AGRICULTURE
PAPER 1
FORM 4 TERM 1 OPENER EXAMS
TIME: 2 HOURS
INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- This question paper consists of three sections A, B and C.
- Answer all the questions in sections A and B any two questions from section C.
SECTION A(30mks)
Attempt all the questions in this section.
- Give two conditions under which shifting cultivation can be practiced. (1mk)
- Differentiate between apiculture and aquaculture.(1mk)
- Give four government policies which influence Agricultural production.(2mks)
- State four methods of clearing land.(2mk)
- State four importance for treating water for domestic use.(2mks)
- Give four qualities of a fertile soil.(2mks)
- State four types of farm records.(2mks)
- Give four role of nitrogen in a plant.(2mks)
- State four factors which influence the rooting of a cutting.(2mks)
- Give four reasons for growing seedling in a nursery.(2mks)
- Name two methods of pruning.(2mks)
- Give two causes of blossom end rot in tomatoes.(2mks)
- Define the following terms as used in Agriculture.
- Land sub-division.(1mk)
- Land consolidation.(1mk)
- State four harmful effects of weed.(2mks)
- State two categories under which pest can be classified or mode of feeding.(2mks)
- Name four causes of crop diseases.(2mks)
SECTION B:20mks:
Attempt all questions in this section.
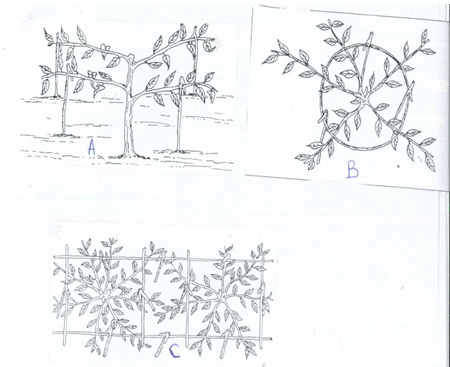
- Below is a diagram of one of the tertially practices that are carried out in land preparation. Study it and answer the questions below
- Identify the tertially practice shown above.(1mk)
- Give four reasons for carrying out the above practice.(2mks)
- Apart from the above practice name any other two tertiary practices that are carried out in a farm.(1mk)
- The table below is one of the record that is kept by livestock farmer in the farm
Dam No Breed colour Parents: sire 1st Service 2nd service 3rd service 4th service Remarks No of service Date of service Date of service Date of service Date of service Time of service Time of service Time of service Time of service Bull No Breed Bull No Breed Bull No Breed A.........
B..........
Result………………. Expected date of calving C………………………………….. Weight of calf at birth Sex of the calf No of calf - Identify the type of record.(1mk)
- Fill in the blank spaces.(3mks)
A……………………………………………………
B……………………………………………………
C……………………………………………………
- A farmer was advised to apply 150 kg of CAN/ha,while top dressing the maize crop.CAN contains 21% N.Calculate the amount of Nitrogen applied per ha.(4mks)
- Below are various pegging methods of tea. Study them and answer the questions that follows.
- Identify the pegging methods shown above.(1 ½mks)
A-
B-
C - Apart from the above method .Name any other method which is used to bring tea to bearing.(1mk)
- Give one advantage of using the method given in b above.(1mk)
- State one reason why the method in (b) above is not commonly used.(½mk)
- Identify the pegging methods shown above.(1 ½mks)
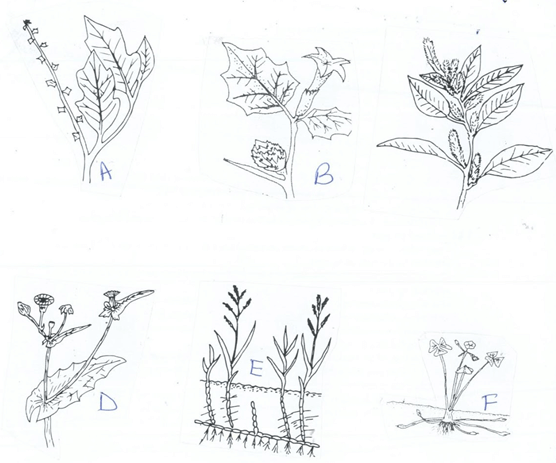
- Below are some of the common weeds in Kenya. Study them and answer the questions which follow.
- Identify the weeds A,B,C D.(2mks)
- What contributes to the competitive ability of weed C(1mk)
- Why is it difficult to control weed E and weed F.(1mk)
SECTION C
Attempt two questions in this section.(40mks)
-
- Describe the advantages of organic farming in Kenya.(5mks)
- Explain the overall effects of HIV/AIDS and ill health on Agricultural production.(5mks)
- Describe five reasons of carrying out minimum tillage in agriculture production.(5mks)
- Describe the uses of water in a farm.(5mks)
-
- Explain five ways of maintaining soil fertility.(5mks)
- Explain the factors which affects the spacing of any crop.(5mks)
- Describe five management practices carried out in a nursery bed.(5mks)
- Describe the field management practices in tomato production.(5mks)
-
- Describe the effects of land consolidation.(6mks)
- Explain cultural methods of controlling pests.(14mks)
MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A(30mks)
Attempt all the questions in this section.
- Give two conditions under which shifting cultivation can be practiced.(1mk)
- Abundant land
- sparse population
- low number of livestock per unit area
- Where land is communally owned.
- Differentiate between apiculture and aquaculture.(1mk)
- Apiculture-rearing of bees in hives
- Aquaculture-rearing of fish in a fish pond
- Give four government policies which influence Agricultural production.(2mks)
- heavy taxation
- subsidies
- quality control
- conservation of natural resources
- stepping up the control of pest, diseases and parasites.
- State four methods of clearing land.(2mk)
- tree felling
- burning
- slashing
- uses of chemicals
- State four importance for treating water for domestic use.(2mks)
- to kill germs
- to soften it
- to remove foreign materials
- to remove chemical impurities
- To remove bad taste and colours
- Give four qualities of a fertile soil.(2mks)
- should have good soil depth
- free from soil borne and diseases.
- proper drainage.
- proper drainage
- good water holding capacity
- adequate supply of nutrient
- correct soil pH
- State four types of farm records.(2mks)
- production record
- inventory record
- field operations records
- health records
- marketing record
- labour record
- breeding record
- Give four role of nitrogen in a plant.(2mk)
- play important role in protein formation
- it forms part of chlorophyll
- regulate the availability of phosphorous to plant.
- increases the size of grains in cereals
- State four factors which influence the rooting of a cutting.(2mks)
- Leaf area
- light intensity
- relative humidity
- oxygen supply
- chemical treatment
- temperature
- Give four reasons for growing seedling in a nursery.(2mks)
- ensure transplanting of health and vigous seedlings only.
- Facilitates production of many seedlings in a small area.
- easy to carry out root management practices.
- make it possible to provide best conditions for growth.
- facilitate the planting of small seeds to grow strong before transplanting.
- reduce the period of the crop in the field
- Excess seedling can be sold.
- Name two methods of pruning.(2mks)
- pinching out
- annual pruning
- coppiccing/polarding
- Give two causes of blossom end rot in tomatoes.(2mks)
- lack of calcium in the soil
- irregular watering
- excess Nitrogen
- Define the following terms as used in Agriculture.
- Land sub-division.(1mk)
- Dividing of land into small pieces.
- Dividing of land into small pieces.
- Land consolidation.(1mk)
- Gathering together of small scattered pieces of land under one holding.
- Gathering together of small scattered pieces of land under one holding.
- Land sub-division.(1mk)
- State four harmful effects of weed.(2mks)
- compete with crops for nutrients
- some weeds are parasitic
- some weeds lowers the quality of produce
- some weeds are poisonous
- some weeds acts as alternative host for pest and diseases.
- some weeds block irrigation channels
- some weeds are irritating
- some lower the quality of pasture
- some have allelopathic effect
- State two categories under which pest can be classified or mode of feeding.(2mks)
- Piercing and sucking
- biting and chewing
- Name four causes of crop diseases.(2mks)
- fungal
- bacterial
- viral
- bad weather conditions
- deficiency of some elements in the soil
SECTION B:20mks:
Attempt all questions in this section.
- Below is a diagram of one of the tertially practices that are carried out in land preparation. Study it and answer the questions below
- Identify the tertially practice shown above.(1mk)
- Ridging
- Ridging
- Give four reasons for carrying out the above practice.(2mks)
- encourage tuber expansion
- easy harvesting of tuber crops
- Control soil erosion
- conserve moisture in the soil
- Apart from the above practice name any other two tertiary practices that are carried out in a farm (1mk)
- Rolling
- Levelling
- Identify the tertially practice shown above.(1mk)
- The table below is one of the record that is kept by livestock farmer in the farm
Dam No Breed colour Parents: sire 1st Service 2nd service 3rd service 4th service Remarks No of service Date of service Date of service Date of service Date of service Time of service Time of service Time of service Time of service A......... Bull No Breed Bull No Breed Bull No Breed B..........
Result………………. Expected date of calving C………………………………….. Weight of calf at birth Sex of the calf No of calf - Identify the type of record.(1mk)
- Breeding record
- Breeding record
- Fill in the blank spaces.(3mks)
A - Bull number and breed
B - Pregnancy diagnosis Date
C - Actual date of calving
- Identify the type of record.(1mk)
- A farmer was advised to apply 150 kg of CAN/ha,while top dressing the maize crop.CAN contains 21% N.Calculate the amount of Nitrogen applied per ha.(4mks)
- 21kg of N if in 100kg of CAN
(21x150 ) kg- 150 kg of CAN.
100
=31.5kg of N/ha
- 21kg of N if in 100kg of CAN
- Below are various pegging methods of tea. Study them and answer the questions that follows.
- Identify the pegging methods shown above.(1½mks)
A- Individual peg
B- Ring and pegs
C- Parallel sticks and pegs - Apart from the above method .Name any other method which is used to bring tea to bearing.(1mk)
- Formative
- Formative
- Give one advantage of using the method given in b above.(1mk)
- Promote a wide plucking table
- Promote a wide plucking table
- State one reason why the method in (b) above is not commonly used.(½mk)
- Take long to bring tea to bearing .
- Take long to bring tea to bearing .
- Identify the pegging methods shown above.(1½mks)
- Below are some of the common weeds in Kenya. Study them and answer the questions which follow.
- Identify the weeds A,B,C D.(2mks)
A-thorn apple (Double thorn)
B-Datura stramonium
C- Pigweed - What contributes to the competitive ability of weed C (1mk)
- Produces a lot of seed
- it has a short life cycle
- Why is it difficult to control weed E and weed F.(1mk)
- They have an underground storage structures.
- Identify the weeds A,B,C D.(2mks)
SECTION C
Attempt two questions in this section.(40mks)
-
- Describe the advantages of organic farming in Kenya.(5mks)
- It is environmental friendly
- products have no traces of inorganic chemicals residues
- improves soil structure
- enhances water infiltration and retention
- provide food for microbes.
- organic manure improve soil fertility
- Explain the overall effects of HIV/AIDS and ill health on Agricultural production.(5mks)
- Shortage of labour making labour to be very expensive
- Increase the cost of living of AIDS patients and their relatives.
- Leads to low income and poor purchasing power.
- Low living standards which lead to hopelessness and lack of motivation to invest
- low food supply and poverty in general, increasing criminal activities.
- the government and NGOs uses a lot of resources in controlling the pandemics.
- Describe five reasons of carrying out minimum tillage in agriculture production.(5mk)
- to reduce cost of production.
- To control soil erosion e.g through mulching and cover cropping
- to maintain soil structure .continuous cultivation destroys soil structure and should be avoided.
- conserve soil moisture ie.soil is not exposed to strong sun heat there reducing evaporation
- Prevent the distribution of the roots underground structures
- Prevent exposure of humus to adverse conditions eg strong sun heat which can cause volatilization.
- Describe the uses of water in a farm.(5mks)
- for domestic purposes
- for watering livestock
- Diluting chemicals used in the farm.
- during processing for farm produce
- during construction of building
- used for irrigation-
- For cooling machines
- as a source of power.
- Describe the advantages of organic farming in Kenya.(5mks)
-
- Explain five ways of maintaining soil fertility.(5mks)
- Control of soil erosion which aim at promoting good rain water retention and reducing the surface runoff.
- Crop rotation: help to control crop pest and diseases and maximum utilization of soil nutrients.
- Control of soil pH:Most soil organisms do well at a certain soil Ph.
- Proper drainage :Done by breaking the hard layers.
- Weed contol:weed compete with crops for nutrients, space sunlight and moistur
- Intercropping: when different species of crops yields are normally high.
- Minimum tillage: overcultivation destroys the soil structure leading to soil erosion.
- Use of manures-add nutrients to the soil and moderate soil pH
- use of inorganic fertilizers: add nutrients to the soil 5x1=5mks
- Explain the factors which affects the spacing of any crop.(5mks)
- Type of machinery used :Space should allow free passage of machinery.
- Soil fertility :crops in fertile soil are planted at closer spacing as it is able to support the crops.
- Size of the plant: Plant which grow big at maturity should be planted at a wider spacing.
- Moisture availability: In areas where there is high rainfall crops are planted at close spacing
- Use of crops: If grown for supply of forage crops are planted at closer spacing.
- Pest and diseases: When properly spaced it is not easy for the pest and diseases to spread.
- Growth habitat of the crop spreading crops are widely spaced.
- Describe five management practices carried out in a nursery bed.(5mks)
- Mulching –Prevent excessive evaporation and also moderates the soil temperature.
- Watering-done in the morning and evening
- weed control-nursery should be kept free from weed by uprooting weed using hands.
- Pricking out-excess seedlings should be uprooted and planted in an adjacent seedling bed
- Shading :Should be elected over the nursery bed avoiding dark conditions.
- Pest and diseases control-pest and diseases should be controlled throughout
- Hardening off-before the transplanting the seedling are hardened frequently and reducing the amount of shaded
- Describe the field management practices in tomato production.(5mks)
- Pruning for the tall varieties
- Staking for the tall varieties
- Tomato pest and diseases control ;should be carried out
- Gapping to replace the dry one and those eaten by pest
- Weeding –should be free from weed
- Regular watering when dry
- Top dressing –should be topdressed with the right amount of fertilizers.
- Explain five ways of maintaining soil fertility.(5mks)
-
- Describe the effects of land consolidation.(6mks)
- Proper supervision
- Saves on time and transportation cost
- Easy to provide agricultural advice by extension officer.
- Possible to carryout sound planning
- Facilitates carrying out of soil conservation practice.
- One can construct permanent structures in the farm.
- It is economical to carryout farming operations.
- If registered it gives farmers legal ownership and title deed which can be used to obtain loans.
- Control of weed, pests and diseases in enhanced.
- Explain cultural methods of controlling pests.14mks
- Timely planting make the plant to escape pest
- Timely harvesting –so that the crop is not attacked when in field by storage pest.
- Proper tillage-Expose the pest to predators and strong sun heat.
- Close season-you stop growing of suspected crop for some period.
- Trap cropping-A top crop is planted before or with the main crop and it is more preferred by pest.
- crop rotation-crops which are more preferred are alternated with crops which are not attacked by the particular pest.
- Plant resistant crop varieties-new varieties of crops have been develop which are not attacked by pests.
- Field hygiene-keeping the field free from any plant materials harbouring pest.
- Alteration of environment-creating of certain micro-climate is sprung
- crop nutrition-application of fertilizer and organic manure boost the growth of the crop escaping the attack.
- Destruction of alternative host. Weeds remove plants which are alternative host of pest.
- Use of clean planting materials :Materials which are free from present to prevent introduction or spread of pest and diseases.
- Proper spacing :It makes if difficult for pest to craw from one crop to another
- Irrigation :used to control pest like mole and aphids.7x2=14mks
- Describe the effects of land consolidation.(6mks)
Download Agriculture Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Form 4 Term 1 Opener Exams 2021.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students