INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Write your name and admission number in the spaces provided.
- Sign and write the date of examination in the spaces provided
- Answer all the questions in the spaces provided
- All working must be shown where necessary
- Electronic calculators and mathematical tables may be use.
- Study the information given below and answer the questions that follow.
Element
Atomic radius(nm)
Ionic radius nm
Formula of oxide
Melting point(0c)
A
0.364
0.421
A2O
-119
D
0.830
0.711
DO2
837
E
0.592
0.485
E2O3
1466
G
0.381
0.446
G2O3
242
J
0.762
0.676
JO
1054
- Which elements are non-metals. Give a reason? (2mks)
-
- Write a formula of a compound formed when J combines with A(1mk)
- What type of bond exist between J and D.(1mk)
- Explain why the melting point of the oxide of E is higher than that of the oxide of G.(2mks)
-
- Which two elements would react with each other most vigorously. Give a reason. (2mks)
- Which element would be suitable for making utensils for boiling water. State two properties that make the elements suitable for the use. (2mks)
- Elements Q and R have electronic configuration 2.8.2 and 2.8.6. respectfully.
- Explain why the ionic radius of R is expected to be greater than its atomic radius. (1mk)
- Write the equation for the reaction between Q and R.(1mk)
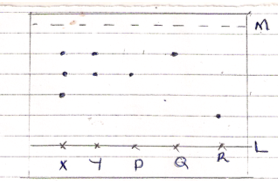
- The chromatogram below is of and acid enzyme x and y and three simple sugar P, Q and R.
-
- Name two simple sugars present in both x and y.(2mks)
- Name lines L and M. (2mks)
- What property is exhibited by simple sugar x.(1mk)
- Two pieces of paper were lowered into different Bunsen burner flames and removed quickly. The results were as shown below.
Which paper was lowered into a Bunsen burner whose air hole were closed. Explain(2mks) - Oxygen can be obtained industrially by fractional distillation of liquid air
- Why is the gas mixture passed through sodium hydroxide solution? (1mk)
- In the final stage, which gas is distilled out first? Explain. (1mk)
- Name two commercial uses of oxygen gas. (1mk)
-
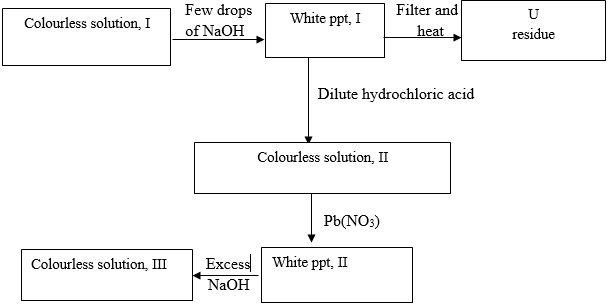
- Study the flow diagram and answer the questions below.
- Identify
- White ppt I (1mk)
- Solution II (1mk)
- Residue U (1mk)
- Write ionic equation for the reactions colourless solution (II) with Pb(NO3) 1mk
- Write observations that would be made when ammonia solution is added drop wise till in excess to the colourless solution(II) 2mks
- Below are PH values of some solutions
Solution
Z
Y
X
W
PH
6.5
3.5
2.2
7.2
- Which solution is likely to be
- Acidic rain. (1mk)
- Potassium hydroxide (1mk)
- A basic substance V reacted with both solutions Y and X. What is the nature of V? (2mks)
- Name two substances that shows the characteristics in question (ii) above. (2mks)
- Which solution is likely to be
- Identify
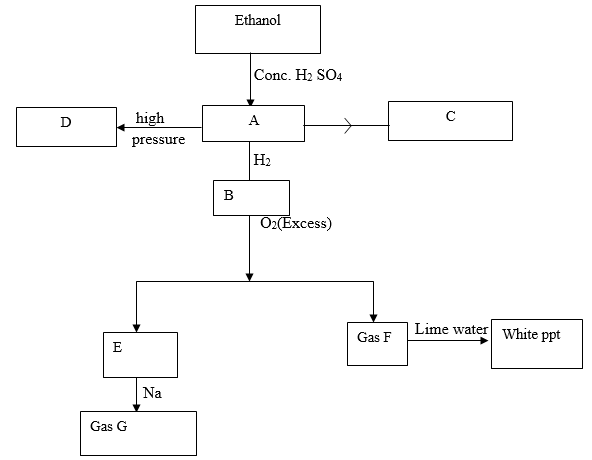
- Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify substances A, B, F and G (4mks)
- Write down the equation for the formation of
- Substance C
- E and F
- Gas G
- Substance D was formed to have molecular mass of 42,000. Determine the number of molecules present in the substances (H=1, C=12) 2mks
- State
- The condition necessary for the conversion of ethanol to substance A.(1mk)
- The catalyst required in the conversion of A and B.(1mk)
-
- The table below gives the solubility of hydrated copper(ii) sulphate in mol dm-3 at different temperatures.
Temperature(0C)
Solubility mol dm-3
20
8 x 10-2
40
12 x 10-2
60
16 x 10-2
80
22 x 10-2
100
30 x 10-2
- On the grid provided plot a graph of solubility of copper(II) sulphate (vertical axis) against temperature. (3mks
- From the graph, determine the mass of copper(II) sulphate deposited when the solution is cooled from 700c to 400. (Molar mass of hydrated copper(ii) sulphate = 250g)
- In an experiment to determine the solubility of sodium chloride ,5.0 cm3 of a saturated solution of sodium chloride weighing 5.35g were placed in a volumetric flask and diluted to a total volume of 250cm3. 25.0 cm3 of the dilute solution of sodium chloride completely reacted with 24.1 cm3 of 0.1 M silver nitrate solution.
AgNO3(aq) + NaCl(aq) → AgCl(s) + NaNO3(aq)
Calculate;- Moles of silver nitrate in 24.1cm3 of solution. (1mk)
- Moles of sodium chloride in 25.0cm3 of solution. (1mk)
- Moles of sodium chloride in 250cm3 of solution(1mk)
- Mass of sodium chloride in 5.0cm3 of saturated chloride solution (Na=23.0 Cu=35.5) (1mk)
- Mass of water in 5.0 cm3 of saturated solution of sodium chloride(1mk)
- The solubility of sodium chloride in g/100 g of water. (2mks)
- The table below gives the solubility of hydrated copper(ii) sulphate in mol dm-3 at different temperatures.
- The flow chart below shows some of the processes involved in large scale production of sulphur(VI) acid. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
- Name the process
-
- Name substance A. (1mk)
- Write an equation for the process that takes place in the absorption tower. (1mk)
- Vanadium (V) oxide is commonly used catalyst in the process.
- Name another catalyst which can be used for this process. (1mk)
- Give two why reasons vanadium (V) oxide is commonly used catalyst. (2mks)
- Sate and explain the observations made when concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid is added to crystals copper(ii) sulphate in a beaker(2mks)
- The reaction of concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid with sodium chloride produces hydrogen chloride gas. State the property of concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid illustrated in the reaction. (1mk)
- Name two uses of sulphuric (VI) acid.2mks
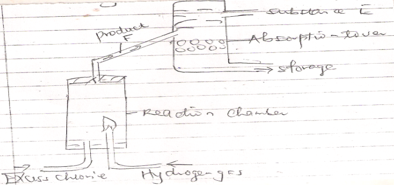
- The diagram below shows a set up that can be used for industrial manufacture of hydrochloric acid. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Name
- Produce F
- Substance E
- Explain the applications of hydrochloric acid in textile industry. (1mk)
- Hydrochloric acid was added to iron powder in a test tube and shaken thoroughly to mix to 1cm3 of the resulting solution, six drops of aqueous solution of ammonia were added.
- State the observation made on adding ammonia solution. (1 mk
- Explain the observation sated above and write an ionic equation for the reaction. (2mks)
- Concentrated hydrochloric is 35% pure with density 1.18g/cm3.Calculate it’s concentration in moles per litre. (3mks)
- Name
MARKING SCHEME
-
- A 1/2mk and G1/2 mk 1mk
The ionic radius is larger 1 mk than the atomic radius implying they gain electrons. - JA2 1mk
Metallic(1mk - The oxide of E is ionic1mk with a giant ionic structure that requires a lot of energy to break the oxide of G is molecular.(2mks)
-
- A and D 1mk
A is a non-metal with the smallest ½mk atomic radius hence most electronegative
D is a metal with the smallest atomic radius hence most electropositive. ½mk - E . 1mk Has high melting point ½mk and good ½mk conductor of heat being a metal .
- A and D 1mk
-
- R gains 2es and hence there is less nuclear 1mk charge /attraction than its atom/gains 2es nuclear attracts 20es against 16 electrons in the atom.
- Q(s) + R(s ) → QR(s) 1mk
- A 1/2mk and G1/2 mk 1mk
-
-
- P and Q (2mks)
- L-Baseline (1mk)
M- Solvent front (1mk) - Most sticky/less soluble(1mk)
- B(1mk)
Flame B burns completely because its very hot but A has unburnt region hence it contains unburnt region.91mk) -
- Sodium hydroxide solution absorbs carbon (IV) oxide gas(1mk)
- Nitrogen gas. Because it has the lowest boiling points.(2mks)
- Used in oxyacetylene flame.
Burning fuels for propelling rockets.
To remove iron impunities during steel making. Any 2 – 1mk
-
-
-
- Zn (OH) 2(g) (1mk)
- Zn CL2(aq) (1mk)
- ZnO(s) (1mk
- 2Cl- (aq) + Pb2+(aq) (1mk)
- White ppt formed (1mk)
Dissolve in excess (1mk) -
- I Z (1mk)
II Y (1mk) - Amphoteric (1mk)
- Zn (OH)2(s) / zinc hydroxide. (1mk)
- I Z (1mk)
-
-
- A-Ethane C2 H4 CH2 =CH2
B- Ethane C 2 H6 CH3 CH3
F – Carbon (IV) oxide CO2
G- Hydrogen H2 (4mks) -
- C 2H(g) + Br2(l) → C2H4Br2 or CH2Br-CH2Br (1mk)
- 2C2H6(g) + 7O2(s) → 4CO2(g) + 6H2O (g)
If not balanced = 0mk
Wrong or missing symbols = 1/2mk - 2Na(s) + 2H2 O(l) → 2NaOH9aq) + H2(g) (2mks)
Balanced = 2mks
Not balanced =0mk.
- Mass of monomer = 2(12 + 2)= 28
No.of molecules = 42000 = 15000 molecules (2mks)
28 -
- Temperature of 1800 c (1mk)
- Nickel catalyst (1mk)
- A-Ethane C2 H4 CH2 =CH2
-
-
- - scale(I)
-Plotting all points correctly (I)
- Curve (shape) - 0.188- 0.12 = 0.068 mol(I)
Therefore mass of hydrated copper(II) sulphate
= 0.68 x 250 = 17g
- - scale(I)
-
- Moles of AgNO3 = 0.1 x 24.1 = 2.41 10-3
1000 - Moles of NaCI = Moles of AgNO3
= 241 x 10 -3 - Moles of NaCL in 250cm3 = 2.41 x 10-3 x 250
25
=2.41 x 10-2 - R.F.M Na CI = 23 + 35 .5 = 58.5
Mass of NaCl in 5cm3 = 2.41 x 10-2 x 58.5
= 1.41g - Mass of water = 5.35 – 1.41
= 3.94g - 3.94 of water contains 1.41g of NaCl
100 g of water = 1.41 x 100
3.94
=35.7
- Moles of AgNO3 = 0.1 x 24.1 = 2.41 10-3
-
-
- Contact process=1mk
-
- Sulphuric(IV) acid.(1mk)
- H2SO 4(aq) + SO3(g) → H2S2O7(l)
-
- Platinized asbestos (1mk)
- -It is not highly poisoned(2mks)
-It is cheap
- Crystals turn blue to white .Concentrated sulphuric(IV) acid removes water of crystals from hydrated copper(II) sulphate.(2mks)
- Concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid is less volatile hence displaces more volatile acids from their salts.(1mk)
- Used in;- accumulators.
- in manufacture of fertilizers.
- in etching of metals.
- in manufacture of detergents.(any 2mks)
-
-
- Hydrogen chloride gas (HCL (g) 1mk
- Water (H2O (l) 1mk
- ……………………………..
-
- Green ppt(1mk
- Insoluble iron (II) hydroxide was formed(1mk)
Fe2+(aq) + 2OH (aq) → Fe(OH)2(s) 1mk
- Mass of 1000cm3 of solution = 1000 x 1.18 1/2mk
= 1180g 1/2mk
Mass of HCl = 35 x 1180 ½ mk
100
= 413g ½ mk
Molarity = 413 ½ mk
36.5
= 11.3151 M ½mk
-
Download CHEMISTRY PAPER 2 - FORM 4 END TERM 1 EXAMS 2020.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students