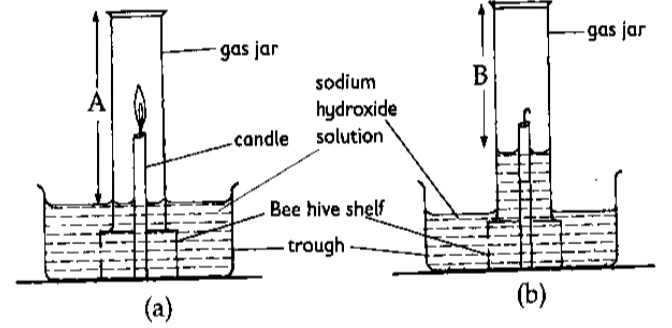
-
- State the observations made after the experiment. (1 mk)
- What was the length of the air column in the gas jar before and after burning? (1 mk)
- Determine the percentage of air used up by the burning candle. (A=10cm, B=79cm)
(2 mks)
- State two sources of errors in the experiment. (2 mks)
- Why is it necessary to leave the apparatus to cool before taking the final reading? (1 mk)
-
- Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction sodium peroxide and water. (1 mk)
- If 39g of sodium peroxide was used, calculate the volume of oxygen gas prepared at r.t.p. (3 mks)
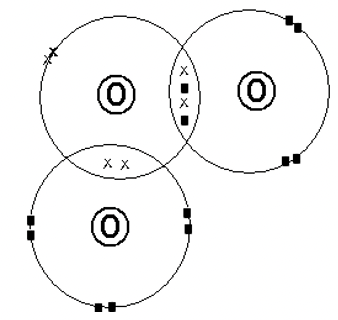
- Using dot and cross diagrams, draw the structure of ozone (O 3 ). The atomic number of oxygen is 8. (2mks)
- State two properties of oxygen gas that makes it suitable to collected by over water method. (2mks)
-
-
- The diagram below shows two allotropes of carbon
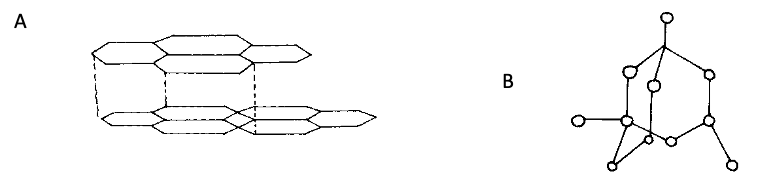
- Identify allotrope (2mks)
A……… B……………………….. - Give a reason why allotrope A is used as a lubricant (1mk)
- State one use of allotrope B (1mk)
- Identify allotrope (2mks)
- The diagram below is a set-up used in the laboratory preparation of Carbon (II) oxide. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
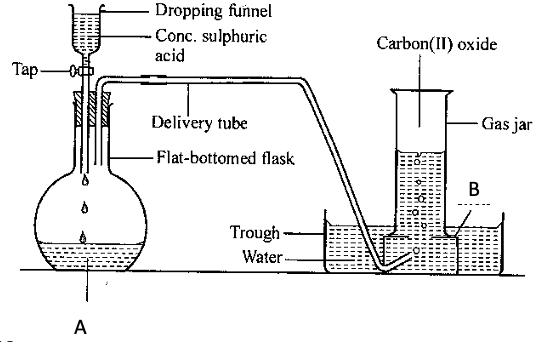
- Name
- Substance A (1 mk)
- Apparatus B (1 mk)
- Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction taking place in the flask. (2 mks)
- State one use of carbon (II) oxide gas (1 mk)
- Name
- Give the chemical name of trona (Na 2 CO 3 .NaHCO 3 .2H 2 O) (1 mk)
- The diagram below shows two allotropes of carbon
- The grid below shows part of the periodic table. Use it to answer the questions that follow. The letters are not the actual symbols.
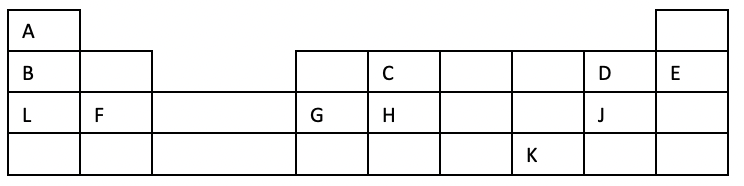
-
- Write the equation for the reaction that occurs between elements L and D. (1 mk)
- Explain why element H has a higher boiling points than element D. (2 mks)
- State one use of element E (1 mk)
- Compare and explain the atomic radius of B and C. (2 mks)
-
- Write a balanced equation for reaction between element L and oxygen. (2 mks)
- 11.5g of L was completely burnt in oxygen. Calculate the volume of gas that was used. |
(3 mks)
(L = 23, O = 16.0, molar gas volume at room temperature is 24dm 3 )
- The ionization of magnesium can be represented diagrammatically as shown in the figure below.
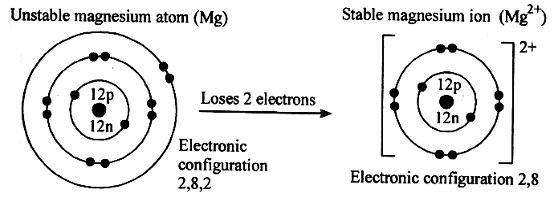
Define the following terms: (4 mks)- Ionization energy
- Electron affinity
- Electronegativity
- Electropositivity
-
-
- The diagram below represents an experiment which was carried out by a student, to investigate the effect of passing an electric current on molten sodium chloride.
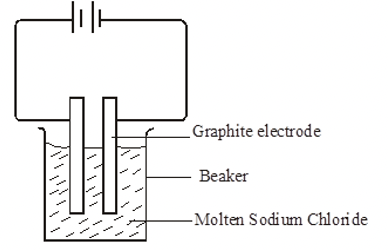
- Molten sodium chloride is a binary electrolyte. State the meaning of the term binary electrolyte. 1 mark
- State observations made at the
- anode 1 mark
- Cathode 1 mk
- Write an equation to show what happens at the cathode and anode. 2 mks
- At the cathode
- At the anode
- Show the direction of flow of electrons on the set up 1 mk
- Define the following terms; (4 mks)
- Electrolyte
- Anode
- Cathode
- Electrode
- State the use of the battery (cell) in the electrolytic cell. 1 mk
- State two industrial applications of electrolysis. 2 mks
- The diagram below represents an experiment which was carried out by a student, to investigate the effect of passing an electric current on molten sodium chloride.
-
- Four athletes A, B, C and D were suspected of using NSAID and EPO drugs as blood boosters to enhance their performance. Their blood samples were taken and analyzed using chromatography. The results obtained were recorded in the chromatogram below.
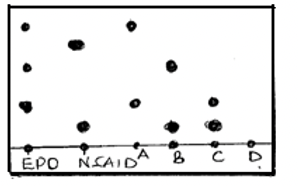
- State and explain two factors that determine the distance travelled by a sample along the filter paper. (2 mks)
- On the diagram above indicate the baseline and the solvent front. (1 mks)
- Which athlete(s) tested positive of the use of EPO drug only? (1 mks)
- Which athlete(s) tested positive of use of both EPO and NSAID drugs. (1 mks)
- Which athlete had his blood sample negative of EPO and NSAID drugs? (1 mk)
- Name a suitable solvent used in papers chromatography. (1 mk)
- Below is a structure of aluminium chloride dimer. Study it and answer the questions that follow
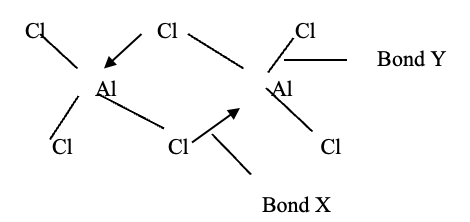
- Identify bond
- X ……………………………………………………………….. (1mk)
- Y ……………………………………………………………………… (1mk
- Four athletes A, B, C and D were suspected of using NSAID and EPO drugs as blood boosters to enhance their performance. Their blood samples were taken and analyzed using chromatography. The results obtained were recorded in the chromatogram below.
-
- The diagram below shows a heating curve for a sample of compound X.
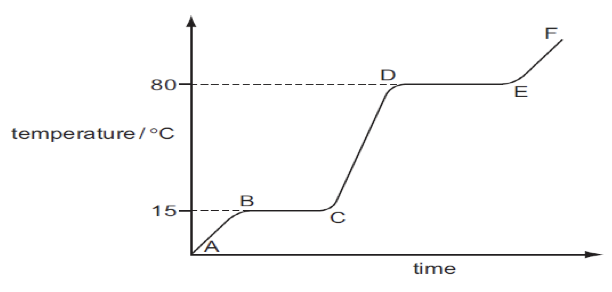
- Is X a solid, a liquid or a gas at room temperature, 20 °C? (1mk)
- Name the change of state which occurs in region DE. (1mk)
- Explain how the curve shows that a pure sample of compound X was used. (1 mk)
- Compound X is a hydrocarbon. It contains 85.7% of carbon. The mass of one mole of X is 84 g.
- What is the percentage of hydrogen in the compound? (1mk)
- Calculate the empirical formula of X. Show your working. (3 mks)
- What is the molecular formula of compound X? (2 mks)
- The diagram below shows a heating curve for a sample of compound X.
- The flow chart below shows the industrialization of ammonia and the process used in the manufacture of some ammonium compounds. Study it and answer the questions that follow
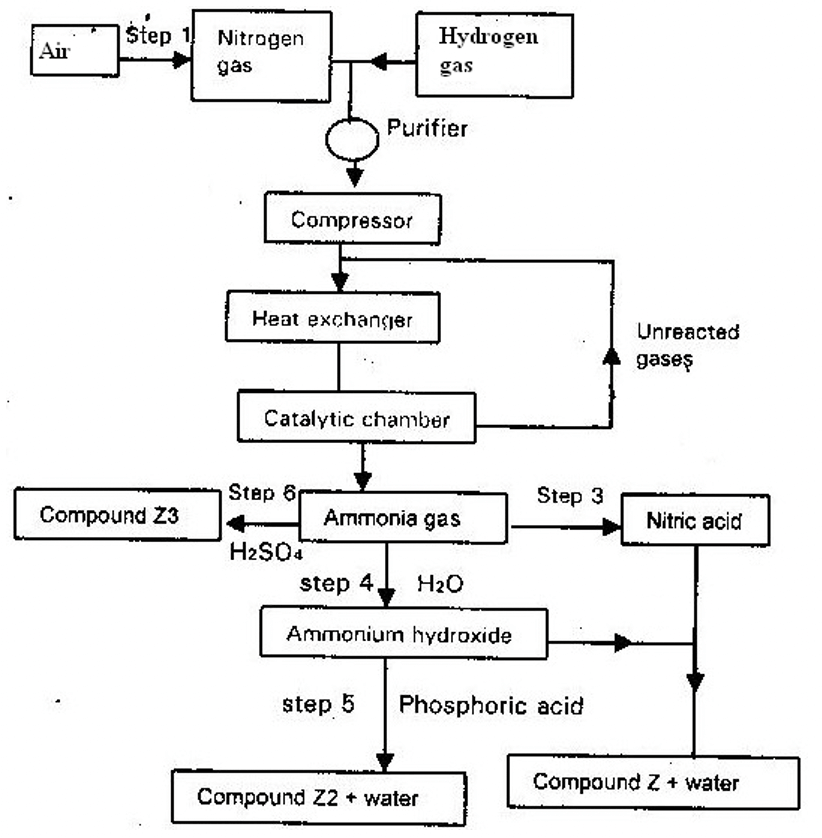
- Give the name of the
- Process in step 1 (1 mk)
- Reaction that takes place in step 5 (1 mk)
- Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction between nitrogen and hydrogen. (1 mk)
- Explain why it is necessary to compress nitrogen and hydrogen in this process . (2 mks)
- Write an equation for the reaction which takes place in step 6 (1 mk)
- Name the catalyst and reagents used in step 3. (2mks)
- Name compound Z1. (1mk)
- Give one commercial use of compound Z2. (1mk)
- Give the name of the
MARKING SCHEME
- The set up below was used to determine the percentage of oxygen in air. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
-
- State the observations made after the experiment. (1 mk)
- The water level rises inside the gas jar and goes down in the trough.
- What was the length of the air column in the gas jar before and after burning? (1 mk)
Amount of air in the gas jar before burning= A
Amount of air in the gas jar after burning= B - Determine the percentage of air used up by the burning candle. (A=10cm, B=79cm) (2 mks)
Amount of air used is given by subtracting height B from A = A-B.
Therefore, the percentage of oxygen is given by:
(height A - height B) x 100 = (A - B) x 100 = C%
height A A
Substituting values of A and B in the equation gives the value of C as 21%. Hence about 21% of air is used during the burning of the candle. This is the approximate percentage of oxygen in air.
- State the observations made after the experiment. (1 mk)
- State two sources of errors in the experiment. (2 mks)
The experimental result is not the same as the theoretical value of the percentage of oxygen in air by volume.
This is due to experimental error, which may result from:- The sodium hydroxide solution may not absorb all the carbon (IV) oxide gas.
- The candle may go off before all the oxygen is used up due to the build-up of carbon (IV) oxide levels.
- Why is it necessary to leave the apparatus to cool before taking the final reading? (1 mk)
- Heating causes expansion of gases, therefore the apparatus should be allowed to cool before the final reading is taken.
-
- Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction sodium peroxide and water. (1 mk)
2Na2O2(s) + 2H2O(l)4NaOH(aq) + 3O2(g)
- If 39g of sodium peroxide was used, calculate the volume of oxygen gas prepared at r.t.p. (3mks)
Na = 23.0, H = 1.0, O= 16.0, M.G.V at r.t.p = 24dm3
Molar Mass Na2O2 = 2x23 + 2x16 = 78
No. of moles Na2O2 = 39/78 = 0.5 moles
No. of moles oxygen gas formed = (0.5/2) x3 = 0.75 moles
Volume of oxygen gas = 0.75 x 24 = 18dm3 - Using dot and cross diagrams, draw the structure of ozone (O3). The atomic number of oxygen is 8. (2mks)
- State two properties of oxygen gas that makes it suitable to collected by over water method. (2mks)
- Slightly soluble in water.
- Has a density almost the same as that of air
- Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction sodium peroxide and water. (1 mk)
-
-
- The diagram below shows two allotropes of carbon
- Identify allotrope (2mks)
- A: Graphite B: Diamond
- Give a reason why allotrope A is used as a lubricant (1mk)
- Made up of layers that slide over each other
- State one use of allotrope B (1mk)
- Used in making of drill bits
- Identify allotrope (2mks)
- The diagram below is a set-up used in the laboratory preparation of Carbon (II) oxide. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
- Name
- Substance A (1 mk)
- Methanoic acid
- Apparatus B (1 mk)
- Beehive shelf
- Substance A (1 mk)
- Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction taking place in the flask. (2 mks)
Conc. H2SO4
HCOOH(aq)CO(g) + H2O(1)
(Methanoic acid) - State one use of carbon (II) oxide gas (1 mk)
Carbon (II) oxide has the following industrial uses:- Extraction of certain metals from their ores, e.g. iron and zinc.
- Manufacture of other chemicals such as methanol, ethanoic acid, synthetic petrol and carbonyl chloride.
- Name
- Give the chemical name of trona (Na2CO3.NaHCO3.2H2O) (1 mk)
- Sodium sesquicarbonate
- The diagram below shows two allotropes of carbon
- The grid below shows part of the periodic table. Use it to answer the questions that follow. The letters are not the actual symbols.
-
- Write the equation for the reaction that occurs between elements L and D. (1 mk)
L(s) + D2(g)LD2(S)
- Explain why element H has a higher boiling points than element D. (2 mks)
- Element H forms a giant atomic (covalent) structure held by strong repeated covalent bonds that require high amount of energy to break hence high melting and boiling points.
- D is made up of simple molecular structure held by weak van de Waal’s forces of attraction that require less amount of energy to break hence low melting and boiling points.
- State one use of element E (1 mk)
- Used in street lights and advertising signs. When subjected to an electric current at low pressure; it emits a bright orange-red glow. When mixed with other gases, it gives a variety of colours.
- Compare and explain the atomic radius of B and C. (2 mks)
- Atomic radius of C is smaller than the atomic radius of B. This is because B has a stronger nuclear charge due to an increased number of positive charges in the nucleus.
- Write the equation for the reaction that occurs between elements L and D. (1 mk)
-
- Write a balanced equation for reaction between element L and oxygen. (2 mks)
4L(s) + O2(g)2L2O(s)
- 11.5g of L was completely burnt in oxygen. Calculate the volume of gas that was used. (3 mks)
(L = 23, O = 16.0, molar gas volume at room temperature is 24dm3)
Number of moles of L = 11.5/23 = 0.5 moles
Number of moles Oxygen used = 0.5/4 x 1 = 0.125 moles.
Volumes of oxygen gas used = 0.125 x 24 = 3.0 dm3
- Write a balanced equation for reaction between element L and oxygen. (2 mks)
- The ionization of magnesium can be represented diagrammatically as shown in the figure below.
Define the following terms: (4 mks)- Ionization energy
- The minimum amount of energy required to remove an electron the last energy level of an isolated neutral atom to form a positively charged ion in gaseous state.
- Electron affinity
- The maximum amount of energy released when an electron is added to the last energy level of an isolated neutral atom to form a negatively charged ion in gaseous state.
- Electronegativity
- The ease of gaining electrons by an atom.
- Electropositivity
- The ease of losing electrons by an atom.
- Ionization energy
-
-
- The diagram below represents an experiment which was carried out by a student, to investigate the effect of passing an electric current on molten sodium chloride.
- Molten sodium chloride is a binary electrolyte. State the meaning of the term binary electrolyte. 1 mark
- An electrolyte that ionizes producing only two ions, one cation and one anion only.
- State observations made at the
- anode 1 mark
- Bubbles of a green-yellow gas are observed
- Cathode. 1 mk
- Grey deposits seen at the cathode
- The size of the cathode increases
- anode 1 mark
- Write an equation to show what happens at the cathode and anode. 2 mks
- At the cathode
Na+l) + e-Na(s)
- At the anode
Cl-((l) Cl2(g) + 2e-
- At the cathode
- Show the direction of flow of electrons on the set up 1 mk
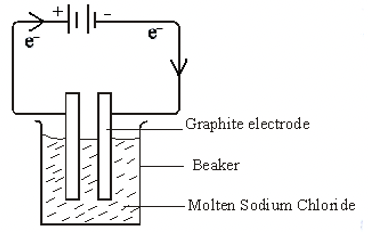
Note: The arrow must be shown on the diagram for the mark to be awarded.
- Molten sodium chloride is a binary electrolyte. State the meaning of the term binary electrolyte. 1 mark
- Define the following terms; (4 mks)
- Electrolyte
- Substance that conducts electricity either molten or aqueous states and get decomposed in the process.
- Anode
- The electrode connected to the positive terminal of the battery.
- The electrode where oxidation takes place.
- Cathode
- The electrode connected to the negative terminal of the battery.
- The electrode where reduction takes place.
- Electrode
- Solid substance that allows electric current to go into and out of an electrolyte.
- Electrolyte
- State the use of the battery (cell) in the electrolytic cell. 1 mk
- Acts as an electron pump.
- State two industrial applications of electrolysis. 2 mks
Electrolysis has the following industrial applications:- Electroplating
Electroplating is a process in which a metal is coated or plated with another metal using an electric current. This usually involves coating a cheap and corrosive metal with a more expensive metal, which is resistant to corrosion and more attractive.
The metals most commonly used for electroplating are chromium, copper, tin, silver and gold. For example, tin cans are normally made of steel which is then tin-plated. Tin is more resistant to corrosion and gives the can a shiny appearance. Car bumpers, bicycle handles and water taps are made of steel which is then chromium-plated. Chromium is more resistant to corrosion, scratching and wear. It can also be polished to give the item a shiny and attractive finish. Silver and copper are commonly used for plating utensils. Gold is plated on precious items such as watches and rings. - Extraction of metals
Highly reactive metals like sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium and aluminium are extracted from their molten ores by electrolysis. Compounds of such metals are usually very stable and therefore difficult to reduce by chemical means. - Purification of metals
Some metals are purified by electrolysis. For example, copper formed by reduction of its ores is impure for most of its industrial uses. It is purified by electrolysis. In this process the impure copper is made the anode in an electrolytic cell. The cathode contains a strip of pure copper and the electrolyte is copper (II) sulphate solution. - Manufacture of Pure Chemicals such as hydrogen, chlorine gas and sodium hydroxide.
- Electroplating
- The diagram below represents an experiment which was carried out by a student, to investigate the effect of passing an electric current on molten sodium chloride.
-
- Four athletes A, B, C and D were suspected of using NSAID and EPO drugs as blood boosters to enhance their performance. Their blood samples were taken and analyzed using chromatography. The results obtained were recorded in the chromatogram below.
- State and explain two factors that determine the distance travelled by a sample along the filter paper. (2 mks)
- Solubility: The most soluble component travels the furthest from the base line.
- Stickiness: The less sticky component travels the longest distance from the base line.
- On the diagram above indicate the baseline and the solvent front. (1 mks)
- Which athlete(s) tested positive of the use of EPO drug only? (1 mks)
- A
- Which athlete(s) tested positive of use of both EPO and NSAID drugs. (1 mks)
- B, C
- Which athlete had his blood sample negative of EPO and NSAID drugs? (1 mk)
- D
- Name a suitable solvent used in papers chromatography. (1 mk)
- Propanol
- State and explain two factors that determine the distance travelled by a sample along the filter paper. (2 mks)
- Below is a structure of aluminium chloride dimer. Study it and answer the questions that follow
Identify bond- X ……………Dative bond……… (1mk)
- Y …………………Covalent bond………… (1mk)
- Four athletes A, B, C and D were suspected of using NSAID and EPO drugs as blood boosters to enhance their performance. Their blood samples were taken and analyzed using chromatography. The results obtained were recorded in the chromatogram below.
-
- The diagram below shows a heating curve for a sample of compound X.
- Is X a solid, a liquid or a gas at room temperature, 20 °C? (1mk)
- Liquid
- Name the change of state which occurs in region DE. (1mk)
- Evaporation
- Explain how the curve shows that a pure sample of compound X was used. (1 mk)
- The substance melts and boils at constant temperatures.
- Is X a solid, a liquid or a gas at room temperature, 20 °C? (1mk)
- Compound X is a hydrocarbon. It contains 85.7% of carbon. The mass of one mole of X is 84 g.
- What is the percentage of hydrogen in the compound? (1mk)
100 – 85.7 = 14.3 % - Calculate the empirical formula of X. Show your working. (3 mks)
empirical formula = ................................
Element C H RAM 12 1 % Mass 85.7 14.3 No. of moles 85.7
12
= 7.14214.3
1
= 14.3Divide by smallest 7.142
7.142
=114.3
7.142
= 2Empirical formula CH2 - What is the molecular formula of compound X? (2 mks)
E.F.M *n = M.F.M
(CH2) *n = 84
(12 + 2)*n = 84
14n = 84
n = 84/14
= 2
Molecular Formula (CH2)2
C2H4
- What is the percentage of hydrogen in the compound? (1mk)
- The diagram below shows a heating curve for a sample of compound X.
- The flow chart below shows the industrialization of ammonia and the process used in the manufacture of some ammonium compounds. Study it and answer the questions that follow
- Give the name of the
- Process in step 1 (1 mk)
- Fractional distillation of air
- Reaction that takes place in step 5 (1 mk)
- Neutralization
- Process in step 1 (1 mk)
- Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction between nitrogen and hydrogen. (1 mk)
3H2 + N2 → 2NH3
Hydrogen Nitrogen Ammonia - Explain why it is necessary to compress nitrogen and hydrogen in this process. (2 mks)
- High pressure brings the molecules closer/increases the concentration of gas molecules/leads to more collusion.
Or - High pressure shift the equilibrium to the right hence the yield of more ammonia gas,
- High pressure brings the molecules closer/increases the concentration of gas molecules/leads to more collusion.
- Write an equation for the reaction which takes place in step 6 (1 mk)
2NH3(g) + H2SO4(aq) → (NH4)2SO4(aq) - Name the catalyst and reagents used in step 3 (2 mks)
- Catalyst : platinum Rhodium/gauze
- Reagent : water and Oxygen
- Name compound Z1 (1mk)
- Ammonium nitrate
- Give one commercial used of compound Z2 (1 mk)
- A fertilizer/as a fertilizer.
- Give the name of the
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Chemistry Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Form 3 Term 2 Opener Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

