INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- This paper consists of three section A,B and C
- Answer ALL the questions in section A and B and any TWO questions in section C.
Section A - 30 marks
Answer all the questions in the spaces provided
- State four aspects of rainfall that are important in Agriculture. ( 2 marks )
- State four factors which determine the depth of ploughing during seedbed preparation. ( 2 marks )
- Give four reasons for subsoiling on a piece of land. ( 2 marks )
- Give a reason for carrying out each of the following practices in a vegetable farm.
- pricking out. ________________________________________________________________( ½mk)
- Hardening off _______________________________________________________________( ½mk)
- Mention any four advantages of land consolidation as practiced in Agriculture. ( 2 marks)
- State two non-chemical methods of controlling storage pests in the granary. ( 1 mark )
- State four precautions that should be taken when harvesting tea. ( 2 marks )
- List three disadvantages of drip irrigation. ( 1 ½ marks )
- State four characteristic of nitrogenous fertilizer. ( 2 marks )
- List four micro-catchment systems. ( 2 marks )
- List three methods of fertilizer application in crops production. ( 1 ½ marks)
- State three forms of soil water. ( 1 ½ marks )
- State three methods of cutworms control. ( 1 ½ marks)
- Give four conditions required for settlement scheme to be successful. ( 2 marks )
- Give three reasons for stooking maize. ( 1 ½ marks)
- State four ways in which soil profile influence crop production. ( 2 marks )
-
- State three ways in which inorganic mulch helps to conserve water in the soil. ( 1 ½ marks)
- State two factors that influence wind erosion. ( 1 mark )
Section B ( 20 marks )
Answer all the questions in the spaces provided.
- The diagram below shows a method of bringing tea into bearing. Study it carefully and use it to answer the questions that follow.
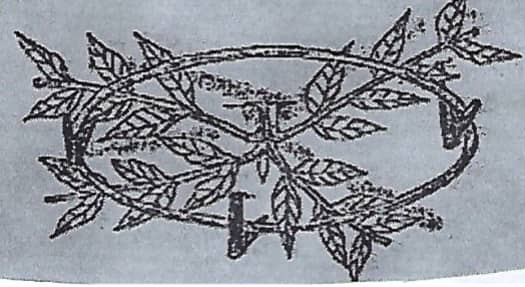
- Identify the method shown in the diagram. ( 1 mark )
- is it necessary to prune a young tea plant as illustrated in the diagram above. ( 1 mark )
- Outline the procedure followed when using the pruning method shown. ( 3 marks)
- The following diagram shows a method of compost preparation.
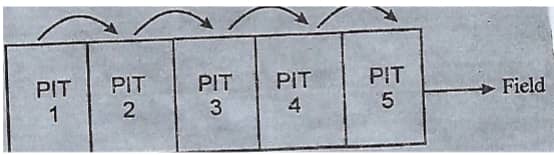
- Identify the method. ( 1 mark )
- Give four factors that should be considered when siting the compost pit. ( 2 marks )
- State two factors that determine the time the manure would be ready for use in the field. (2 marks)
- The diagram below shows a field crop pest. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow.

- Identify the pest. ( 1 mark )
- Outline two harmful effects of the pests. ( 2 marks )
- State two methods which are used to control the pests. ( 2 marks )
- The illustrations labelled E-G below represents common weeds in pasture land. Study them carefully and answer the following questions.
- Identify the weeds labelled E-G . ( 1 ½m marks)
- Name the major problems posed by each of the specimen
E – G when in pasture land ( 1 ½ marks ) - Give two reasons why the three type of weeds may overtake and smoother pasture species when they are allowed to grow together. ( 3 marks )
SECTION C ( 40 marks)
Answer any two questions.
-
- Describe the production of Napier grass under the following sub-heading;
- Varieties ( 2 marks)
- Land preparation. ( 4 marks)
- Planting ( 2 marks )
- Harvesting ( 2 marks )
- State five factors considered when designing a crop rotation programme. ( 5 marks )
- State five effects of land fragmentation. ( 5 marks )
- Describe the production of Napier grass under the following sub-heading;
-
- Explains five biological measures used to conserve soil and water in the farm. ( 10 marks )
- State five reasons for carrying minimum tillage. ( 5 marks)
- Outline five ways government policy contributes to Agriculture. ( 5 marks )
-
- explain five cultural measures to control pests. (10 marks )
- Give four factors influencing timely planting ( 4 marks )
- Explain four methods used to prepare planting material. ( 6 marks )

MARKING SCHEME
-
- Rainfall intensity – volume/amount of rainfall
- Rainfall reliability
- Rainfall distribution 4 x ½ = 2
-
- Type of crop to be grown
- The implements available
- Soil moisture contents
- presence of certain weeds 4 x ½ = 2
-
- Breaking hardpans
- Improves drainage
- Facilitates adequate gaseous exchange
- Bring to the surface minerals which might have leached. 4 x ½ = 2
-
-
- Avoid competition
- Vigorous growth of seedlings 1 x ½ = ½
- Seeds to acclimatize to actual field conditions. 1 x ½ = ½
-
-
- Save cost and time incurred when moving from one place to another.
- improve production through effective supervision.
- For effective farm planning and budgetary.
- facilitate use of machines
- facilitate long term land development and investment 4 x ½ = 2
-
- Making granary vermin proof/rat guards.
- Cleaning of the store
- Cleaning of bushes around the store
- Time harvesting.
- proper moisture/proper drying
- Use of rat traps/cats to kill rats
-
- Avoid compressing the picked leaves
- Use open woven/well ventilated baskets
- keep the picked leaves in a cool shaded area before taking them to the factory.
- Take leaves to the factory the same day. 4 x ½ = 2
-
- Pipes used are expensive
- Requires clean water to avoid blockage of perforation
- Requires skills to install
- Plants roots are only restricted to the wet soil. 3 x ½ = 1 ½
-
- Highly soluble in water
- Easily leached
- Highly volatile
- Have scorching effect
- Highly hygroscopic
- Have residual effect 4 x ½ = 2
-
- Negarim
- Contour bunds
- Contour ridges
- Semi –circular bunds
- Trapezoid bunds
- Contour stone bunds
- permeable rock dams
- Water spreading bunds
-
- Broadcasting
- Placement
- Side dressing/ring application/band application
- Foliar spraying
- Drip 3 x ½ = 1 ½ mks
-
- Super flous water
- Capillary water
- Hygroscopic water 3 x ½ = 1 ½
-
- Using appropriate insecticide/appropriate chemical.
- Physical killing
- Biological/Birds/chicken 3 x ½ = 1 ½
(Accept specific chemical such as aldrin)
-
- There should be high population pressure on the reserves
- There should be adequate economic incentive to persevere
- The social costs of moving from home community and the discipline imposed for sound agriculture and extra effort.
- Settlers should come from far distances from the schemes inorder to break from traditional society and stay on the scheme.
- Settlers should have enough capital. 4 x ½ = 2
-
- To allow cobs to dry
- To avoid theft
- To allow enough time for land to be prepared. 3 x ½ = 1 ½
-
- It determines the type of crop to be grown
- It determine the type of implements to be used
- It influences the amount of moisture held by the soil
- It influences availability of nutrients
- It influences the mineral contents depending on bed rock/parent rock.
- It influences water infiltration. 4 x ½ = 2
-
-
- reduces runoff thus increasing amount of water into the soil
- Reduces evaporation thus increases amount of water retained in the soil.
- Increases amount of water retained in the soil. 3 x ½ = 1 ½
-
- Soil cover
- Soil type
- Topography
- Wind speed/velocity
- Human activity e.g overcultivation
- Soil moisture content. 2 x ½ = 1
-
-
- Pegging/use of ring and pegs 1 x 1 = 1 mark
- To encourage development of a lot of lateral branches that forms a wide plucking table. 1 x 1 = 1
-
- Cut the plant when it reaches 25 cm to 30 cm back 15cm above the ground level.
- when branches have grown 60cm to 75 cm high, they are forced to lie at an angle of 30-45 degrees using a ring made of sticks or wire.
- Three pegs are used to hold the ring in its position. 3 x 1 = 3 marks
-
- Indore/pit method 1 x 1 = 1 mark
-
- Direction of the prevailing wind in relation to the homestead
- should be sited on a well drained place.
- The site should be accessible
- located in well sheltered place
- Should be located near the farm. 4 x ½ = 2 marks
-
- Type of material used
- Age of the material used
- Level of management practices during preparation 2 x 1 = ( 2 marks)
-
- Cotton stainer (Dysdercus spp) 1 x 1 = 1 mark
-
- Reduces the quality of the produce
- Reduces the quantity of the produce
- Increases the cost of production 2x 1 = 2 mks.
-
- Use of appropriate pesticides/insecticides
- Early planting
- crop rotation 2 x 1 = 2
-
- E – Thorn apple/Datura stramonium
F – Mexican marigold/ Tagetes minuta
G – Black jack/Bidens pilosa 3 x ½ - 1 ½ - E – Poisonous to livestock
F – Taints milk and other farm products
G – sticks on wool in sheep, lowering its quality 3 x ½ 1 ½ -
- Due to overgrazing
- Due to grazing on very young pasture /earlydefoliation.
- Due to loss of fertility 2 x 1 = 2 marks
- E – Thorn apple/Datura stramonium
-
- Napier grass production
- .Varieties
- French Cameroon ( 1 mark )
- Bana grass ( 1 mark )
- Land preparation
- Prepare the land early/during dry seasons
- Clear vegetation and remove all the stumps
- carryout primary cultivation to remove all perennial weeds
- Harrow the land/carryout secondary cultivation to produce a medium tilth
- Dig the holes/furrows at appropriate spacing, (Any 4 x 1 = 4 mks)
- Planting
- plant at the onset of rains.
- use healthy planting materials
- Apply well decomposed manure/compound fertilizer/NPK fertilizer.
- Place the planting materials in the furrows/holes in a slanting manner…
- Cover the planting materials with soil.
- For cutting two nodes should be covered underground and one node remain above the ground (Any 2 x 1 = 2 marks )
- Harvesting
- Harvesting when stems are 1.5m high/3-5 months old.
- Cut the stems at 2.5- 5cm above the soil surface
- Cut with a sharp panga to avoid destroying the stump. ( Any 2 x 1 = 2 marks )
- .Varieties
-
- Crop root depth
- crop nutrient requirement
- weed control
- pests and disease control
- soil fertility
- soil structure ( Any 5 x 1) = 5 marks
- Effects of land fragmentation
- wastage of time moving from one holding to another.
- Difficulty in controlling pests and diseases.
- Difficulties in following a sound from plan
- Difficulties in supervision of scattered plots
- Difficulties in controlling livestock parasites and diseases.
- Difficulties in carrying out soil and water conservation measures.
- Difficulties in restricting grazing in one holding leading to overstocking, soil erosion and land denudation
- Difficulties in offering agricultural extension advice
- poor productivity 5 x 1 = 5 marks
- Napier grass production
-
-
- Use of grass/filter strips – are uncultivated areas left intentionally across the slope or along the contours to slow the speed of water and trap eroded soil.
- Cover crops – these are crops planted which grow in a spreading manner covering the soil and protecting it against splash erosion. They control soil erosion by: Reducing the impact of raindrops, encouraging infiltration, minimizing the volume of surface runoff and decay of the leaf fall reduces erodability of the soil by improving soil structure.
- Contour farming-: This is ploughing along the contours or across the slope and planting crops along the contours. This helps to slow down the speed of water and trap eroded soil.
- Mulching – This is covering the soil either with organic materials or inorganic materials. It prevents splash erosion, reduce speed of runoff, increase water infiltration, reduces evaporation and improve on water retention capacity.
- strip cropping this involves growing crops which give little soil cover alternating with those having good soil cover. Strips of grass can be included. Different strips control the movement of soil particles hence controlling soil erosion.
- Grassed or vegetated water ways – water channels with vegetation. The vegetation traps eroded materials and slow down water hence reducing its erosivity.
- Afforestation/re-afforestation planting trees helps protecting the soil below from raindrops erosion.
Any 5 point: Stating ( 5 marks )
Description ( 5 marks)
- Reason for carrying out minimum tillage
- Reduce the cost of cultivation
- To control soil erosion
- To maintain soil structure
- To conserve moisture
- To prevent disturbance of roots and underground structures
- To prevent exposure of humus to adverse conditions.
- Ensure retention of useful organisms in soil.
- Save time in land preparation. Any 5 x 1 = 5 marks )
- Five ways government policy contributes to Agriculture.
- Subsidize the price of inputs to ensure productions affordable.
- Conservation of natural resources to ensure sustainability.
- Imposition of high import tax to promote local products.
- Quality control of diseases to prevent spread and high quality products.
- Quality control to ensure effective competition in both local and international market.
5 x 1 = 5 marks
-
-
- Cultural measures to control pests.
- Timely planting: - these escapes pest attack than late planted ones.
- Timely harvesting – Avoid some storage pests eg. Weevils attacking the crop while in he field.
- Proper tillage – exposes the pests eg soil borne pests to scorching effect of the sun or eaten by birds/predators.
- Close season –susceptible crop is not grown inorder to control certain pests or group of pests.
- Trap cropping –planting a crop with the main crop purposely attracting pests away from the latter.
- Crop rotation – Assist in starving the pest to death.
- Planting resistant varieties eg hairy cotton against jassid bug, goose necked sorghum against birds.
- Field hygiene- involves rogueing and removal of crop residues from the field.
- Alteration of environment condition –creation of certain micro-climates that are conducive to some pests egopening pruning in coffee discourages antestia bugs, mulching reduces thrips.
- Crop nutrition – application of fertilizer and manures makes the crop to grow strong and able to resist and escape attack.
- Describe of alternative host – the removal of weeds reduces pest infestation.
- Use of clean planting materials – help to prevent introduction and spreading of pests.
- Proper spacing becomes difficult for pests to move from one plant to the other.
- Use of organic manures eg farm yard manure discourages pests eg eelworms.
- Irrigation – overhead irrigation controls aphids in cabbages.
Any 5 points: stating ( 5 marks )
: Desociation ( 5 marks )
- Factors influencing timely planting.
- Rainfall pattern/moisture condition of the soil
- crops make maximum use of the rainfall.
- Type of crop to be planted.
- Type of soil – crops should be planted early in moist soils.
- Market demand – proper timing ensures that produce is marketed when prices are high.
- Weed control – crops planted early establish earlier than weeds.
- Prevalence of pest and diseases – crop establish early escape serious and disease attack.
4 x 1 = 4 marks
- Rainfall pattern/moisture condition of the soil
- Four methods used to prepare planting materials.
- Breaking seed dormancy.
- Seed dormancy is a stage whereby a seed cannot germinate, this should be broken before planting to allow germination.
- Seed dressing
- This is coating of a seeds with fungicides and pesticides to protect them from soil borne pests and diseases.
- Seed inoculation
- This involves coating of legume with an inoculant to encourage nodulation hence nitrogen fixation.
- Chitting
- Selected potatoes setts for planting are sprouted before planting to break their dormancy.
( 6 marks )
(Award ½ mark for stating the method 1 mark for describing).
- Selected potatoes setts for planting are sprouted before planting to break their dormancy.
- Breaking seed dormancy.
- Cultural measures to control pests.
Download Agriculture Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Joint Pre-Mock Exams 2021/2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students