PHYSICS
FORM 4
END TERM EXAMS
TERM 1 2021
PAPER 1
TIME 2 ½hrs
INSTRUCTIONS
- This paper consists of 2 sections: A and B
- Answer all the questions in these sections
- Mathematical tables and calculators may be used.
SECTION A (25 MARKS)
Answer ALL the questions in this section in the spaces provided.
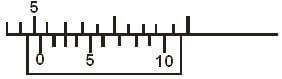
- The figure below shows the scale of a measuring instrument when measuring the thickness of an object.
Figure 1- Name the instrument to which the scale belongs. (1 mark)
- Find the reading of the instrument shown. (2 marks)
- A solid weighs 32.5N on the surface of the moon. The force of gravity on the moon is 1.7Nkg-1. Determine the mass of the solid. (3 marks)
- A mercury barometer reads 760mmHg at sealevel and 700mmHg at the top of a mountain. If the density of mercury is 13,600kg/m3 and average density of air is 1.30kg/m3, calculate the height of the mountain. (3 marks)
- Briefly explain why rooms are at a lower level and ventilators at a higher level. (2 marks)
- State the Archimedes principle. (1 mark)
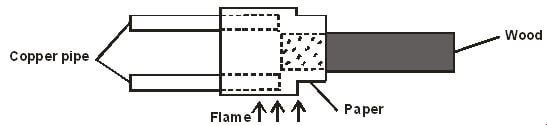
- Figure 2 below shows a piece of wood fitted into a copper pipe and a piece of paper wrapped tightly around the junction.
Explain why the side of the paper around wood burns first when flame is applied at the junction. (2 marks)
Figure 2 - State why it is necessary to leave an air space in closed glass bottle of water when it is to be kept in a refrigerator. (1 mark)
- A student pulls a block of wood along a horizontal surface by applying a constant force. State the reason why the block moves at a constant. (1 mark)
- The efficiency of a pulley system is always less than 100%. State two reasons. (2 marks)
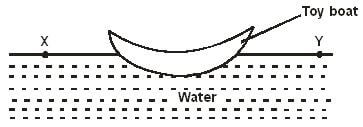
- Figure 3 shows a small toy boat floating on water in a basin. X and Y are two points near the toy.
Figure 3
When a hot metal rod is dipped into the water at point X the toy is observed to move towards Y.Explain this observation. (2 marks) - How much current is taken by a bulb whose rate is 100 and which is designed for mains supply of 240V? (3 marks)
- What is the gravitational potential energy stored in a spring when stretched through 4cm by a force of 2N. (2 marks)
SECTION B (55 MARKS)
Answer ALL the questions in this section in the spaces below.
-
- Define centripetal acceleration. (1 mark)
- Distinguish between angular and linear velocity. (2 marks)
- The figure 4 below shows an object of mass 0.2kg whirled in vertical circle of radius 0.5m at uniform speed of 5m/s.
Determine the tension of the string at;- Position A. (3 marks)
- Position B. (3 marks)
- At what point is the string likely to cut. Explain. (2 marks)
-
- Explain why it is advisable to use the pressure cooker for cooking at high altitudes. (2 marks)
- Water of mass 3kg initially at 20℃ is heated in an electric kettle rated 3.0kW. Thewater is heated until it boils at 100℃. Taking specific heat capacity of water=4200Jkg/K, heat capacity of kettle=450J/kg, specific latent heat of vapourisation of water =2.3MJ/kg, calculate;
- The heat absorbed by the water. (2 marks)
- Heat absorbed by the electric kettle. (2 marks)
- The time taken for the water to boil . (2 marks)
- How much longer it will take to boil away all the water? (3 marks)
-
- A ball is dropped from the top of a vertical cliff 45m high. Given that the velocity just before striking the sandy beach is 30m/s, and the ball penetrate the sand to a depth of 10cm determine its average retardation. (3 marks)
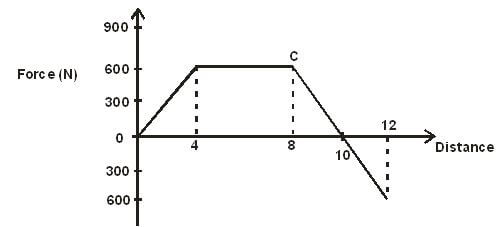
- The figure below shows a force distance graph for a car being towed on a level ground.
- Calculate the total work done. (2 marks)
- If the velocity just before reaching C is 0.6 m/s. Calculate the power developed by the engine at this point. (2 marks)
-
- State the pressure law; (1 mark)
- Explain how a gas exerts pressure. (2 marks)
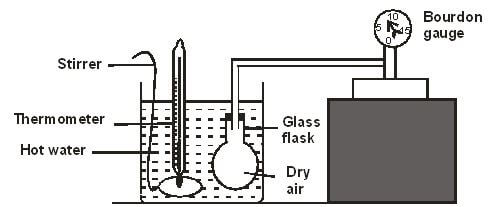
- The figure below shows a set up used to verify pressure law.
- State the measurement that may be taken in the experiment. (2 marks)
- Explain how the measurement in (i) above may be used to verify pressure law. (2 marks)
- A car tyre is at pressure of 5.0x105 Pa at a temperature of 37℃. While it is running the temperature rises to 75℃. What is the new tyre pressure?(Assume the tyre does not expand) (3 marks)
-
- State the law of conservation of energy. (1 mark)
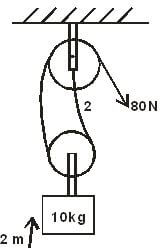
- The diagram below shows a pulley system, a mass of 10kg is raised 2m by an effort of 80N.
- Calculate the distance moved by effort. (2 marks)
- How much potential energy does the load gain? (1 mark)
- How much work is done by the effort? (1 mark)
- What is the efficiency of these pulleys? (2marks)
- Explain why it easier to tighten or loosen a nut using a spanner with a long handle than one with a short handle. (1 mark)
- A stone of mass 4.0kg immersed in water and suspended from a spring balance with a string. The beaker was placed on a compression balance whose reading was 85N. The density of the stone was 3000kg/m-3while the density of the liquid was 800kg/m-3. Determine the;
- Volume of the liquid displaced. (2marks)
- Upthrust on the stone. (4marks)
- Reading on the spring balance.

MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A (25 MARKS)
Answer ALL the questions in this section in the spaces provided.
- The figure below shows the scale of a measuring instrument when measuring the thickness of an object.
Figure 1- Name the instrument to which the scale belongs. (1 mark)
- Vernier calliper
- Find the reading of the instrument shown. (2 marks)
- Main scale 5.00
Vernier scale (2 x 0.01) = 0.02
5.00 + 0.02 = 5.02 cm
- Main scale 5.00
- Name the instrument to which the scale belongs. (1 mark)
- A solid weighs 32.5N on the surface of the moon. The force of gravity on the moon is 1.7Nkg-1. Determine the mass of the solid. (3 marks)
- M = w/g
= 32.5/1.7
= 19.117 kg / 19.12 kg
- M = w/g
- A mercury barometer reads 760mmHg at sealevel and 700mmHg at the top of a mountain. If the density of mercury is 13,600kg/m3 and average density of air is 1.30kg/m3, calculate the height of the mountain. (3 marks)
- Difference in pressure 760 – 700 = 60mm
60/1000 x 13600 x 10 = h x 1.3 x 10
h=8160/(1.3 ×10)
h=627.69 m
- Difference in pressure 760 – 700 = 60mm
- Briefly explain why rooms are at a lower level and ventilators at a higher level. (2 marks)
- Warm air being lighter raises and escapes through the ventilators while the colder air gets in through the windows and doors.
- Warm air being lighter raises and escapes through the ventilators while the colder air gets in through the windows and doors.
- State the Archimedes principle. (1 mark)
- When a body is partially or totally immersed in a fluid, it experiences an upthrust equal to the weight of the fluid displaced.
- When a body is partially or totally immersed in a fluid, it experiences an upthrust equal to the weight of the fluid displaced.
- Figure 2 below shows a piece of wood fitted into a copper pipe and a piece of paper wrapped tightly around the junction.
Explain why the side of the paper around wood burns first when flame is applied at the junction. (2 marks)
Figure 2
- Wood being a poor conductor of heat does not allow the excess heat so it gets charred
- Wood being a poor conductor of heat does not allow the excess heat so it gets charred
- State why it is necessary to leave an air space in closed glass bottle of water when it is to be kept in a refrigerator. (1 mark)
- Air space is to allow for expansion of water when it freezes preventing the glass bottle from breaking
- Air space is to allow for expansion of water when it freezes preventing the glass bottle from breaking
- A student pulls a block of wood along a horizontal surface by applying a constant force. State the reason why the block moves at a constant. (1 mark)
- Frictional force is equal to the applied force but in opposite direction. The net applied force is zero.
- Frictional force is equal to the applied force but in opposite direction. The net applied force is zero.
- The efficiency of a pulley system is always less than 100%. State two reasons. (2 marks)
- Friction between moving parts of the pulley system / friction.
Weight of the movable part of pulley // work done in lifting the moving parts of pulley system.
- Friction between moving parts of the pulley system / friction.
- Figure 3 shows a small toy boat floating on water in a basin. X and Y are two points near the toy.
Figure 3
When a hot metal rod is dipped into the water at point X the toy is observed to move towards Y.Explain this observation. (2 marks)- The hot metal rod breaks the surface tension of the water; surface behaving like stretched skin is pulled towards Y.
- The hot metal rod breaks the surface tension of the water; surface behaving like stretched skin is pulled towards Y.
- How much current is taken by a bulb whose rate is 100Ω and which is designed for mains supply of 240V? (3 marks)
- P = IV
I = P/V
= 100/240
= 0.42 A
- P = IV
- What is the gravitational potential energy stored in a spring when stretched through 4cm by a force of 2N. (2 marks)
- P.E = Fe/2
= (2 ×0.04)/2
=0.04 Joules
- P.E = Fe/2
SECTION B (55 MARKS)
Answer ALL the questions in this section in the spaces below.
-
- Define centripetal acceleration. (1 mark)
- This is a force that maintains a body in circular motion and directed towards the centre
- This is a force that maintains a body in circular motion and directed towards the centre
- Distinguish between angular and linear velocity. (2 marks)
- Angular velocity is rate of change of angular displacement with time while linear velocity is rate of change of linear displacement with time.
- Angular velocity is rate of change of angular displacement with time while linear velocity is rate of change of linear displacement with time.
- The figure 4 below shows an object of mass 0.2kg whirled in vertical circle of radius 0.5m at uniform speed of 5m/s.
Determine the tension of the string at;- Position A. (3 marks)
- T = MV2/r-mg
= (0.2 × 52/0.5)- (0.2 ×10)
= 10 – 2 = 8N
- T = MV2/r-mg
- Position B. (3 marks)
- T = MV2/r
= ((0.2 × 25)/0.5)
T = 10N
- T = MV2/r
- At what point is the string likely to cut. Explain. (2 marks)
- At C, because tension is high at 12N
T = MV2/r+mg
- At C, because tension is high at 12N
- Position A. (3 marks)
- Define centripetal acceleration. (1 mark)
-
- Explain why it is advisable to use the pressure cooker for cooking at high altitudes. (2 marks)
- At high altitude there is low pressure; this lowers the pressure cookers raising the boiling point and more heat is absorbed and food cooks faster
- At high altitude there is low pressure; this lowers the pressure cookers raising the boiling point and more heat is absorbed and food cooks faster
- Water of mass 3kg initially at 20℃ is heated in an electric kettle rated 3.0kW. Thewater is heated until it boils at 100℃. Taking specific heat capacity of water=4200Jkg/K, heat capacity of kettle=450J/kg, specific latent heat of vapourisation of water =2.3MJ/kg, calculate;
- The heat absorbed by the water. (2 marks)
- Q = MCΔθ
= 3kg x 4200JKg-1k-1 x 80
= 240 x 4200 = 1008000J / 1.008kJ
- Q = MCΔθ
- Heat absorbed by the electric kettle. (2 marks)
- Q = MkCkΔθ
= 450 x 80 = 36000J
- Q = MkCkΔθ
- The time taken for the water to boil . (2 marks)
- pt = total heat absorbed
pt = 36000 + 10080001
3000t = 1044000
t = 1044000/3000
t = 348 sec
- pt = total heat absorbed
- How much longer it will take to boil away all the water? (3 marks)
- pt = mLv
3000t = 3 x 2.3 x 106
t = (3 ×2.3 × 106)/3000
t = 2300 seconds
- pt = mLv
- The heat absorbed by the water. (2 marks)
- Explain why it is advisable to use the pressure cooker for cooking at high altitudes. (2 marks)
-
- A ball is dropped from the top of a vertical cliff 45m high. Given that the velocity just before striking the sandy beach is 30m/s, and the ball penetrate the sand to a depth of 10cm determine its average retardation. (3 marks)
- v2 = u2 + 2as
O2 = 9002 + 2 x a x 0.10
-900 = 0.20 a
a = (-900)/0.20
a = -450 m/s2 (negative a must)
- v2 = u2 + 2as
- The figure below shows a force distance graph for a car being towed on a level ground.
- Calculate the total work done. (2 marks)
- Total work done = Area under graph
( ½ x 4 x 600) + (600 x 4) + (½ x 2 x 600) + (2 x ½ x 600)
1200 + 2400 + 600 + 600
= 4800 J
- Total work done = Area under graph
- If the velocity just before reaching C is 0.6 m/s. Calculate the power developed by the engine at this point. (2 marks)
- P = force x velocity
= 0.6 m/s x 600
= 360 W
- P = force x velocity
- Calculate the total work done. (2 marks)
- A ball is dropped from the top of a vertical cliff 45m high. Given that the velocity just before striking the sandy beach is 30m/s, and the ball penetrate the sand to a depth of 10cm determine its average retardation. (3 marks)
-
- State the pressure law; (1 mark)
- The pressure of a fixed mass of gas is directly proportional to absolute temperature provided that volume is kept constant.
- The pressure of a fixed mass of gas is directly proportional to absolute temperature provided that volume is kept constant.
- Explain how a gas exerts pressure. (2 marks)
- When a gas is heated it expands increasing the number of collusions per unit area which in turn raise the pressure
- When a gas is heated it expands increasing the number of collusions per unit area which in turn raise the pressure
- The figure below shows a set up used to verify pressure law.
- State the measurement that may be taken in the experiment. (2 marks)
- Temperature of water
- Pressure gauge reading
- Explain how the measurement in (i) above may be used to verify pressure law. (2 marks)
- Collect various values of pressure under different temperatures
- Plot a graph of pressure against temperature and study the values
- A car tyre is at pressure of 5.0x105 Pa at a temperature of 37℃. While it is running the temperature rises to 75℃. What is the new tyre pressure?(Assume the tyre does not expand) (3 marks)
- P α T →P=KT →K=P/T
P1 – 5.0 x 105 Pa
P2 = ?
T1 = 273 + 37 = 300k
T2 = 75 + 273 = 348k
P1/T1 = P2/T2
500000/300= P2/348
P2 = (500000 ×348)/300
= 580000
P2 = 5.8 x 105 Pa
- P α T →P=KT →K=P/T
- State the measurement that may be taken in the experiment. (2 marks)
- State the pressure law; (1 mark)
-
- State the law of conservation of energy. (1 mark)
- The sum of kinetic energy and potential energy of a system is constant
Or - Energy can neither be created nor destroyed but can be transformed from one form to another
- The sum of kinetic energy and potential energy of a system is constant
- The diagram below shows a pulley system, a mass of 10kg is raised 2m by an effort of 80N.
- Calculate the distance moved by effort. (2 marks)
- V.R = 2 = (Distance moved by load)/(Distance moved by effort)
2 = x/2
2x = 2m
x = 1m
- V.R = 2 = (Distance moved by load)/(Distance moved by effort)
- How much potential energy does the load gain? (1 mark)
- P.E = mgh
= 10 x 10 x 2
= 200J
- P.E = mgh
- How much work is done by the effort? (1 mark)
- Work input = Effort x Effort distance
= 80N x 1m
= 80 Joules
- Work input = Effort x Effort distance
- What is the efficiency of these pulleys? (2marks)
- MA/VR x 100% = efficiency
(100/80)/2 x 100% = 5000/80
Eff = 62.5%
- MA/VR x 100% = efficiency
- Explain why it easier to tighten or loosen a nut using a spanner with a long handle than one with a short handle. (1 mark)
- With long handle spanner the effort used is less than short handle spanner so one does a lot of work
- With long handle spanner the effort used is less than short handle spanner so one does a lot of work
- Calculate the distance moved by effort. (2 marks)
- State the law of conservation of energy. (1 mark)
- A stone of mass 4.0kg immersed in water and suspended from a spring balance with a string. The beaker was placed on a compression balance whose reading was 85N. The density of the stone was 3000kg/m-3while the density of the liquid was 800kg/m-3. Determine the;
- Volume of the liquid displaced. (2marks)
- V = 4/3000
V = 1.33 x 103m3 (At least 2 d.p)
- V = 4/3000
- Upthrust on the stone. (4marks)
- Upthrust = Weight of liquid displaced = vρg
Liquid; 800 x 1.33 x 103 x 10
= 10.64 N
Upthrust in water = v
1.33 x 103m3 x 10 x 1000
= 13.33N
- Upthrust = Weight of liquid displaced = vρg
- Reading on the spring balance.
- Weight of stone in air = 40N
Readings → 40 – 10.64 = 29.36N
Or
40 – 13.33 = 26.67N
- Weight of stone in air = 40N
- Volume of the liquid displaced. (2marks)
Download Physics Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Form 4 End Term 1 Exams 2021.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students