BIOLOGY
PAPER 2
(THEORY)
FORM 4 TERM 1 OPENER EXAMS
TIME: 2 HOURS
INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- This paper consists of two sections: Section A and B
- Answer all questions in section A
- Answer question 6( compulsory) and either question 7 or 8
SECTION A
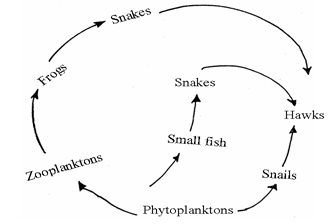
- The diagram below represents a feeding relationship in an ecosystem.
- Name the type of ecosystem represented by the above food web. (1mk)
- Name the organisms in the food web that
- Are producers (1mk)
- Occupies the highest trophic level (1mk)
-
- Write a food chain that ends with the hawk as quaternary consumer. (1mk)
- State two short term effects on the above ecosystem if all the small fish were killed (2mks)
- How does oil spills lead to death of fish. (1mk)
- Name one other cause of water pollution apart from oil spills. (1mk)
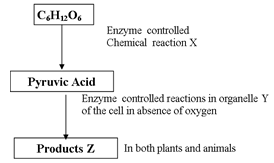
- Study the flow chart below of a process that takes place in both plants and animals.
- Name the above process. (1mk)
-
- In the above process name the chemical reaction represented by X. (1mk)
- Name the part of the cell where the enzyme controlled reactions in b (i) above takes place. (1mk)
- Name the products Z in
- Plants (1mk)
- Animals (1mk)
- What would be the fate of pyruvic acid if oxygen supply is availed in the mitochondria of an animal cell (2mks)
- What is meant by the term oxygen debt? (1mk)
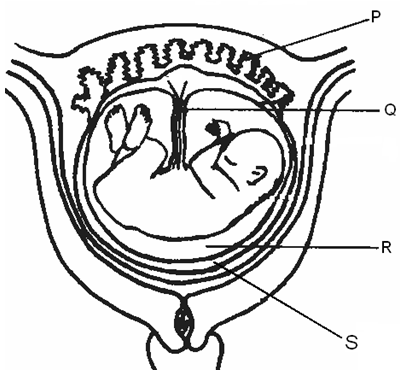
- The diagram below represents human foetus in a uterus.
- Name the part labeled S. (1 mk)
-
- Name the types of blood vessels found in the structure labeled Q. (2mks)
- State the differences in composition of blood in the vessels named in (b)(i) above (2mks)
- Name two features that enable the structure labeled P carry out its function. ( 2mks)
- State the role of the part labeled R. (1mk)
- The table below shows the concentration of sodium and iodine ions in pond water and in the cell sap of water lettuce plant.
Sodium ion concentration Iodine ion concentration Pond water 180 0.4 Cell sap 90 500 - Giving reasons, name the process through which each of the ions is taken up by the plant.
- Sodium ion. (2mks)
- Iodine ion. (2 mks)
- The lettuce plant was then treated with a chemical substance that inhibits the synthesis of ATP. Giving reasons, state which ion uptake was affected by the treatment. (2 mks)
- Explain why fresh water fish cannot survive in marine habitat. (2 mks)
- Giving reasons, name the process through which each of the ions is taken up by the plant.
- The equation bellows shows a chemical reaction that takes place in green plants under certain conditions
Carbon (IV) Oxide + Water→ Glucose + X- Name the; (2mks)
- Substance represent by X
- Process represented by the equation
- Other than the reactants, state two conditions necessary for this reaction to occur. (2mks)
- Name three types of cells in which the process occurs (3mks)
- State one factor that affect the process named in a)(ii) above (1mark)
- Name the; (2mks)
SECTION B
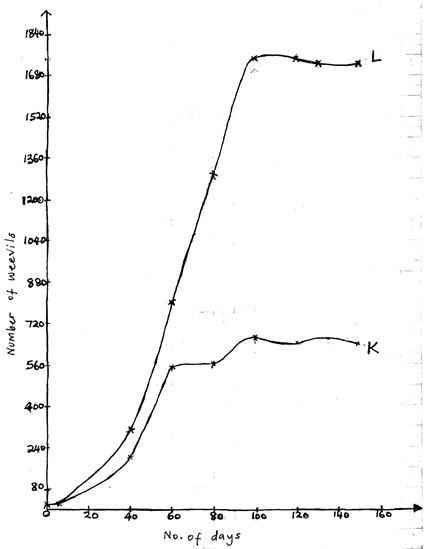
- A group of students carried out a study of the population growth of flour weevils. They put16grams and 64 grams of maize flour into two equal boxes K and L respectively. They then introduced equal numbers of weevils into the boxes. The boxes were kept under similar environmental conditions. The weevils were counted at intervals and the results recorded in the table below.
No. of days after introduction of weevils Approximate No. of weevils present K L 0
5
40
60
80
100
120
135
150
20
20
200
550
560
650
640
650
645
20
20
300
800
1300
1750
1750
1740
1748
- Using a suitable scale, draw two graphs on the same axes from the results in the table. Plot approximate number of weevils present on the Y – axis. (8mks)
- What were the approximate numbers of weevils present in the two boxes on the 70th day.(2mks)
Number in K
Number in L -
- On the what day was the population of weevils in K 580. (1mk)
- Between which days was the population difference greatest. (1mk)
- Account for the shape of graph L between day 5 and day 100. (4mks)
- State factors that would make the human species assume the graph curve between day 100 and day 150. (4mks)
- Describe how the human male reproductive system is adapted to perform its function.(20mks)
-
- Define transpiration (1mark)
- Give THREE types transpiration (3mark)
- Describe EIGHT factors that affect the rate of transpiration
MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A
- The diagram below represents a feeding relationship in an ecosystem.
- Name the type of ecosystem represented by the above food web. (1mk)
- Aquatic;
- Aquatic;
- Name the organisms in the food web that
- Are producers (1mk)
- Phytoplanktons;
- Phytoplanktons;
- Occupies the highest trophic level (1mk)
- Hawks;
- Hawks;
- Are producers (1mk)
-
- Write a food chain that ends with the hawk as quaternary consumer. (1mk)
Phytoplanktons→Zooplanktons→Frogs →Snakes → Hawks;
(Reject if arrow is not indicated) - State two short term effects on the above ecosystem if all the small fish were killed (2mks)
- Snakes would decrease due to less food;
- Zooplanktons would increase due to fewer predators;
- Write a food chain that ends with the hawk as quaternary consumer. (1mk)
- How does oil spills lead to death of fish. (1mk)
- Oil clogs fish gills;
- Oil cuts off dissolved oxygen in water leading to suffocation;
(Accept any one right)
- Name one other cause of water pollution apart from oil spills. (1mk)
- Domestic wastes and sewage;
- Silting;
- Industrial effluents;
- Agro – chemicals;
(Accept any one right)
- Name the type of ecosystem represented by the above food web. (1mk)
- Study the flow chart below of a process that takes place in both plants and animals.
- Name the above process. (1mk)
- Anaerobic respiration;
(Reject respiration alone)
- Anaerobic respiration;
-
- In the above process name the chemical reaction represented by X. (1mk)
- Glycolysis;
- Glycolysis;
- Name the part of the cell where the enzyme controlled reactions in b (i) above takes place. (1mk)
- Cytoplasm;
- Cytoplasm;
- In the above process name the chemical reaction represented by X. (1mk)
- Name the products Z in
- Plants (1mk)
- Alcohol/ ethanol, carbon IV oxide and energy;
(Reject if only one product is given) + Energy
- Alcohol/ ethanol, carbon IV oxide and energy;
- Animals (1mk)
- Lactic acid, energy
- Lactic acid, energy
- Plants (1mk)
- What would be the fate of pyruvic acid if oxygen supply is availed in the mitochondria of an animal cell (2mks)
- Pyruvic acid will be further oxidized by oxygen (in a series of enzymatic reactions/ Kreb’s Cycle) into carbon IV oxide, water and energy;
(Reject if all products are not mentioned)
- Pyruvic acid will be further oxidized by oxygen (in a series of enzymatic reactions/ Kreb’s Cycle) into carbon IV oxide, water and energy;
- What is meant by the term oxygen debt? (1mk)
- The amount of oxygen required to get rid of the lactic acid that accumulates in the body tissues when supply of oxygen is less than demand
- The amount of oxygen required to get rid of the lactic acid that accumulates in the body tissues when supply of oxygen is less than demand
- Name the above process. (1mk)
- The diagram below represents human foetus in a uterus.
- Name the part labeled S. (1 mk)
- chorion
- chorion
-
- Name the types of blood vessels found in the structure labeled Q. (2mks)
- umbilical vein; umbilical artery
- umbilical vein; umbilical artery
- State the differences in composition of blood in the vessels named in (b)(i) above (2mks)
- More food nutrients and more oxygen in veins;; less food nutrients more excretory products in the arteries.
- More food nutrients and more oxygen in veins;; less food nutrients more excretory products in the arteries.
- Name the types of blood vessels found in the structure labeled Q. (2mks)
- Name two features that enable the structure labeled P carry out its function. ( 2mks)
- Highly vascularised/large surface area
- Presence of secretory cells;
- State the role of the part labeled R. (1mk)
- cushions/absorbs shock
- cushions/absorbs shock
- Name the part labeled S. (1 mk)
- The table below shows the concentration of sodium and iodine ions in pond water and in the cell sap of water lettuce plant.
Sodium ion concentration Iodine ion concentration Pond water 180 0.4 Cell sap 90 500 - Giving reasons, name the process through which each of the ions is taken up by the plant.
- Sodium ion. (2mks)
- Diffusion; because its uptake occurs according to the concentration gradient.
- Diffusion; because its uptake occurs according to the concentration gradient.
- Iodine ion. (2 mks)
- active transport; because its uptake occurs against concentration gradient;
- active transport; because its uptake occurs against concentration gradient;
- Sodium ion. (2mks)
- The lettuce plant was then treated with a chemical substance that inhibits the synthesis of ATP. Giving reasons, state which ion uptake was affected by the treatment. (2 mks)
- Iodine; its uptake depends on energy derived from ATP;
- Iodine; its uptake depends on energy derived from ATP;
- Explain why fresh water fish cannot survive in marine habitat. (2 mks)
- This is because the fresh water fish would lose water molecules to the marine habitat since the marine environment is hypertonic
- This is because the fresh water fish would lose water molecules to the marine habitat since the marine environment is hypertonic
- Giving reasons, name the process through which each of the ions is taken up by the plant.
- The equation bellows shows a chemical reaction that takes place in green plants under certain conditions
Carbon (IV) Oxide + Water Glucose + X- Name the; (2mks)
- Substance represent by X
- Oxygen
- Oxygen
- Process represented by the equation
- Photosynthesis
- Photosynthesis
- Substance represent by X
- Other than the reactants, state two conditions necessary for this reaction to occur. (2mks)
- Presence of light ;
- Presence of chlorophyll;
- Presence of suitable temperature ;
- Name three types of cells in which the process occurs (3mks)
- Palisade cells;
- Guard cells;
- Spongy mesophyll cells;
- State one factor that affect the process named in a)(ii) above (1mark)
- Avoilability of water
- Carbon (iv)oxide concentration
- Temperature
- Availability of water
- Name the; (2mks)
SECTION B
- A group of students carried out a study of the population growth of flour weevils. They put 16 grams and 64 grams of maize flour into two equal boxes K and L respectively. They then introduced equal numbers of weevils into the boxes. The boxes were kept under similar environmental conditions. The weevils were counted at intervals and the results recorded in the table below.
No. of days after introduction of weevils Approximate No. of weevils present K L 0
5
40
60
80
100
120
135
150
20
20
200
550
560
650
640
650
645
20
20
300
800
1300
1750
1750
1740
1748
- Using a suitable scale, draw two graphs on the same axes from the results in the table. Plot approximate number of weevils present on the Y – axis. (8mks)
Axes -2
Curve- 2
Curve labelling-2
Scale -2 - What were the approximate numbers of weevils present in the two boxes on the 70th day.(2mks)
Number in K - 555
Number in L - 1020 -
- On the what day was the population of weevils in K 580. (1mk)
86th day - Between which days was the population difference greatest. (1mk)
100-120
- On the what day was the population of weevils in K 580. (1mk)
- Account for the shape of graph L between day 5 and day 100. (4mks)
- Increase in population ; because there is adequate food ; the number of reproducing individuals is increasing ; wastes products have not accumulated to toxic levels;
- Increase in population ; because there is adequate food ; the number of reproducing individuals is increasing ; wastes products have not accumulated to toxic levels;
- State factors that would make the human species assume the graph curve between day 100 and day 150. (4mks)
- Diseases
- Lack of food
- Death rate equal to birth rate
- Using a suitable scale, draw two graphs on the same axes from the results in the table. Plot approximate number of weevils present on the Y – axis. (8mks)
- Describe how the human male reproductive system is adapted to perform its function.(20mks)
- The testes found outside the body; to provide a cooler environment for sperm production;
- Scrotal sacs suspend the testes outside the body cavity -
- Seminiferous tubules consist of actively diving cells; which give rise to sperms;
- interstitial cells secrete the male hormones(androgens)
- Epididymis which is highly coiled and long; to store sperms;
- Sperm duct / vas deferens ; connect the epididymis to the urethra; is muscular: its contraction pushes sperms out allowing ejaculation
- Seminal vesicle; provides an alkaline fluid which contains nutrients for spermatozoa.
- Prostate gland ;alkaline secretion to neutralize the vaginal; fluids, also activates the sperms;
- Cowper’s gland; neutralizes the acidity along the urethra;
- Urethra used for the expulsion of urine to the exterior as well as sperms ./ allows passage of sperms during ejaculation
- Penis made up of spongy tissue; muscles and blood vessels filled with blood to enable vessels filled with blood to enable it penetrate during coitus;
-
- Define transpiration (1mark)
- The process by which plants lose water inform of water vapour to the atmosphere
- The process by which plants lose water inform of water vapour to the atmosphere
- Give THREE types transpiration (3mark)
- Lenticular transpiration
- Stomata transpiration
- Cuticular transpiration
- Describe EIGHT factors that affect the rate of transpiration
- Environmental factors
- Temperature-High temperature raises internal temperature of the leaf which in turn increases latent heat of vaporization enhancing evaporation from the leaf. Low temperature lowers the internal temperature of the leaf which in turn lowers evaporation
- Humidity- in low humidity saturation deficit between the leaf and the atmosphere is high thus water vapour diffuses faster increasing the rate of transpiration. In high humidity saturation deficit is low thus water diffuses slowly reducing the rate of transpiration
- Wind .wind carries away water vapour as fast as diffuses from the leaf hence water vapour does not accumulate around the leaf and this raises diffusion gradient between the inside and outside the leave hence increasing the rate of transpiration and vice vasa.
- Light intencity.Light intensity increases the rate of photosynthesis forming sugar which is osmotic ally active causing stomata to open hence water diffuses out of the leaf at higher rate increasing the rate of photosynthesis and vice vasa
- Atmospheric pressure. Low atmospheric pressure reduces the weight of gases acting on the leaf causing a lot of evaporation from the leaf hence high rate of transpiration. High atmospheric pressure increases the weight of gases acting on the leaf hence minimal evaporation from the leaf leading to reduced rate of evaporation
- Structural factors
- Cuticle. Plants whose leaves are covered with thick cuticle have reduced rate of transpiration while plant with thin layer of cuticle have high rate of transpiration
- Leaf size and shape. Plant with broad leaves exposes a large surface area for water loss compared to plant with small or needle like leaves
- Hairy leaves.Plants whose leaves are covered with hairs have reduced rate of transpiration since the hairs trap a layer of moist air on the surface of the lowering the diffusion gradient thus reducing the rate of transpiration
- Stomata. Plants with leaves with stomata on the upper surface ,high number of stomata, large sized aperture have increased rate of transpiration and vice vas
- Glossy leaf surfaces. Glossy leaf surfaces reflect light landing on the leaf surface thus reducing the internal heating of the leaf hence low transpiration rate
- Environmental factors
- Define transpiration (1mark)
Download Biology Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Form 4 Term 1 Opener Exams 2021.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students